December 2025
The biobased films market is projected to grow from USD 5.47 billion in 2025 to USD 13.97 billion by 2035, supported by a strong 11.5% CAGR from 2026–2035. This report covers full segmentation by material, application, and end use; detailed regional analysis across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and MEA; competitive benchmarking of key companies; value chain and trade flow examination; and profiling of leading manufacturers and suppliers globally.
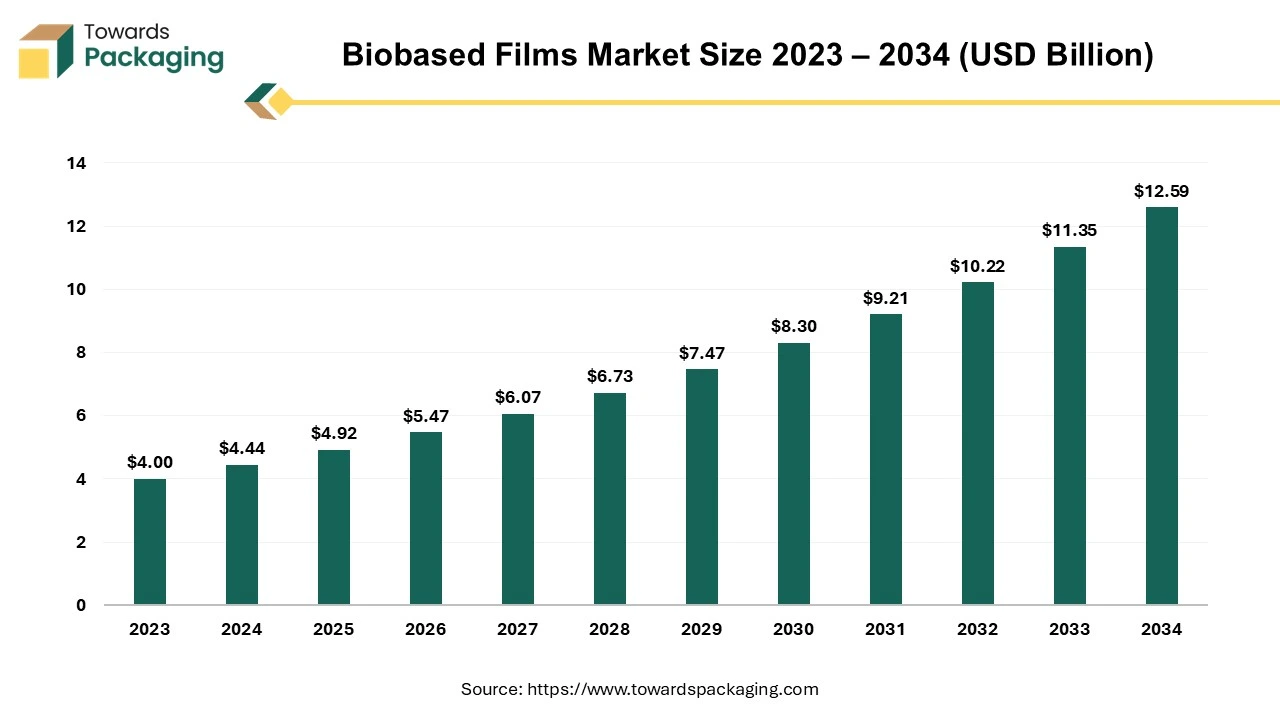
The biobased films market is anticipated to grow remarkably over the projected time period. Bio-based materials are produced from renewable resources and are an excellent alternative to fossil plastic materials. The properties are similar to regular raw materials, but the CO2 footprint of bio-based materials is demonstrably better through LCA. The input granulate is purely natural material such as sugarcane, corn, etc.
Bio based films can be used in the same applications as traditional grades made of fossil-based feedstock and guarantee the same excellent technical performance and machinability. These films are widely used in packaging, agriculture, and other industries due to their eco-friendly properties and ability to reduce reliance on fossil-fuel-based plastics.
The increasing environmental awareness among consumers and companies along with the growing government regulations and policies aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting biodegradable alternatives is expected to augment the growth of the biobased films market during the forecast period. Furthermore, the developments in the biopolymer technology coupled with the corporate sustainability initiatives and a shift towards circular economies is also anticipated to augment the growth of the market. Additionally, the growing food and beverage industry as well as the rising adoption of biobased materials in agriculture for mulch films and plant protection is also projected to contribute to the growth of the market in the near future.
The rapid expansion of the agricultural sector is expected to augment the growth of the biobased films market within the estimated timeframe. This is owing to the growing global population, increased demand for food, prompting investments in the agricultural technologies and practices to improve the productivity. The governments across the globe are additionally supporting the sector with policies dedicated to strengthen the food security and reducing dependency on imports.
According to the Eurostat data, the value of agricultural output in the European Union (27 countries) increased substantially, reaching 545,441 million euros in 2022. The most prominent growth occurred between 2021 and 2022, where the output surged from 455,632 million euros to reach 545,441 million euros, indicating strong recovery as well as expansion. Most of the value of the agricultural output in the year 2022 came from France (97,345M€), Germany (77,924M€), Italy (72,679M€), Spain (63,068M€), and Netherlands (40,556M€).
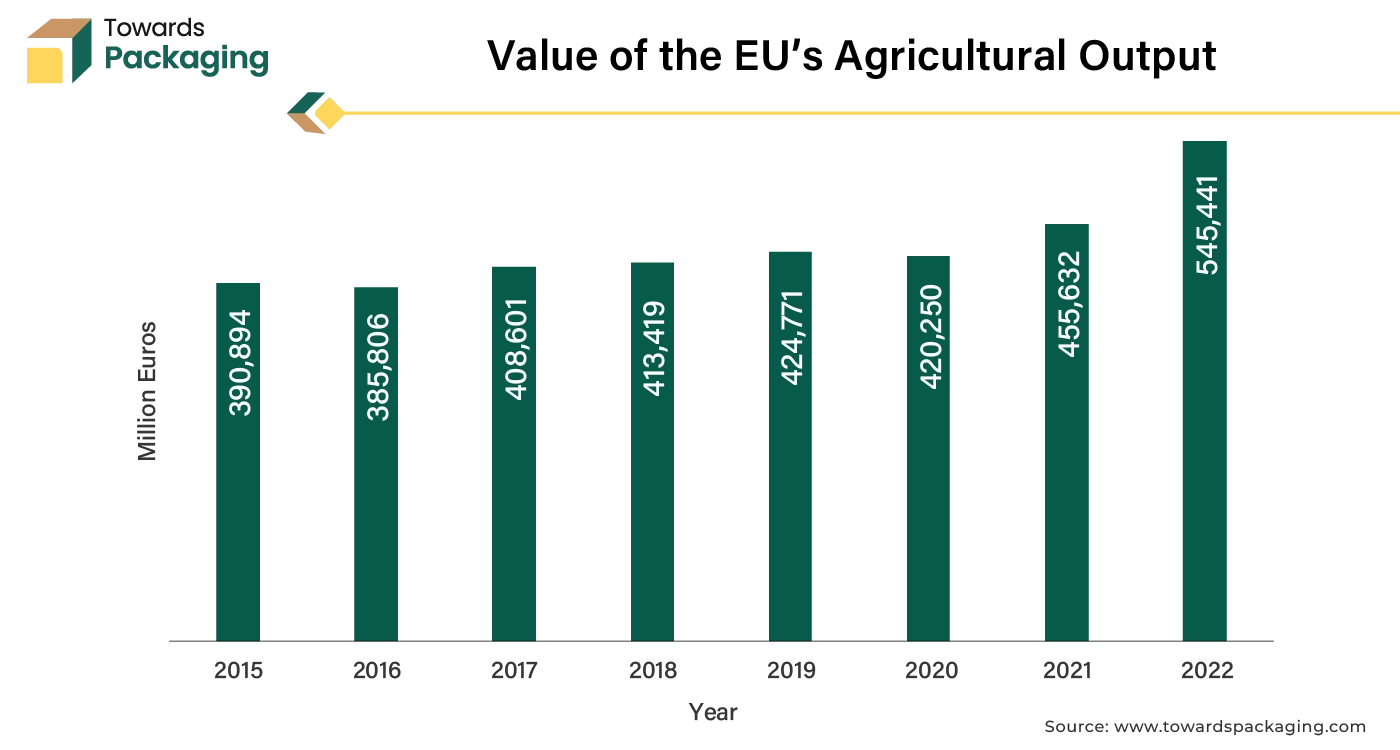
This upward trend highlights the growing importance of the agricultural sector in the European Union, which is expected to contribute to the growth of the biobased films, to support agricultural operations. The utilization of films improves many aspects of crop development and makes it possible to cultivate a wide variety of vegetables with greater efficiency. For many vegetables, earlier harvests, greater yields, and improved quality are possible. Also, the films facilitate a substantial decrease in soil moisture loss.
As a result, the ground stays moist, reducing the need for further watering. According to field tests, the vegetable harvest is nearly twice as large as it would be with an approach that does not use agricultural films. Additionally, as farmers are also focusing on the sustainability, the adoption of the biobased films is expected to expand, further driving their demand across global markets.
The barriers in commercializing novel biobased polymers such as such as polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and polyethylene furanoate (PEF) are expected to limit the growth of the biobased films market within the estimated timeframe. The aforementioned materials, which are made from renewable resources such as plant oils, corn starch, and sugarcane, have potential for sustainability but face a few challenges when it comes to market acceptance. The difficulty of establishing the required processing technologies and scaling up production is one of the main challenges.
For example, even though big companies could be interested in utilizing these materials, acceptance is hampered by their restricted mass availability. Also, without steady demand, large-scale production is impossible, which again slows the growth of the market. To maintain competitive pricing and supply chain security, the market also needs many vendors for the same grade of polymer, which makes scalability even more difficult.
The cost remains another important concern. Compared to the conventional plastics derived from fossil fuels that are still the more cost-effective choice for the majority of applications, novel biobased polymers frequently have higher production costs. Wider adoption is discouraged by this cost discrepancy, specifically in the price-sensitive segments. Also, the low price of the traditional plastics frequently reflects externalized environmental costs, giving the impression that they are falsely less expensive.
Additionally, many biobased polymers still have issues with supply chain management and end-of-life matters. Large companies like Nestlé and PepsiCo are showing increasing interest in these materials, but it will take years or perhaps decades of consistent investment and innovation to get beyond these obstacles. These factors collectively slow the market penetration of the biobased films, as manufacturers and end-users continue to rely on the cheaper and more readily available fossil-based alternatives, hindering the transition toward sustainable materials.
The increasing investments in the recycling infrastructure owing to the growing concerns over environmental degradation caused by plastic waste as well as pollution in oceans and waterways, harm to wildlife and greenhouse gas emissions is expected to create substantial growth opportunity for the biobased films market in the near future. Regulators are taking initiatives to limit the plastic waste as well as promote sustainable activities. Many economies have also adopted partial or complete bans on the single-use plastics, increasing the demand for the alternative materials. For instance:
The Australian Capital Territory on January 1, 2024 prohibited all types of plastic shopping bags having handles, paper or cardboard bags coated in plastic, as well as non-woven polypropylene bags weighing less than 90 grams and lacking stitched seams. The ACT also prohibited the use of single-use plastic plates and bowls, thick plastic carry bags, polystyrene trays, loose-fill packaging, and plastic micro beads from July 1, 2024.
China announced restrictions on the manufacture and sale of single-use plastic bags and cutlery in January 2020, along with a strong timeline for their eventual elimination from the market. In less than a year, some single-use items were to be substituted out for alternatives. China's revised Solid Waste Law stipulates that violation with plastic use regulations might result in fines of between 10,000 and 100,000 Yuan.
In accordance with EU law, Scotland, England and Wales have all outlawed single-use plastic utensils, bowls, plates, balloon sticks, trays and polystyrene food and drink vessels. Retailers have been required to charge for the plastic carrier bags since 2015; the money raised goes to environmental and charitable initiatives. The regulation has resulted in a 95% decrease in the utilization of carrier bags and raised millions of pounds.
These regulations support the development of the new biopolymer technologies while also making it easier for sustainable alternatives to compete with the traditional plastics by solving their cost differences. As governments continue to strengthen regulations and prioritize sustainability, the biobased films market is well-positioned for substantial growth in the coming years.
The biobased films market is expected to undergo a transformation due to the AI's impact on the production and research. The materials industry has seen a global shift towards sustainable practices due to the urgency of dealing with climate change and the depletion of the finite resources; bio-based materials have been identified as one of the most promising breakthroughs in this field. Additionally, as public interest grows, numerous certifications and labels are emerging to control quality and structure the market for the new laws implemented by public institutions.
Artificial intelligence will be important in the production of bio-based materials, specifically during the research and development phase. As a result, tech firms are creating AI platforms that let scientists utilize AI technology appropriate for the materials science at every stage of the production of the bio-based materials. Customers can use machine learning (ML) algorithms from companies like Osium AI to predict material properties, model complex materials science phenomena as well as find patterns and correlations that human analysis might miss. This eliminates the lengthy physical testing and expedites the development of the new materials.
It is evident that various difficulties of the conception stage can be minimized with the incorporation of AI in the R&D stage of the development of bio-based materials. The AI based system helps materials scientists to concentrate on the desired compositions based on their requirements throughout the formulation stage. When creating bio-based materials, this makes it easier for the companies to deal with the feedstock supply limits and minimize their dependency on essential elements. Optimizing the processes involved in material production is another essential function of the tools.
The AI platform provides process optimization solutions that help organizations to decrease production costs, improve production volume, and create sustainable procedures. Thus, AI is important in driving the innovation, improving the operational efficiency, and expanding the market reach of the biobased films in response to the growing environmental concerns and demand for the sustainable alternatives.
The polylactic acid (PLA) segment is likely to grow at a considerable CAGR during the forecast period. PLA is a potential biodegradable polymer derived from plant resources. It provides enough transparency and gloss, comparable with polystyrene (PS) films. Furthermore, PLA facilitates the production of biodegradable plastics with exceptional antibacterial and antifungal qualities in addition to having a high degree of mechanical strength and heat resistance.
Additionally, PLA uses considerably less resources and energy for manufacturing than traditional plastics. The multipurpose bio-based polymer has use in the food, pharmaceutical, textile, 3D printing and agricultural sectors. These factors are likely to support the segmental growth of the market during the forecast period. The development of advanced PLA products such as Bioworks' PlaX which is a plant-derived PLA polymer combined with a proprietary plant-based resin to enhance its functionality is a prime example of innovation driving growth.
The food and beverage segment held largest market share in the year 2024. This is owing to the increasing demand for the convenience and time-saving options across the globe. Furthermore, the rise of the ready-to-eat meals, snacks, and delivery services along with the growing health-conscious population and popularity of the plant-based alternatives, clean-label products, and functional beverages are also likely to contribute to the growth of the segment within the estimated timeframe. Additionally, the expansion of e-commerce, increase in the food delivery apps and more payment technologies are further expected to support the segmental growth of the market in the near future.
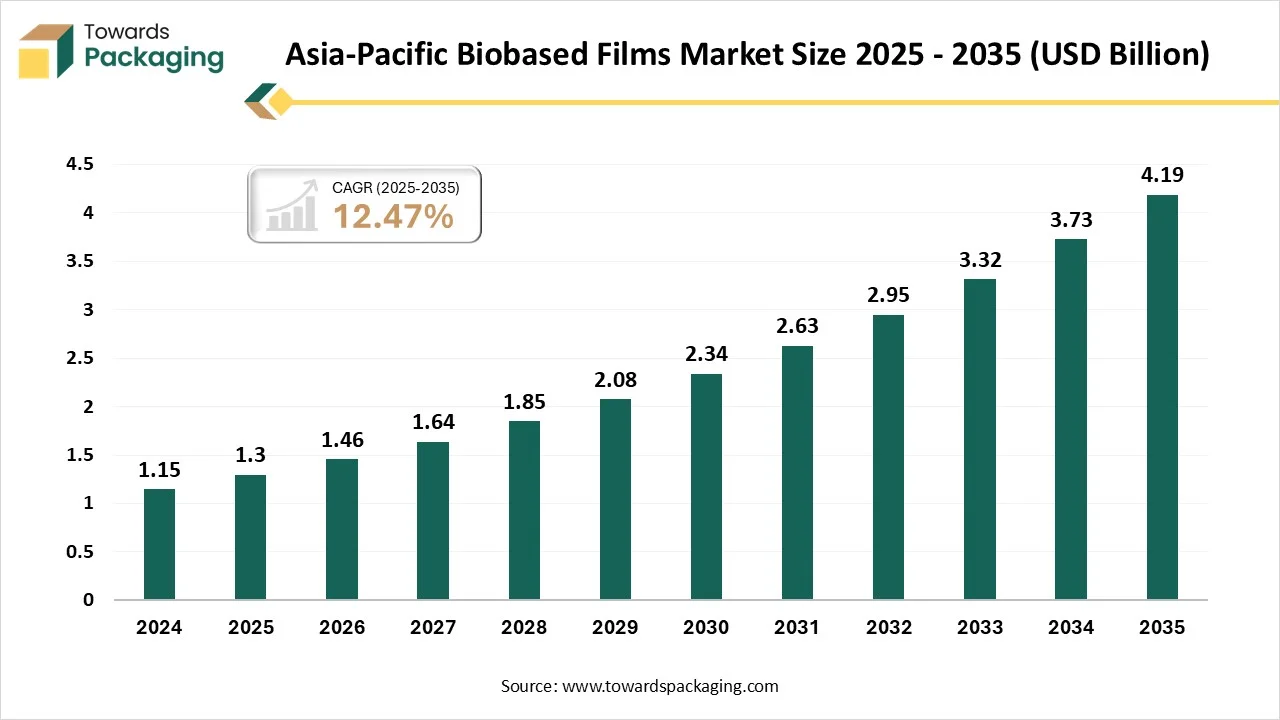
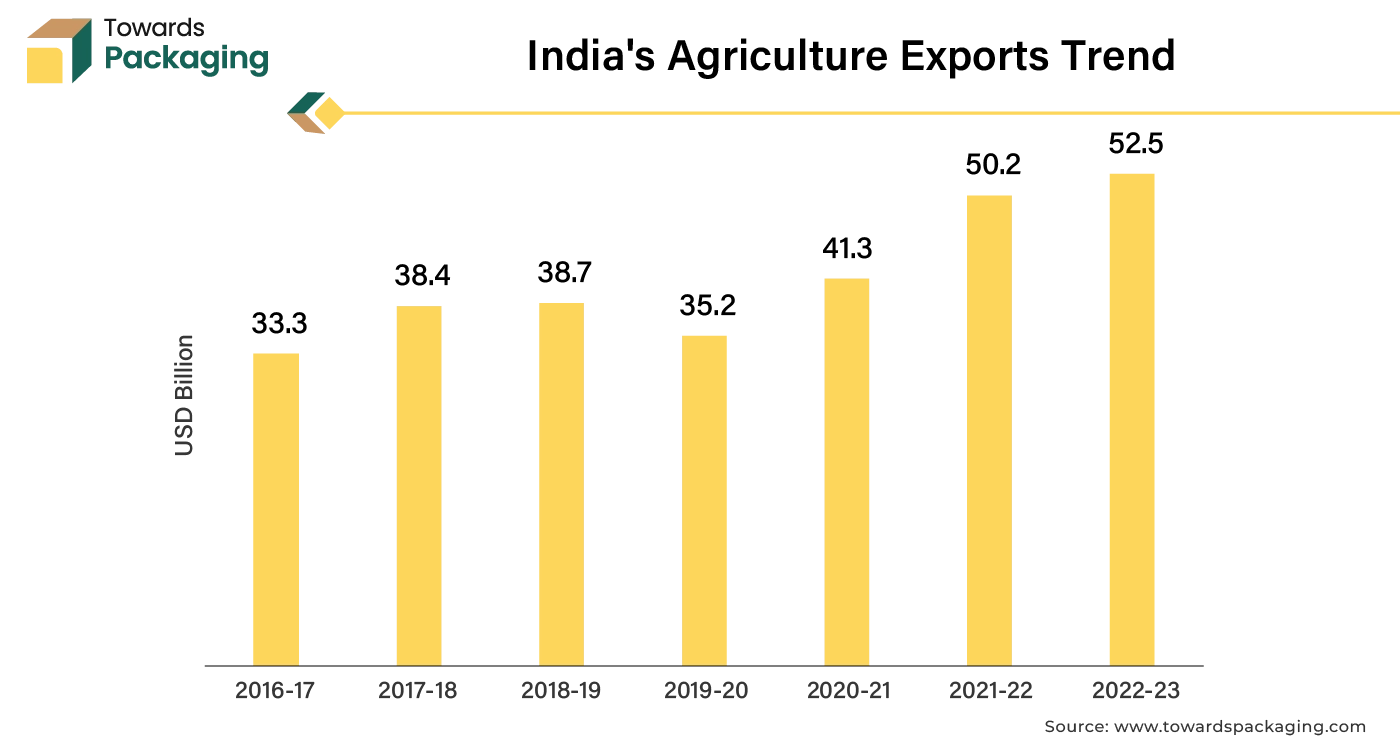
Asia Pacific is likely to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This is due to the rapid expansion of the industries such as food and beverage and agriculture in the region. According to the India Brand Equity Foundation, India's agriculture sector was expected to increase at a rate of 3.5% in 2022–2023 and 3.0% in 2021–2022. India's agricultural exports totaled US$52.50 billion in 2022–2023. The nation's overall agricultural exports in 2021–2022 totaled US$ 50.2 billion, a 20% increase over US$ 41.3 billion in 2020–21.
Also, the growing urban population and rising middle class with increasing disposable income is likely to contribute to the regional growth of the market. Furthermore, the low cost of the raw materials and labor are also expected to contribute to the regional growth of the market.
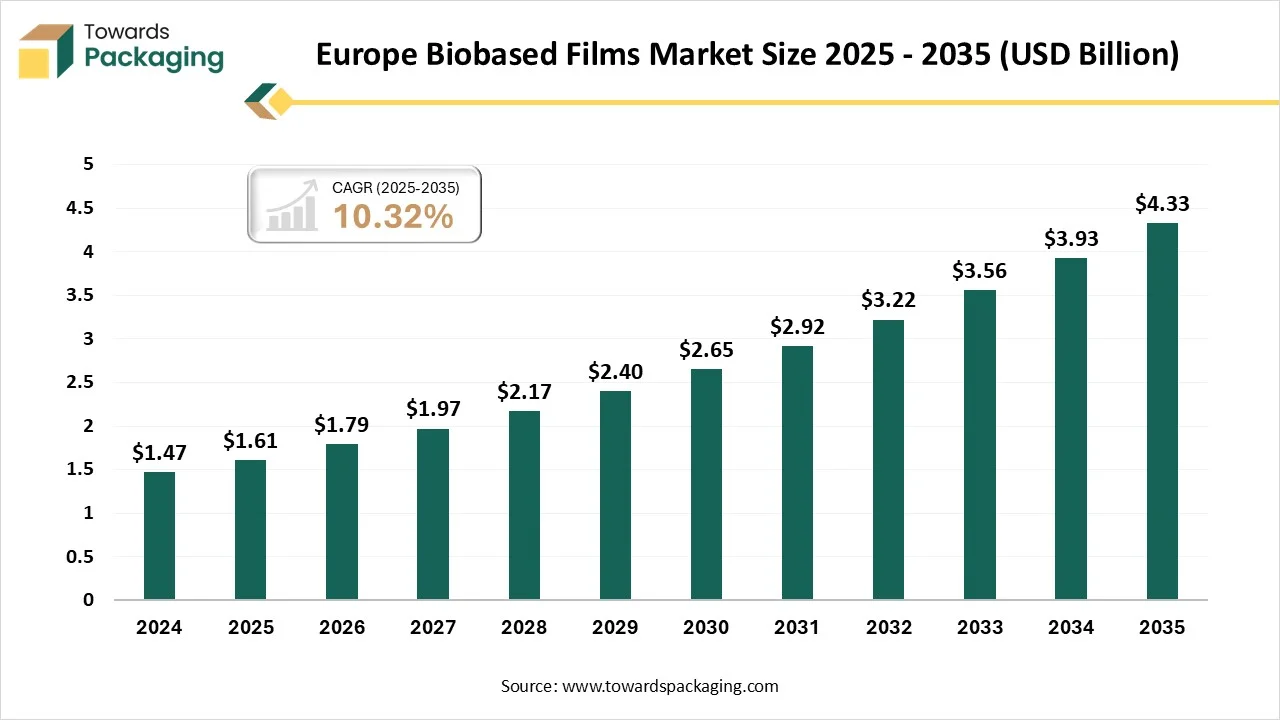
Europe held substantial market share in the year 2024. This is owing to the implementation of the stringent regulations to reduce the plastic waste across the region. Under the EU Directive 2019/904 on Single-Use Plastics (SUP), the EU has prohibited several single-use plastic items since July 2021, like cutlery, straws, cotton bud sticks, plates, stirrers and balloon sticks. The SUP Directive has implemented a number of measures for various single-use plastics, like waste management and cleanup requirements for manufacturers, with the goal of reducing these goods. Additionally, the growing consumer preference for the eco-friendly products along with the increasingly prioritizing circular economy models is also expected to contribute to the regional growth of the market. Furthermore, the presence of set ambitious sustainability and carbon neutrality targets is also expected to contribute to the regional growth of the market.

By Material Type
By End-User Industry
By Region
December 2025
December 2025
December 2025
November 2025