April 2025
The semiconductor packaging market is expected to increase from USD 49.89 billion in 2025 to USD 119.96 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.24% throughout the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
![]()
A semiconductor is a material that can be used as the basis for computers and other electronic devices because of its unique electrical properties. Usually, it is a solid chemical element or compound that, in some situations, transmits electricity and, in others, does not. Due to this, it’s the perfect medium for managing electrical current in household equipment. The characteristics of semiconductor lie between those of an insulator and a conductor. Semiconductor are used to create transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), and diodes.
A variety of electronic solutions known as semiconductor packaging materials are used to connect integrated circuit chips (IC Chips) to printed circuit boards, other packages, or the package substrate. These materials are essential to 3D integration technologies, heterogeneous integration, and semiconductor wafer-level packaging methods. Electronics as a field has grown quickly in recent years, with integrated circuit (IC) technology leading the way. Smaller, lighter, and more powerful semiconductor devices are becoming the norm as 5G and 6G mobile technologies advance. For semiconductor chips to be physically protected, electrically connected, and to meet standard criteria, packaging is essential.
The packaging of semiconductors has advanced tremendously in modern times. A paper that was just published in Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Technology covered the most current developments in semiconductor packaging. The landscape of semiconductor packaging comprises a number of integration strategies. With two or more chips on the same package substrate or fan-out redistribution layer (RDL) substrate, 2-D IC integration found in consumer goods like smartphones and smartwatches is called System-in-Package (SiP). Direct fabrication of fine metal layers on top of a build-up package substrate or high-density interconnect (HDI) is required for the 2.1-D IC integration.
Chips are supported by a passive through-silicon via (T5V) interposer in 2.5D IC integration, which is connected to package substrate by Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. company’s Radeon R9 Fury X GPU. The global packaging market size is estimated to grow at a 3.16% CAGR.
The U.S. is launching a new federal funding competition aimed at accelerating the development of advanced semiconductor packaging technologies. The Department of Commerce announced a $1.6 billion investment, as part of the 2022 CHIPS and Science Act, to enhance chip packaging capabilities and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, particularly in Asia, where countries like Taiwan and South Korea dominate the sector.
Currently, the U.S. holds just 3% of the global chip packaging market. To change this, the government is providing incentives to major semiconductor companies, such as Intel, SK Hynix, Amkor Technology, and Samsung, encouraging them to establish chip packaging plants within the U.S. This move is designed to bolster domestic production and make the U.S. a key player in the global semiconductor industry.
The funding will focus on key areas of research and development, including improving data transfer speeds and heat management, both critical for next-generation technologies. It will also support advancements in high-performance computing and energy-efficient semiconductor systems, particularly for artificial intelligence applications.
The initiative aims to create a robust domestic packaging industry over the next decade, ensuring that advanced chips, both U.S.-made and imported, can be packaged domestically. This will also drive innovation in chip design and architecture, helping the U.S. regain leadership in semiconductor manufacturing.
This program is the largest funding opportunity yet from an $11 billion R&D fund established under the CHIPS Act, which also allocates $39 billion in grants, $75 billion in loans, and tax incentives to encourage semiconductor manufacturing on U.S. soil. Previous funding has already been awarded to companies like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) for a chip packaging facility in Arizona and to Intel and Samsung for new plants in Arizona and Texas.
By investing in not only chip production but also packaging, R&D, and other key areas, the U.S. aims to become more competitive in the semiconductor market. However, it remains to be seen whether these efforts will result in the production of competitively-priced chips. Other regions, like Europe, have tried similar initiatives in the past but faced challenges, especially with growing competition from China.
The new federal funding will drive research in five main areas: packaging equipment and tools, power delivery and heat management, connector technology, electronic design automation, and modular chip components known as chiplets. The Commerce Department plans to issue multiple grants of up to $150 million in each category to encourage innovation and maintain the U.S.'s competitive edge in the global semiconductor industry.
Increasing Densification and Miniaturization in the Electronics Industry
The global semiconductor packaging market is significantly driven by the growing trend of downsizing and densification in the electronics industry. Manufacturers of electronic devices encounter difficulties fitting complicated functions into constrained spaces as gadgets get smaller and more compact. This tendency is especially noticeable in consumer electronics, where users want svelte designs without sacrificing functionality, such as wearables, smartphones, and Internet of Things devices. Semiconductor makers are creating advanced devices with greater integration levels and squeezing more functions into fewer components in order to overcome these issues. Innovative packaging materials that can support these intricate chip designs while maintaining performance, dependability, and thermal management are becoming increasingly necessary as a result of this development.
Since integrated circuit packaging materials offer heat dissipation, mechanical support, electrical insulation, and signal integrity all within the small footprint of semiconductor packages, they are essential to the process of downsizing. The strict specifications of tiny electronics are met by materials like organic substrates, leadframes, encapsulation resins, and thermal interface materials, which provide small-yet-effective packaging options. Moreover, the electronics industry's densification—the packing of more components into less spaces—raises the need for advanced packaging materials that can withstand complicated interconnections, increasing pin densities, and strict reliability requirements. All things considered, the trend toward densification and shrinking propels ongoing innovation and expansion in the semiconductor and IC packaging materials market to satisfy the changing demands of the electronics sector.
High Cost of Raw Material
The rising urbanization has increased the rate of the raw materials and there is lack of trained workforce for the development of the semiconductor packaging which can hamper the growth of the market over the forecast period. The market for semiconductor packaging materials is severely challenged by the high cost of modern materials. Advanced materials with improved functionality, performance, and dependability can be developed and produced using specialized production techniques and significant research and development (R&D) expenditures. These elements lead to increased manufacturing costs, which can then be on to semiconductor manufacturers and consumers, decreasing the cost-effectiveness of advanced packaging materials in comparison to more conventional options.
In addition, businesses in the semiconductor sector are always looking for methods to cut expenses and increase profit margins due to the industry's intense competition and cost-sensitivity. Adopting new materials can be expensive initially, which could discourage some businesses—especially smaller ones—from utilizing these technologies. This would result in slower adoption rates and less market penetration.
Increasing Adoption of Inorganic Growth Strategies
The need for sophisticated packaging materials and high-performance semiconductor components is rising as sectors embrace cutting-edge technologies like autonomous systems, 5G connectivity, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things. To achieve the strict criteria for performance, reliability, and thermal management, these technologies need complex packaging solutions. For instance, chips with high processing power and effective heat dissipation are required for Al and ML applications, which creates a need for creative packaging materials that can meet these requirements. In a similar vein, semiconductor packages that facilitate high-speed data transmission, low-latency communication, and connectivity among various devices are necessary for the deployment of 5G networks and the growth of loT devices.
These capabilities are made possible by advanced packaging materials, which presents business potential for firms that specialize in semiconductor and IC packaging materials. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like partnership and collaboration to develop the advanced technology packaging and increase the capacity of production to meet the rising demand of the consumers.
Semiconductor wafers are essential components in integrated circuits, forming the backbone of modern technology. Packaging these wafers serves a critical role, protecting them from contamination, light, heat, and physical impacts, while also connecting them to their environment. Despite this, traditional packaging methods were often undervalued, relying on outdated equipment and outsourcing to low-cost OSATs (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test companies).
Advanced packaging, which first appeared around 2000, has recently gained momentum as a key innovation in semiconductor technology. The demand for advanced packaging is driven by the need for high-performance, low-power chips, which are essential for emerging technologies like 5G, autonomous vehicles, IoT, and VR/AR. As Moore’s Law slows down, and the pace of node advancement decreases, advanced packaging has become crucial for the continued innovation of semiconductors.
Several advanced-packaging technologies are now at the forefront of the industry:
Traditional techniques, like wire-bonding, still find use but face limitations in high-temperature environments. Flip chips offer advantages such as a smaller form factor and faster signal propagation, making them increasingly popular.
Wafer-level packaging is becoming more common, particularly in mobile and network applications. Fan-Out Packaging currently dominates the market, driven by the high demand for mobile devices and high-performance computing (HPC). 2.5-D Stacking is expected to see significant growth in HPC applications, especially in data centers. 3-D Packaging is rapidly growing in memory applications, particularly for data centers and graphics accelerators. Leading companies like TSMC, Intel, and Apple are at the forefront of these advanced packaging technologies.
To succeed in the advanced packaging market, manufacturers must collaborate closely with fabless customers during the chip design and development stages. The industry presents high technology and investment barriers, making it challenging for new entrants to catch up with established leaders. Therefore, joint development of packaging solutions is essential for acquiring and retaining premium customers.
The market for advanced packaging is set to continue growing, fueled by the demand for faster, more efficient semiconductor chips for advanced applications. There is also potential for further innovation, with new materials like glass for interposers being explored, though they have yet to reach market readiness.
The organic substrate segment held the dominant share of the semiconductor packaging market in 2023, owing to the wide range of advantages offered for the semiconductor packaging. The organic substrate is extensively utilized since they are cost-effectiveness and magnificent electrical performance. Organic Substrate hold the dominant share of the semiconductor packaging market and are driven by rise in demand from consumer communication and electronics industries. The use of organic substrate packaging material is done on the foundation layer of printed circuit boards (PCBs) to deliver high reliance and significant electrical performance. Organic packaging materials decrease the overall weight of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and increase their functionality and dimensional control.
Hence, organic substrate compatibility with standard printed circuit boards (PCBs) fabrication processes ensure rapid production cycle and decreased time-to-market. The advancements like low-loss dielectrics and high-speed laminated materials have boosted their performance in thermal management and signal transmission, making organic substrate the reliable choice in modern semiconductor packaging. The key players operating in the market are focused on the development of advanced organic substrate for electric devices which is expected to drive the growth of the segment over the forecast period.
For instance,
The bonding wire segment is expected to progress at the fastest rate over the forecast period as it is essential for connecting the semiconductor die to the package. The modification towards thinner and finer wires, chiefly in advanced packaging, is driving this segment. Ceramic packages provide high thermal conductivity and are utilized in high-performance applications, like defense and aerospace insulation. Ceramic material are preferred for their reliability in harsh environment. For bonding semiconductor dies to substrate, die attach material is important. Hence, the advances in materials with better electrical and thermal conductivity are driving this segment.
The traditional packaging segment held the largest share of the semiconductor packaging market in 2023. Traditional packaging, including wire bonding and leadframe-based, holds the significant market share as it is used on large-scale in automotive sectors and consumer electronics. It is affordable range and established manufacturing processes make it a reliable choice and highly preferable by the consumers. Traditional packaging techniques comprises wirebond technology, ceramic packaging, and plastic packages among others. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like partnership to develop and increase production of the traditional technology equipment which is estimated to drive the growth of the segment over the forecast period.
For instance,
The advanced packaging segment is expected to grow at the fastest rate over the forecast period. The advanced packaging technologies like embedded die, 3D/5D packaging, System-in-Package, and Fan-in Wafer Level Packaging (FI-WLP) etc. are advancing consistently due to their ability enhance production capacity of device and reduction in size.
The advance semiconductor packaging technology are pivotal for high-demand sectors like Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Additional, advanced packaging extends the limits of silicon and aids in fulfilling application needs including strong resilience in demanding settings like factories, good EMC in automotive electronics, and high dependability in aerospace. Also, it offers a variety of alternatives, such as leaded, unleaded, ball grid array (BGA), wafer chip scale package (WCSP), to mention a few, based on system design trade-offs for cost and performance.
A few noteworthy instances of advanced packaging methods are galvanic isolators with integrated magnets for power and signal isolation, crystal-less MCs with integrated BAW resonators allowing for reliable single-chip solutions. These developments enable ICs in the present and next generations to be more effective and rollable, delivering improved performance and lower system costs. Moreover, increasing launch of the online training session for semiconductor advanced packaging to meet the demand of trained worked force is expected to drive the growth of the segment over the forecast period.
For instance,
The consumer electronics segment held the largest share of the semiconductor packaging market in 2023. The rapid advancement and development of new features in the electronic gadgets such as smartphone, tabs, laptops and other wearable gadgets has increased the demand for the semiconductor packaging. The growing trend towards multifunctional and miniaturization devices progressed the demand for advanced packaging. Moreover, the rise in the number of mobile phone use has increased the demand for the semiconductor packaging, which is estimated to drive the growth of the segment over the forecast period.
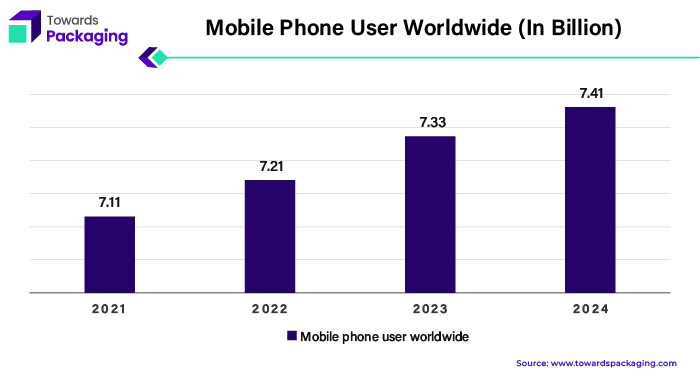
For instance,
Owing to high volume of semiconductor used in devices like tabs, smart phones and wearables, the consumer electronics segment dominated the market. Several important variables are responsible for consumer electronics dominance in the semiconductor and IC packaging material market. Firstly, industries extensive use of semiconductor devices in wearables, gaming consoles, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs drives demand for cutting-edge packaging solutions the satisfy specifications for functionality, performance, and miniaturization.
Moreover, packaging materials that support cutting-edge technologies like high-speed data processing, artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and IoT connectivity are required due to the rapid innovation in consumer electronics. Semiconductor packaging materials are necessary to give these components mechanical protection, temperature control, electrical insulation, and signal integrity. Furthermore, the industry’s emphasis on quick time-to-market, low costs and effective assembly methods propels the use of materials including advanced polymers, leadframes, organic substrates, and encapsulating resins.
The aerospace & defence segment is projected to grow at fastest rate over the forecast period. The aerospace and defence sector demands advance technology, reliable and well developed packaging solutions for harsh environments. Moreover, growing need for business jet and general aviation services as a result of rising living standards, rising disposable income, and growing corporate and leisure flying is rising demand for the aerospace which is consequently drive the growth of the semiconductor packaging market over the forecast period.
The rapid advancement and shift towards autonomous and electric vehicles is rising the demand for the high-performance and reliable semiconductor packaging. This segment is experiencing constant growth in demand for semiconductor advanced packaging technologies. Increasing launch of the autonomous diagnostic and medical equipment, the healthcare sector is relying on advanced semiconductor packaging for compact and reliable solutions.
Asia Pacific region held the largest share of the semiconductor packaging market owing to increasing launch of the semiconductor packaging material by the key players operating in the market to meet the rising demand of the semiconductor packaging is expected to drive the growth of the semiconductor packaging market over the forecast period. Asia Pacific is a leading market for semiconductor and integrated circuit packaging materials due to a number of reasons that contribute to its dominance in the industry.
Major centers of electronics production, including China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore, are located in the region. These hubs have strong semiconductor ecosystems that include a wide range of foundries, packaging plants, equipment suppliers, and research facilities. The integration process generates intense competition in the market, which in turn drives ongoing innovation and technological progress. This is especially noticeable in nations such as South Korea and Japan, which are widely recognized for their pioneering roles in semiconductor manufacture and research.
For instance,
The never-ending quest for technological superiority fuels the need for high-performance packaging materials that can hold up to the demanding specifications of cutting-edge semiconductor devices. This need is further propelled by the booming consumer electronics market in Asia Pacific, which is driven by increased disposable incomes, urbanization and digitalization trends. Additional advantages of the region's strategic location as a global industrial hub include cost-effectiveness, excellent supply chains, and easy access to trained labor.
Asia Pacific's standing as a key market for semiconductor packaging materials is reinforced by significant semiconductor manufacturers, assembly and testing facilities, and equipment providers. The Asia Pacific market for semiconductors and IC packaging materials has grown dramatically as a result of government initiatives, investment incentives, and supportive business environments that foster industry growth and draw in international capital. As a whole, Asia Pacific is the largest and most dynamic market for semiconductor and IC packaging materials worldwide due to its leadership in semiconductor manufacturing, technological innovation, rising consumer electronics demand, manufacturing efficiencies, and supportive business climates.
In the Asia Pacific area, the Indian semiconductor packaging market is expanding at a notable rate. This quick growth is mostly due to the nation's growing electronics manufacturing industry and encouraging government regulations. To encourage investment in the production and packaging of semiconductors, the Indian government has introduced a number of incentive schemes, including the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) plan. As a result, more money has been invested by both domestic and foreign businesses. Recent announcements highlight India's expanding capabilities in the semiconductor industry, such as Vedanta and Foxconn's joint venture to develop a semiconductor fabrication plant in Gujarat. The need for advanced packaging solutions is expected to rise sharply as a result of those modifications.
North America is observed to witness the fastest growth rate over the forecast period, owing to its substantial research and development expenditures, advanced technological infrastructure, and strong ecosystem of semiconductor companies, the U.S. has the largest market share in the North American market. Large semiconductor companies like Texas Instruments, Qualcomm, and Intel are based in the nation, and they are the ones that constantly spur packaging technology innovation. One major factor propelling the market's growth is the United States government's CHIPS Act, which offers substantial financing for domestic semiconductor fabrication and packaging. The goal of this act is to support domestic semiconductor manufacturing while reducing reliance on overseas semiconductor suppliers.
Increasing development of the Artificial intelligence and 5G technology in the U.S. has led to boost the growth of the semiconductor packaging market over the forecast period. Companies like Qualcomm and NVIDIA are at the lead of integrating semiconductor advanced packaging solutions to meet the demands of these high-growth sectors. For instance, in 2023, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., company based in California, U.S. revealed the launch of the Snapdragon X80 5G Modem-RF System and pivotal in maintaining competitive edge in the telecommunications market.
Moreover, the government bodies in the U.S. are initiating investment for developing the semiconductor advanced packaging to meet the rising demand by the automotive industries, which is estimated to drive the growth of the semiconductor packaging market in the U.S. over the forecast period.
For instance,
Europe is estimated to be the second fastest growing region over the forecast period. It is attributable to its robust industrial and automotive industries, which are important users of cutting-edge semiconductor technologies. German firms are pioneers in the development of state-of-the-art industrial automation systems and automotive electronics, which mostly depend on advanced semiconductor packing. Advancements in semiconductor technology are the subject of collaborative research projects actively participated in by European corporations.
For instance, several German attempts to develop next-generation semiconductor packaging technologies are supported by the European Union's Horizon Europe program. The automotive sector dominates the German semiconductor packaging market. Businesses that are substantially investing in cutting-edge packaging technologies for electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving systems include Bosch and Infineon. To meet the growing demand for EV components, Infineon, for instance, has increased the size of its chip packaging facilities in Dresden. The deployment of advanced semiconductor solutions is accelerating due to Germany's drive towards Industry 4.0. Robustness and reliability are becoming increasingly important as smart manufacturing and automation become more prevalent. The semiconductor packaging market of Europe is second fastest growing owing to the artificial intelligence and 5G technology development.
For instance,
Moreover, the key players operating in the Europe are engaged in introduction of the new product which is expected to drive the growth of the semiconductor packaging market in Europe over the forecast period. For instance, in July 2024, the Chips Joint Undertaking program released calls for help regarding competence centers, cloud-based semiconductor design platforms, and semiconductor research and innovation projects in photonics. The call is a component of the Europe's "Chips for Europe" program, which is based on the Chips Act. The US$ 35 million in total Europe money available for the calls should be supplemented by additional funding from participating states in the Chips Joint Undertaking program of Europe.
By Material Type
By Technology Type
By End Use
By Region
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025