April 2025

Principal Consultant

Reviewed By
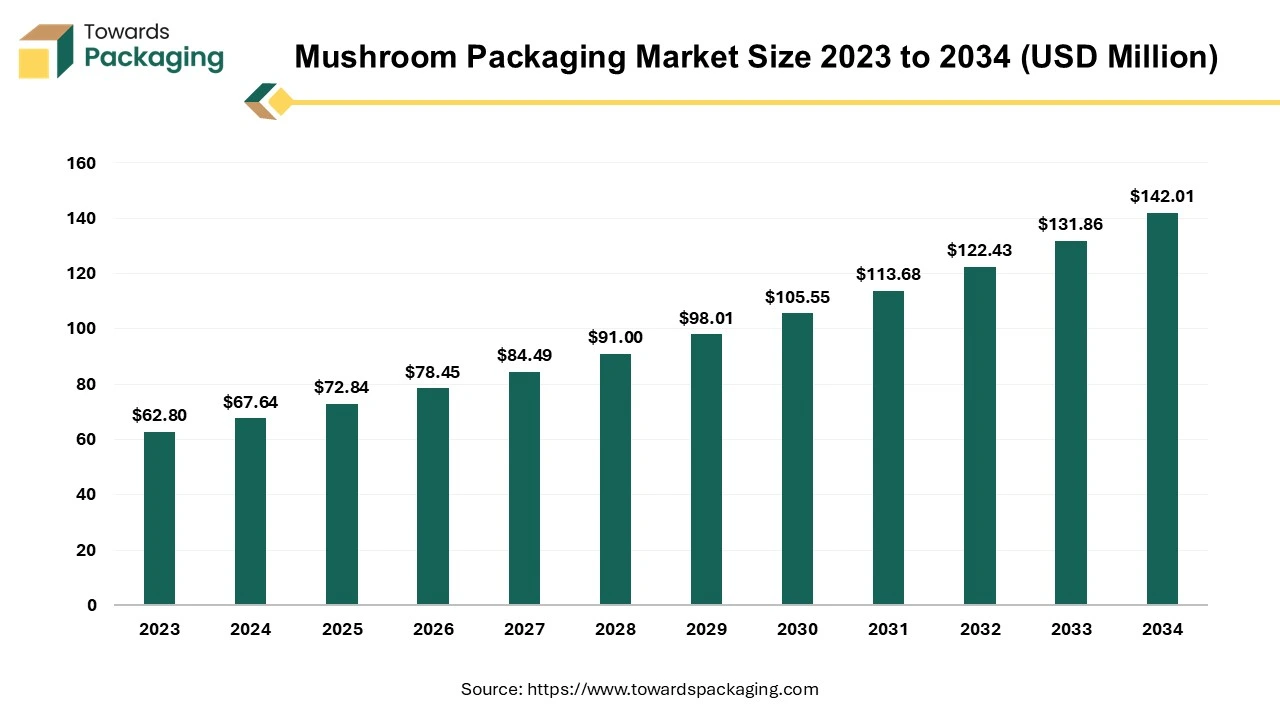
The mushroom packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 72.84 million in 2025 to USD 142.01 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2025 to 2034.
Mushroom packaging is a biodegradable and sustainable packaging alternative to traditional and unrecyclable packaging materials. In today's globalized economy, the demand for affordable and practical packaging solutions has led to the widespread use of traditional plastic materials. However, the consequences of this reliance on unrecyclable packaging, such as environmental degradation, limited garbage space, and a reluctance to embrace a reuse-oriented lifestyle, are becoming increasingly apparent. Plastic waste, a major contributor to pollution in both soil and water, poses a significant challenge, with a recycling rate ranging from 0.5 to 1 billion pieces global and a degradation timeline of 20 to 100 years.
The packaging sector, accounting for approximately 40% of global plastic output, faces heightened scrutiny as digital sales surged by 71% from April to June and 55% from July to September in 2022. Among the commonly used single-use plastic packaging items are polystyrene, known as Styrofoam, prized for its lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and heat-resistant properties. However, its drawbacks include toxic compounds that pose health risks and environmental harm, contributing to the urgent need for sustainable alternatives.
Recognizing the escalating environmental challenges, the search for eco-friendly alternatives has intensified. One innovative solution gaining prominence is mushroom packaging, a biodegradable and sustainable substitute for traditional packaging materials. Fungi, often underestimated creatures, play a vital role in natural waste decomposition and offer a potential solution to the plastic predicament.
Mycelium is at the heart of mushroom packaging, an essential constituent of fungi that rapidly grows, covering seed husks and binding them into a robust, biodegradable substance. Recent studies suggest that mycelium-based materials share properties with polystyrene, making them versatile for applications beyond traditional packaging, including furniture and organic plastics. Its lightweight nature and ease of moulding make it an ideal material for distribution, with the added benefit of contributing to cost-effective raw materials and disposal processes.
As businesses grapple with the environmental consequences of their packaging choices, mushroom packaging emerges as a sustainable and economically viable solution. Beyond its immediate applications, mycelium-based materials promise to prevent future environmental crises. By embracing mushroom packaging, businesses can reduce their ecological footprint and position themselves as leaders in environmentally responsible practices, meeting the evolving expectations of conscious consumers.
Mushroom packaging represents a transformative shift in the business landscape, offering a compelling response to the pressing environmental challenges posed by traditional packaging materials. As businesses increasingly prioritize sustainability, adopting mushroom packaging stands out as a strategic choice, aligning corporate practices with the imperative of safeguarding our planet for future generations.
For Instance,
| Trends | |
| Rising Interest in Compostable Packaging | With a growing emphasis on sustainable and compostable packaging, mushroom-based alternatives are gaining popularity. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of packaging materials, prompting businesses to seek compostable solutions. Mushroom packaging, being biodegradable and compostable, aligns well with this trend. |
| Innovation in Production Processes | Advances in the production processes of mushroom packaging are streamlining its integration into mainstream business practices. Efforts to optimize cultivation methods, reduce production timelines, and enhance scalability are key focus areas. These innovations aim to make mushroom packaging more accessible and cost-effective for businesses of all sizes. |
| Collaborations and Research Initiatives | Collaborations between businesses and research institutions are driving innovation in mushroom packaging. Ongoing research aims to enhance the performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of mycelium-based materials. Partnerships between academia and industry players are crucial in pushing the boundaries of what mushroom packaging can achieve. |
| Global Regulatory Landscape | As environmental regulations tighten globally, businesses are proactively seeking sustainable packaging options to comply with evolving standards. Mushroom packaging, being a natural and biodegradable material, fits well within the framework of environmentally conscious regulations, positioning it as a strategic choice for businesses navigating the regulatory landscape. |
| Expanded Product Applications | The versatility of mushroom packaging is leading to its expanded use beyond traditional shipping applications. Companies are exploring ways to integrate mycelium-based materials into various product lines, including electronics, furniture, and single-use items. This diversification demonstrates the adaptability of mushroom packaging across industries. |
In the dynamic landscape of sustainable business practices, mycelium, the rapidly increasing vegetative portion of fungi found in agricultural and biological waste, has emerged as a game-changer. Mycelium-based packaging is reshaping how businesses approach packaging solutions by offering a sustainable and safe alternative to traditional materials.
Mycelium-based packaging leverages the unique properties of mycelium, cultivated within specially designed moulds. As a natural adhesive, mycelium bonds with sawdust, effectively replacing less eco-friendly materials such as polystyrene. The controlled growth process involves drying and heating the mycelium foundation, arresting its development once it assumes the desired forms.
A standout feature of mycelium is its trifecta of qualities – lightweight, robust, and cost-effective. This entirely natural material is gaining traction as an attractive and affordable substitute for products derived from fossil fuels. It’s remarkable ability to be moulded into diverse shapes, seemingly growing to fill moulds, provides a distinct advantage for manufacturers seeking versatile and sustainable packaging solutions.
Beyond its manufacturing advantages, mycelium stands out for its exceptional end-of-life characteristics. Once it’s helpful life concludes, mycelium-based products can be easily composted at home, making them especially appealing for packaging and other single-use applications. In the natural environment, mycelium breaks down, replenishing the soil with valuable nutrients. Some innovators take it a step further by incorporating grass and wildflower seeds into mycelium packaging, contributing to the bio-circularity of the products.
The adoption of mycelium-based packaging aligns seamlessly with the growing demand for sustainable business practices. Its inherent eco-friendly attributes position it as a strategic choice for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact. The versatile nature of mycelium not only caters to immediate packaging needs but also opens doors for innovative applications across various industries.
As consumer preferences increasingly shift towards environmentally conscious choices, mycelium packaging offers a strategic advantage. Its sustainable and compostable nature resonates with aware consumers, allowing businesses to align their brand with eco-friendly values. By integrating mycelium-based solutions, companies can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, meeting the evolving expectations of a socially and environmentally aware customer base.
The mycelium-based packaging revolution represents a paradigm shift in sustainable business practices. Beyond its technical merits, mycelium aligns with the ethos of circular economies, contributing to a regenerative approach to production and consumption. As businesses navigate the path to a greener future, mycelium is a testament to the symbiotic relationship between innovation, environmental stewardship, and economic viability.
A compelling application of mycelium-based packaging involves substituting polystyrene, known as Styrofoam. Polystyrene poses a substantial environmental challenge as a significant contributor to litter and debris, particularly in our oceans. The critical issue with polystyrene lies in its non-biodegradable and non-compostable nature, making it unsuitable for recycling in most facilities. Consequently, polystyrene persists in landfills for an estimated 500 years, contributing to ocean pollution and endangering aquatic life. Moreover, the production of polystyrene entails high energy consumption and significant greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, mycelium-based alternatives offer a sustainable solution. These alternatives are compostable and biodegradable, breaking down within weeks when discarded in backyard composting systems. As the mycelium packaging decomposes, it disintegrates and enriches the soil by providing valuable nutrients, essentially acting as a natural fertilizer. The production process of mushroom packaging initiates with the growth of the mycelium, which absorbs carbon dioxide during its development, potentially rendering its carbon footprint more favourable when compared to polystyrene. This shift toward mycelium-based packaging showcases a promising step in mitigating the environmental impact of traditional polystyrene materials.
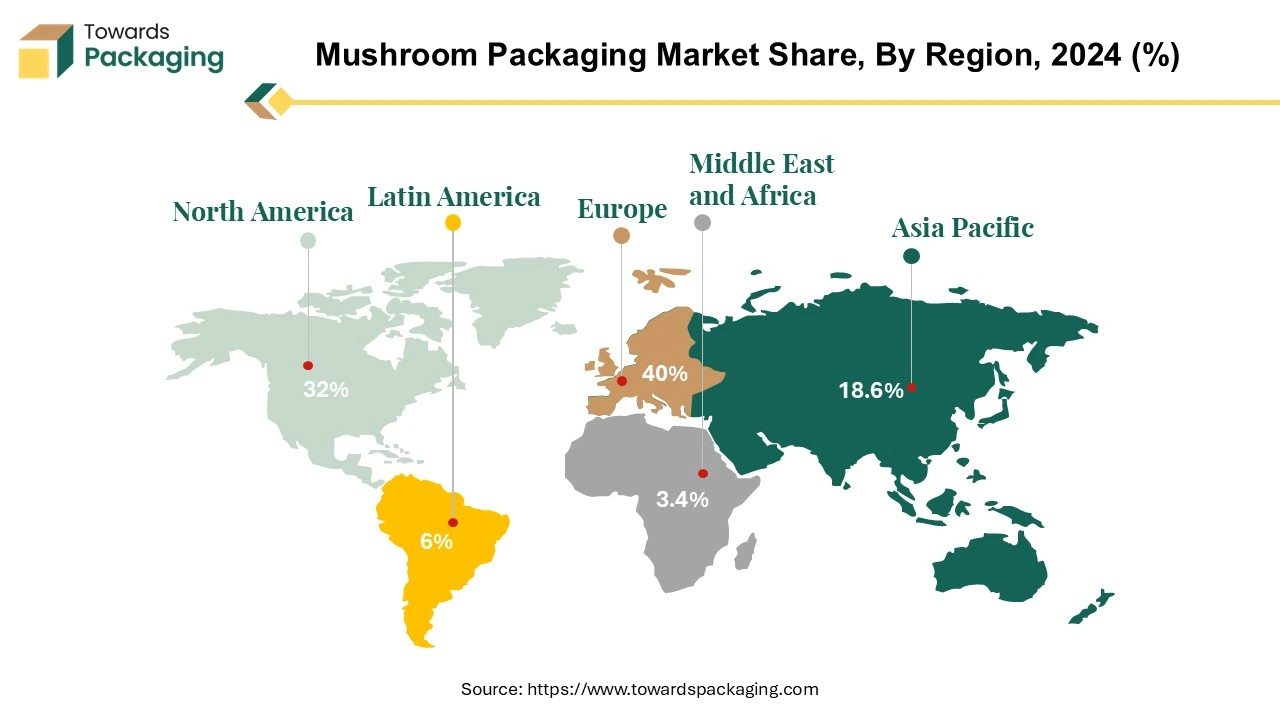
Europe is projected to be a significant driver, accounting for 40% of the market's growth throughout the forecast period. Germany emerged as the focal point for mushroom packaging within the European market. The growth trajectory in this region is expected to outpace that of other global areas.
The European Union (EU) has prioritized the adoption of environmentally friendly packaging alternatives, positioning mycelium as a pivotal element in the continent's sustainability initiatives. The transition from conceptualization to policy implementation has propelled the EU toward the realization of a circular economy. In this transformative change, agricultural waste streams have undergone a transformative revaluation, now considered valuable resources rather than environmental liabilities. Notably, mycelium has emerged as a central component in numerous global and European sustainability endeavours.
The Environment Committee has endorsed a proposed regulation outlining comprehensive requirements for the entire life cycle of packaging, spanning from raw materials to ultimate disposal, signals a significant step in shaping the future landscape of packaging practices.
To address environmental concerns, Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) advocate prohibiting the sale of highly lightweight plastic carrier bags, specifically those below 15 microns. Exceptions would be granted for cases involving hygiene necessities or, when serving as primary packaging for loose food, strategically aligned to combat food wastage. Overarching targets for reducing packaging, MEPs call for distinct waste reduction goals for plastic packaging, envisioning a 10% reduction by 2030, 15% by 2035, and 20% by 2040. Specific minimum percentages of recycled content in the plastic packaging component are proposed to promote sustainability, with targeted benchmarks set for 2030 and 2040.
EU Commission is tasked with conducting a comprehensive assessment by the close of 2025 to explore the feasibility of proposing targets and sustainability criteria for bio-based plastics such as mushroom packaging. Recognized as a pivotal resource for "defossilizing" the plastics economy, this initiative underscores the commitment to advancing sustainable practices in the industry.
A key driver behind the increasing prominence of mycelium-based products, such as mushroom bricks, lies in their remarkable carbon neutrality. This characteristic serves to counterbalance several drawbacks associated with conventional materials. The significance of carbon neutrality is accentuated by the fact that 16 European countries have embraced this ethos, introducing carbon taxes that range from just under €1 to as high as €100 per metric tonne of carbon emissions.
Implementing carbon taxes across Europe has far-reaching implications, compelling businesses to transition to sustainable practices. Companies can strategically sidestep carbon taxes by adopting materials like mycelium, thus contributing to environmental preservation and financial prudence. Notably, Switzerland leads the way with a carbon tax of €108.81 per tonne, followed closely by Liechtenstein at €90.53 and Finland at €62.18.
The imposition of carbon taxes reflects a broader commitment to sustainability, incentivizing businesses to reassess their environmental impact. With its carbon-neutral profile, the mycelium solution aligns seamlessly with the evolving regulatory landscape, positioning itself as a strategic choice for businesses seeking to navigate and thrive within the EU's sustainability framework.
As the mushroom packaging market continues to grow in Europe, driven by regulatory imperatives and corporate environmental responsibility, mycelium-based solutions will likely play an increasingly central role. The percentage of market growth in this sector is anticipated to rise in tandem with the expansion of sustainability initiatives and the escalating awareness of the advantages offered by mycelium over traditional packaging materials.
The European market's adoption of mycelium-based packaging is intricately tied to the region's commitment to sustainability, exemplified by the implementation of carbon taxes. The carbon-neutral nature of mycelium not only addresses environmental concerns but also positions businesses strategically in the face of evolving regulatory landscapes, making it a pivotal player in the burgeoning mushroom packaging market in Europe.
The market for mushroom packaging is characterised by intense competition because there are several key players such as Ecovative Design LLC, Magical Mushroom Company, Sealed Air Corporation, CMP Mushroom, Mushroom Packaging, Dell Technologies, Costa Group, Shroom Labs, UNO PLAST and others. This market has a medium level of market concentration, and several major players are present, using tactics such as product innovation, acquisitions, and mergers to obtain a competitive edge.
The market players are significantly impacting environmental development by adopting sustainable packaging and creating consumer awareness through innovative packaging materials. Ecovative Design LLC and Magical Mushroom Company are Europe-based lead players who have a global impact by reducing carbon through innovative packaging materials adopted by leading companies like Dell and Ikea; they started sustainable packaging by introducing mushroom-based materials in their packaging and other materials.

By Material
By Application
By Region
April 2025
March 2025
March 2025
March 2025