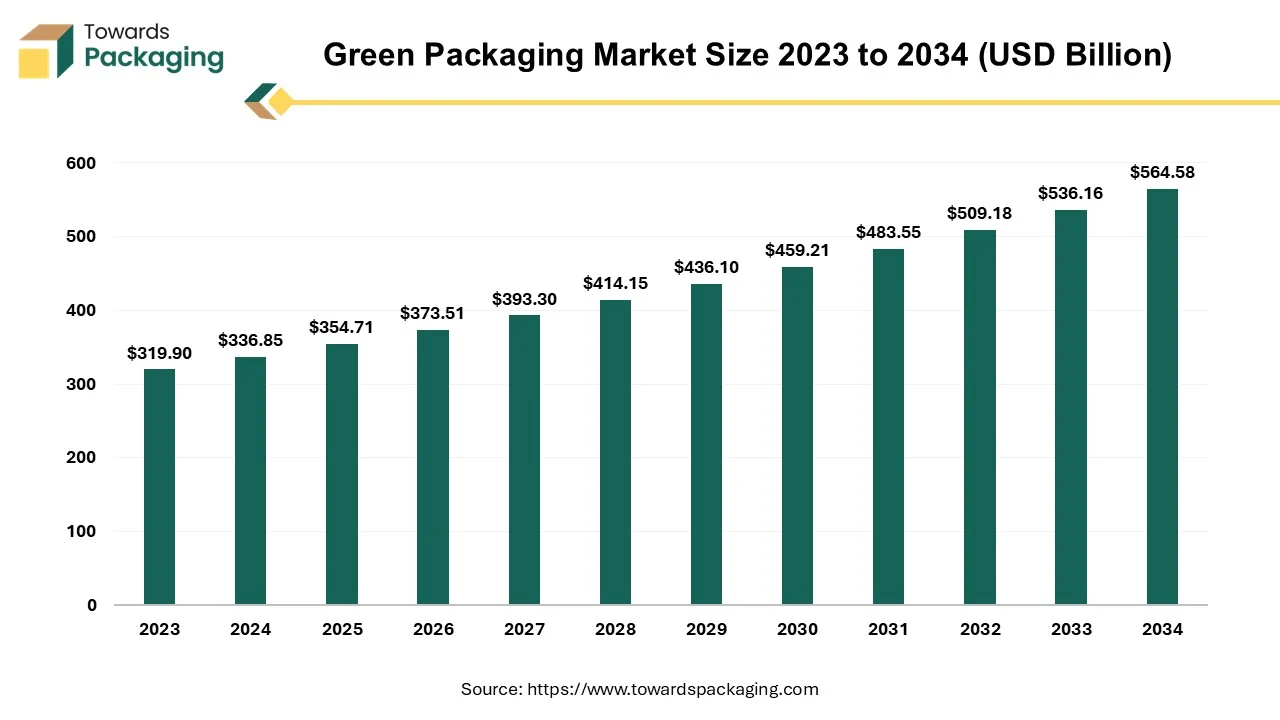
The green packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 373.50 billion in 2026 to USD 594.50 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 5.3% from 2026 to 2035. Our research covers extensive segment data, including recycled content packaging, degradable materials, and reusable packaging. The market is segmented by applications in food & beverages, personal care, healthcare, and shipping. Regional insights highlight Europe as the largest market, while Asia Pacific is anticipated to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period.
Green packaging, also known as sustainable packaging or eco-friendly packaging, refers to packaging materials and practices that minimize environmental impact. The green packaging Reduces excess materials and using lightweight packaging to cut down on waste. Green packaging, also known as sustainable packaging or eco-friendly packaging, refers to the use of materials and production methods that have a minimal environmental impact. As concerns about pollution, climate change, and resource depletion grow, businesses and consumers are shifting toward packaging solutions that are sustainable, recyclable, and biodegradable. The green packaging is derived from renewable sources like cornstarch, sugarcane, or algae. Examples include PLA (polylactic acid) and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates).
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 354.70 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2035 | USD 594.50 Billion |
| CAGR (2026 - 2035) | 5.3% |
| Leading Region | Europe |
| Market Segmentation | By Packaging Type, By Application, By Material and By Region |
| Top Key Players | Amcor, Be Green Packaging, DS Smith, DuPont, Evergreen Packaging |
Al is essential to the creation of effective and environmentally friendly packaging solutions. It helps with waste reduction, packaging process simplification, and the identification of the best packaging materials and designs. Businesses can create environmentally friendly substitutes and get rid of needless packaging materials by utilizing Al-driven technologies. Al also assists in locating and getting rid of items that aren't recyclable or biodegradable, opening the door for more environmentally friendly packaging techniques.
Al can help businesses reduce waste and maximize efficiency in their supply chain processes. Large volumes of supply chain data can be analysed using Al-powered analytics, which can pinpoint areas for efficiency gains and packaging waste reduction. Ordering and packing are two examples of procedures that can be automated to save waste and expedite operations. Al's real-time monitoring system guarantees on-time delivery and high-quality products, which further cuts down on waste.
| Product Description | Loading Port | Unloading Port | Country | Quantity | Weight (kg) |
| STORAGE BOX | 57078, YANTIAN | 2709, LONG BEACH, CA | CN, CHINA | 1271 | 17529 |
| FLEXIBLE INTERMEDIATE BULK CONTAINER | 53313, JAWAHARLAL NEHRU | 1601, CHARLESTON, SC | IN, INDIA | 48 | 18114 |
| GLASS BOTTLES, FLINT | 42870, BREMERHAVEN | 4601, NEW YORK/NEWARK AREA, NJ | DE, GERMANY | 22 | 19734.32 |
| FLATWARE STORAGE BOX CORDLESS INFLATOR | 57037 | 2709, LONG BEACH, CA | CN, CHINA | 936 | 12964 |
| KNAPSACK GLASS BOTTLES | 57020, NINGPO | 2709, LONG BEACH, CA | CN, CHINA | 875 | 12964 |
The rise of online shopping and meal delivery services has increased the demand for sustainable packaging to reduce waste. Brands are adopting compostable mailers, paper-based alternatives, and reusable packaging to meet consumer expectations.
The key players operating in the green packaging market are facing issue due to high initial investments, lack of proper recycling infrastructure and less consumer awareness about sustainable packaging. Many countries and regions lack advanced recycling facilities to properly process biodegradable and compostable packaging. Inefficient waste segregation systems reduce the effectiveness of recyclable materials. Many consumers do not fully understand how to dispose of eco-friendly packaging, leading to improper waste management. Greenwashing (misleading sustainability claims) can reduce trust in eco-friendly packaging and slow adoption.
Some sustainable packaging options are less durable than plastic, making them unsuitable for certain products (e.g., moisture-sensitive goods). Shorter shelf life of biodegradable packaging can be a concern for food and pharmaceutical industries. Traditional packaging industries (plastics, petroleum-based materials) lobby against stricter environmental regulations to protect their market. Some businesses resist change due to concerns about cost, supply chain complexity, and regulatory uncertainty.
Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of packaging materials, with a growing preference for eco-friendly, biodegradable, and recyclable options. This shift in consumer behavior is influencing businesses to adopt green packaging solutions to align with consumer values and enhance brand image. Companies that invest in sustainable packaging are likely to gain competitive advantages by meeting the demand for environmentally conscious products.
The recycled content packaging segment held a dominant presence in the green packaging market in 2024. Many countries have strict recycling laws and targets for reducing plastic waste. Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs require brands to use a certain percentage of recycled content in packaging. The European Union’s Circular Economy Plan and similar regulations in the US, Canada, and India encourage recycled materials in packaging. Global brands like Coca-Cola, Unilever, and Nestlé have pledged to use more recycled materials in packaging. Many companies aim for 100% recyclable or reusable packaging by 2030 to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals.
Retailers and e-commerce platforms (like Amazon) are demanding sustainable packaging from suppliers. Improved sorting and processing make it easier to produce high-quality recycled materials. Chemical recycling allows plastics to be broken down and reused at near-virgin quality. New technologies ensure that recycled content packaging is durable, safe, and visually appealing. Recycled content packaging is dominant because of strong regulations, corporate sustainability goals, cost benefits, consumer demand, and advancements in recycling technology.
The food & beverage segment led the global green packaging market. Green packaging is gaining popularity in the food and beverage industry due to several key factors, including environmental benefits, regulatory requirements, and consumer preferences. Green packaging materials like plant-based bioplastics, recycled paper, and bamboo are free from harmful chemicals (e.g., BPA, phthalates). Plastic bans in Europe, Canada, and parts of the U.S. push brands toward sustainable alternatives. Strict food packaging laws (e.g., FDA, EU regulations) encourage safe, recyclable, and biodegradable materials. Although initial costs may be high, reusable and recyclable packaging reduces waste management expenses. Many companies use returnable packaging systems to lower costs and waste.
The plastic segment registered its dominance over the global green packaging market in 2024. Plastic is cheaper to produce than other sustainable materials like glass, metal, or paper alternatives. It requires less energy for manufacturing and transportation due to its lightweight nature. Large-scale production infrastructure for plastics is already established, making it easy for companies to adopt recycled plastic instead of switching to new materials. Many countries have set minimum recycled content requirements in plastic packaging. Plastic waste management laws (Extended Producer Responsibility – EPR) encourage brands to adopt post-consumer recycled (PCR) plastics. The rise in e-commerce and online food delivery has increased demand for lightweight, protective packaging. Brands are using recyclable mailers, plastic-free bubble wrap, and compostable polybags to reduce waste.
Europe region held the largest share of the green packaging market in 2024. Bans on single-use plastics and policies like the European Green Deal push companies to adopt eco-friendly packaging. Companies set ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals, prioritizing green packaging. Covering the full package life-cycle, the new rule aims to further harmonize national recycling, reuse, and manufacturing policies. With the rules in place, the EU anticipates a major reduction in water consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and the harm that packaging and packaging waste cause to the environment and the health of its people.
In a notable industry move, Mondi, a leading packaging company, acquired the western European assets of Germany-based Schumacher Packaging for €634 million. This acquisition includes advanced box production plants in Germany and aims to enhance Mondi's operations in e-commerce and consumer goods packaging. A number of laws have been put in place by the German government to lessen the waste from plastic and encourage environmentally friendly packaging options. The Packaging Act (VerpackG) and other initiatives mandate that producers assume accountability for the packaging materials' lifespan. This law requires involvement in recycling programs and promotes recyclable goods.
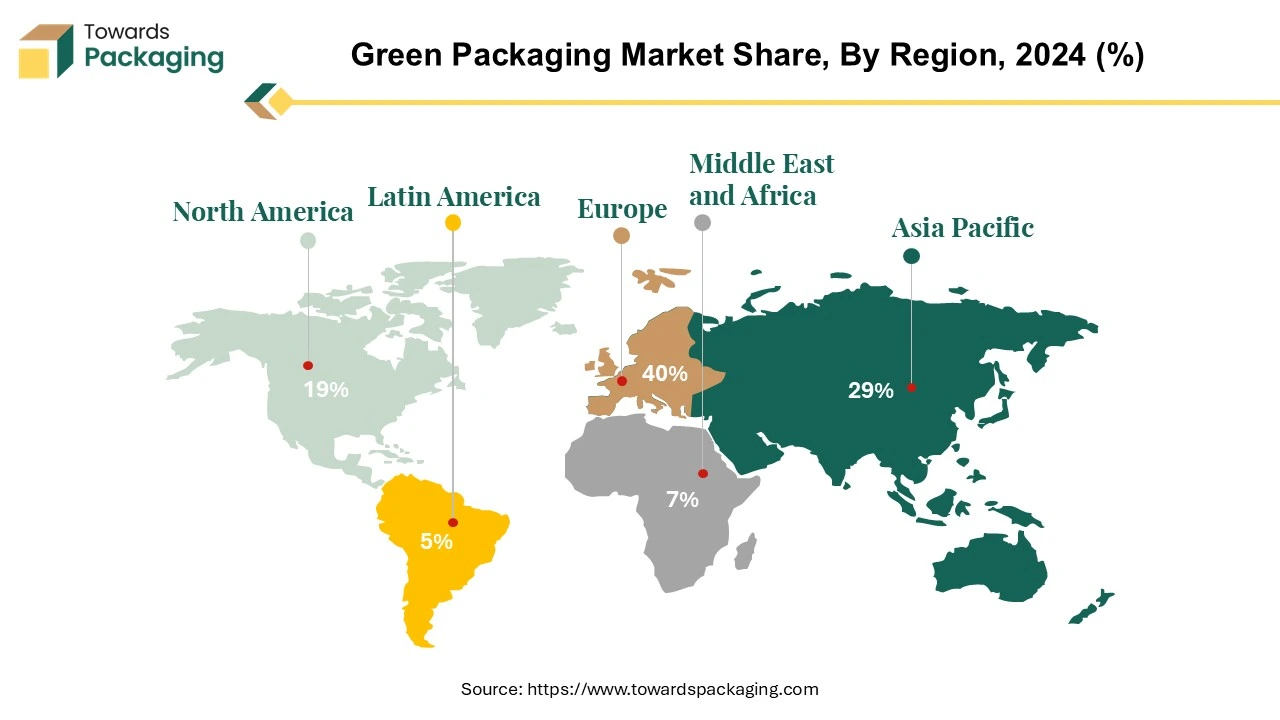
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the green packaging market during the forecast period. The Asia Pacific region is leading the way in the green packaging market due to its strict packaging laws and fastest-growing customer base. Through the introduction of creative designs and the use of innovative materials, businesses throughout the packaging value chain are searching for more sustainable solutions to keep up with consumer demands and governmental laws. Recycled and biodegradable materials are being used in green packaging by major firms, who are also following the trend. Many countries in the region, such as China, India, and Japan, have implemented strict regulations on plastic usage and waste management. - Ban on single-use plastics and incentives for sustainable packaging solutions are boosting demand.
By prohibiting the use of single-use plastics and enticing businesses to switch to environmentally friendly alternatives, policies like the 2020 "Plastic Waste Ban" have had a big impact on the packaging sector. The government's pledge to become carbon neutral by 2060, which is in line with international environmental objectives, lends even more support to this change. The sector is growing as a result of these regulatory frameworks, which not only force manufacturers to innovate but also foster a climate that is conducive to green packaging solutions.
North America is seen to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. The U.S. and Canada have strong regulatory frameworks promoting sustainable packaging. Bans on single-use plastics and extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws in North America require companies to adopt eco-friendly packaging. Major companies like Amazon, Coca-Cola, and Unilever are setting sustainability goals and reducing plastic waste. Many industries in North America region are adopting circular economy models to reduce waste and improve recyclability.
The U.S. green packaging market is showing notable growth due to the laws implemented by government and sustainability initiatives by the industries. Federal and state governments are implementing bans on single-use plastics and promoting Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs in U.S. region. States like California, New York, and Washington have strict packaging waste reduction policies. Development of bioplastics, molded fiber, and edible packaging alternatives. Advancements in compostable materials and improved recycling technologies make sustainable packaging more viable. The U.S. Plastics Pact aims for 100% reusable, recyclable, or compostable packaging by 2025.
Premiumization trends are growing with consumers willing to pay more for good quality and sustainable packaging which is specifically evident in the beverage sector in which glass and aluminium are gaining preference over plastics. Consumers and businesses are driving the urge for eco-friendly and recyclable materials as they become more aware of their environmental effect.
This environment focuses on extension of biodegradable packing solutions which reflects the region’s determination to responsible packaging. The rise of the E-commerce sector is another crucial trend which has increased the demand for flexible packaging and the advantage of online shopping is filled by greater internet go through and smartphone usage whose outcome is responsible packaging.
Countries like the UAE and Africa are including environmental policies whose goal is to reduce plastic waste and encourage recycling too. These growth are making a favourable environment for recyclable , lightweight and bio -based aerosol packaging solutions. On the other hand, those who accept functional and sustainable packaging gain in terms of competitive edge while the recyclable and refillable expectations are fulfilled.

By Packaging Type
By Application
By Material
By Region
December 2025
December 2025
December 2025
December 2025