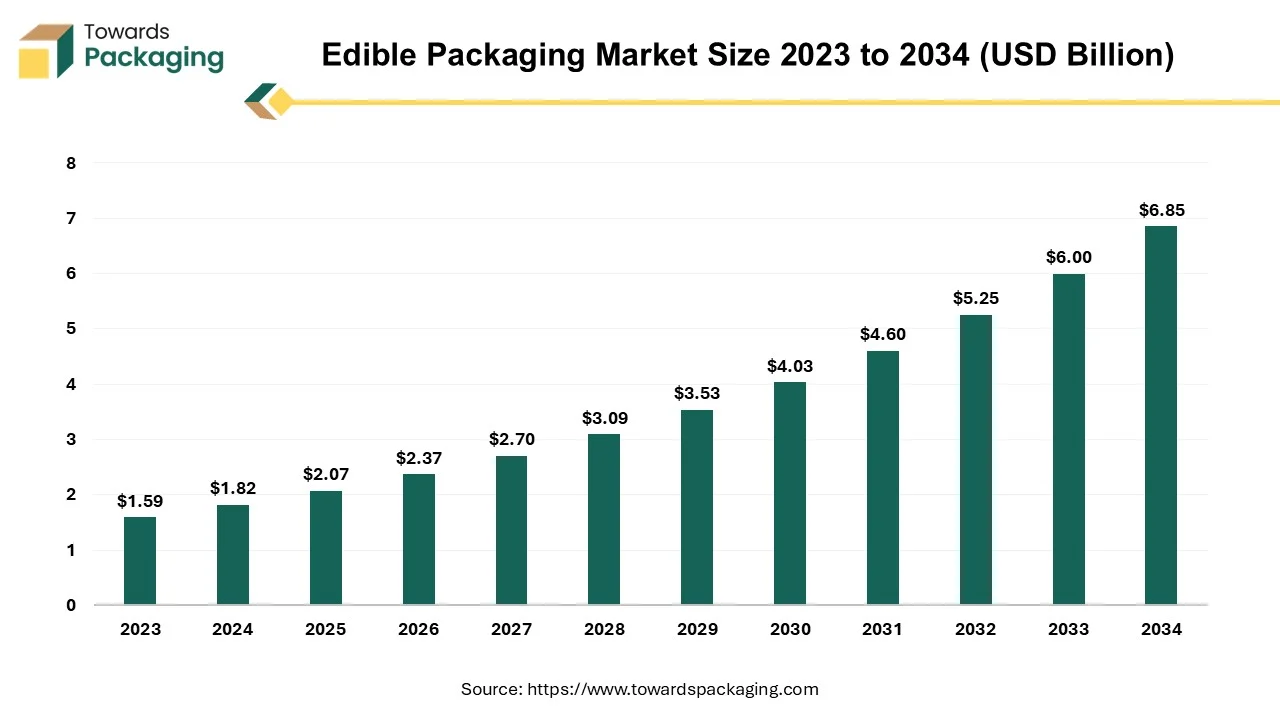
The edible packaging market is forecasted to expand from USD 2.37 billion in 2026 to USD 7.84 billion by 2035, growing at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2026 to 2035. This comprehensive report provides detailed segmentation by source, material, packaging type, and end-use, supported by regional data across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. It features key company profiles including Monosol LLC, Notpla Ltd., Evoware, and Tipa Corp., along with in-depth competitive analysis, market share breakdown, trade flow data, and supplier insights. The study also incorporates value chain analysis covering raw materials, manufacturing, and distribution trends shaping the edible packaging ecosystem.
Edible packaging is known as a type of packaging made from food-grade materials that can be safely consumed along with the product it contains. It is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic or paper packaging, designed to reduce waste and environmental impact. The edible packaging is made up of seaweed & algae, rice & wheat flour, gelatin, starch, fruits extract, and vegetable extracts among others. The seaweed & algae is used for biodegradable wrappers and drink capsules. Rice & wheat flour is common in edible straws and cutlery. Gelatin & starch is used in edible films and coatings.
AI integration can significantly improve the edible packaging industry by enhancing sustainability, efficiency, and innovation. A significant obstacle in creating edible and biodegradable packaging is figuring out the best mix of sustainable and useful materials. Al speeds up this process by modeling how different material compositions behave under various circumstances and forecasting their characteristics. In order to find promising new materials or improve current ones based on characteristics like strength, barrier qualities, and biodegradability, machine learning models can evaluate enormous datasets.
Examples of biopolymers that are widely used as substitutes for petroleum-based plastics are polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). The composition of these polymers can be improved with Al's assistance to guarantee that they fulfill certain performance standards, such preserving product freshness while remaining eco-friendly. As a result, the trial-and-error procedure that is usually involved in the development of new materials is greatly reduced.
Al is redefining tailored packaging with his ability to evaluate vast amounts of customer data. Understanding the tastes and requirements of customers allows Al to suggest edible or biodegradable packaging that fits particular use cases, like food items that need a certain amount of moisture protection or a longer shelf life.
For instance, an Al system would recommend using a film made of edible seaweed to package fresh fruit. This way, the packaging can be eaten with the food, completely eliminating waste. If not properly disposed of, Al can suggest biodegradable packaging for dry items that is based on starch, which will ensure that the material decomposes rapidly in natural settings.
Al is transforming the design process by making it possible to test and prototype packaging materials more quickly. Previously, creating a new packaging solution required extensive physical testing cycles. Designers can save time and money by using Al-driven simulations to test and improve their ideas electronically. Al, for instance, is able to model the relationship between food items and packaging materials, forecasting whether the packaging would decay as anticipated and how well the food will retain its freshness. Businesses can refine their designs using this type of testing without wasting raw resources, which results in packaging solutions that are more environmentally friendly.
A significant obstacle in creating edible and biodegradable packaging is figuring out the best mix of sustainable and useful materials. Al speeds up this process by modeling how different material compositions behave under various circumstances and forecasting their characteristics. In order to find promising new materials or improve current ones based on characteristics like strength, barrier qualities, and biodegradability, machine learning models can evaluate enormous datasets.
Examples of biopolymers that are widely used as substitutes for petroleum-based plastics are polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). The composition of these polymers can be improved with Al's assistance to guarantee that they fulfill certain performance standards, such preserving product freshness while remaining eco-friendly. As a result, the trial-and-error procedure that is usually involved in the development of new materials is greatly reduced.
The food & beverage sector is the largest consumer of edible packaging, particularly in packaged snacks, beverages, and ready-to-eat meals. Increasing demand for on-the-go convenience foods is fueling innovation in edible packaging solutions. As the food and beverage industry expands, there is a growing need for eco-friendly packaging to replace plastics. Major food brands and restaurants are adopting edible packaging to meet sustainability goals and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The food and beverage industry is focusing on natural and organic products, and edible packaging aligns with this trend by offering chemical-free, biodegradable solutions.
The key players operating in the edible packaging market are facing issue due to limited barrier properties and manufacturing challenges, which has estimated to restrict the growth of the market. Many edible packaging materials do not provide strong barriers against oxygen, moisture, and grease, making them less effective for certain food and beverage products. This limits their use in long-term food storage and transportation.
Unlike plastic, edible packaging is more prone to moisture, temperature changes, and microbial growth, limiting its shelf life. Special storage conditions (e.g., refrigeration) may be required, increasing logistics and supply chain costs. Large-scale mass production of edible packaging is still a challenge due to technological and financial constraints. Many edible packaging solutions require customized production processes, which may not align with existing packaging machinery.
Nanotechnology and bio-based materials improve the durability, moisture resistance, and shelf life of edible packaging. Advances in 3D printing can create customized, edible packaging solutions for different industries.
More consumers are embracing zero-waste and sustainable consumption habits, increasing demand for edible packaging. Brands that align with environmental consciousness can gain a competitive edge.
Major food brands investing in edible packaging (e.g., Notpla, Evoware) create opportunities for startups and new market entrants. Collaborations between tech companies, food manufacturers, and sustainable brands can accelerate innovation and adoption.
The plant segment held a dominant presence in the market in 2024. Plants provide natural polymers (like starch, cellulose, and pectin) that break down easily in the environment, reducing plastic waste. Plant-based materials like seaweed, corn starch, and potato starch are non-toxic and safe to eat. With growing environmental concerns, consumers and businesses prefer plant-based alternatives over synthetic plastics. Plants are widely available and can be sustainably cultivated, unlike petroleum-based plastics.
The protein segment accounted for a considerable share of the market in 2024. Proteins are widely used in edible packaging due to their biodegradability, film-forming ability, and nutritional value. Proteins, especially whey, casein, and zein, provide superior oxygen and oil barrier properties compared to polysaccharides and lipids. This helps in preserving food freshness and extending shelf life. Proteins can create thin, flexible, and durable films, making them ideal for food wraps, coatings, and biodegradable packaging. Protein-based films are natural, biodegradable, and environmentally friendly, aligning with the global push for sustainable packaging. Protein films are widely used in the food industry (e.g., meat coatings, dairy wraps, confectionery films).
The films segment led the global edible packaging market. Edible films act as barriers against oxygen, moisture, and contaminants, helping to preserve food freshness and extend shelf life. Protein-based films (e.g., whey, casein, gelatin) provide excellent oxygen barrier properties, preventing oxidation and spoilage. Edible films can be thin, transparent, and flexible, making them easy to apply to various food products. Edible films are made from natural ingredients like proteins (whey, soy, gelatin), polysaccharides (starch, alginate), and lipids.Expansion of Food & Beverages Companies to Project Dominance in 2024
The food & beverages segment dominated the edible packaging market globally. With the growth of fast food chains, packaged foods, and beverage companies, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly packaging to replace plastics. Major brands and restaurants are shifting toward edible packaging to meet sustainability goals and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The increasing popularity of ready-to-eat meals, snacks, and beverages fuels demand for edible wrappers, cups, and coatings.
The booming online food delivery market creates a need for sustainable, disposable packaging alternatives. Consumers are becoming more aware of harmful chemicals in plastic packaging and prefer natural, biodegradable alternatives. Edible packaging made from seaweed, protein, and starch offers chemical-free, safe packaging that aligns with the clean-label trend.
North America region held a large share of the fiber based packaging market in 2024. North America has a high demand for packaged and convenience foods, making edible packaging a viable alternative to plastic wraps and containers. North America leads in biopolymer research, nanotechnology, and 3D food printing, improving the durability and functionality of edible packaging. Companies like Notpla, Loliware, and Evoware are developing advanced edible films, straws, and wrappers. Universities and research centers (e.g., MIT, Harvard) are innovating in protein-based and seaweed-based edible packaging.
Consumers in North America prefer natural, chemical-free, and biodegradable packaging, driving demand for edible packaging made from starch, seaweed, and proteins. North America has some of the largest players in sustainable packaging, including: Loliware (U.S.), Notpla (U.S.), and MonoSol (U.S.). The U.S. and Canada have high investments in plant-based and alternative protein industries, supporting the development of protein-based edible films (e.g., soy, whey, gelatin).
The U.S. government and state laws are pushing for reducing plastic waste, driving demand for eco-friendly alternatives like edible packaging. Bans on single-use plastics (e.g., California, New York, and Washington) are accelerating the adoption of biodegradable and edible packaging. The FDA supports the use of edible coatings and films for food safety and sustainability. The U.S. has a massive processed food, fast food, and beverage industry, increasing demand for sustainable packaging. Fast food chains (McDonald's, Starbucks, Chipotle, etc.) are experimenting with edible straws, cups, and wraps to meet sustainability goals.
The boom in food delivery services (Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub) increases the need for sustainable packaging solutions. Meal kit services like Blue Apron and HelloFresh are exploring waste-free packaging to appeal to eco-conscious consumers. American consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable and biodegradable packaging due to rising environmental concerns. The U.S. leads in biopolymer research, nanotechnology, and edible packaging development.
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the edible packaging market during the forecast period. Many Asia-Pacific countries have implemented strict plastic reduction policies, boosting demand for edible packaging: India banned certain single-use plastics in 2022. China has strict plastic waste regulations and promotes biodegradable packaging alternatives. Japan and South Korea are leaders in eco-friendly packaging innovations.
Rice & Starch (India, Thailand, Vietnam) used for edible cutlery, plates, and wraps. Gelatin & Protein (China, India) used for pharmaceutical and food packaging applications. Consumers in Japan, South Korea, and Australia prefer eco-friendly, biodegradable, and edible packaging due to rising awareness about environmental impact. In India and China, younger, urban consumers are more open to trying innovative, waste-free packaging solutions.
The Asia-Pacific region is investing in edible packaging R&D: Japan and South Korea lead in nanotechnology for food packaging. China and India are developing seaweed-based and protein-based packaging. Australian startups are experimenting with edible coffee cups, straws, and takeaway boxes.
China edible packaging market is growing at rapid rate due to consumers' increased discretionary income. Because eco-friendly and sustainable packaging solutions are perceived as being more environmentally responsible, consumers are willing to pay more for them when the nation's disposable income rises. The demand for this industry in the nation is also anticipated to be driven by the growing end-use of food and beverages as a result of the trend of buying ready-to-eat. Monsol LLC, for example, provides oatmeal and seaweed packaging for single-serve oatmeal.
Europe is seen to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. The European Union (EU) has strict laws aimed at reducing plastic waste: the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (2021) bans plastic straws, cutlery, and packaging. The EU Green Deal and Circular Economy Action Plan push for biodegradable and compostable packaging.
Countries like France, Germany, and the Netherlands have aggressive plastic reduction policies, accelerating the shift to edible and biodegradable packaging. European consumers are highly eco-conscious and prefer products with sustainable packaging. The rise of organic, vegan, and plant-based diets supports edible packaging made from natural ingredients like seaweed, starch, and proteins. "Zero waste" lifestyle trends drive demand for plastic-free and edible packaging alternatives.
Europe has a well-established processed food, beverage, and fast food industry that is looking for sustainable packaging solutions. Major food brands (Nestlé, Unilever, Danone) are investing in edible packaging to align with EU sustainability targets. Growth in on-the-go food, meal kits, and food delivery services (e.g., Deliveroo, Just Eat, Uber Eats) increases demand for eco-friendly packaging.
European supermarkets (Tesco, Carrefour, Lidl, Aldi) are eliminating plastic and exploring edible packaging for fresh produce and bakery items. Luxury brands and beverage companies (e.g., Pernod Ricard, Heineken) are testing edible straws, cocktail cups, and biodegradable wrappers. The EU Horizon 2020 program funds research and development of biodegradable and edible packaging. Tax incentives for sustainable packaging solutions encourage businesses to shift from plastic to edible alternatives. The EU Farm to Fork Strategy promotes sustainable food systems, encouraging edible packaging to reduce waste.

By Source
By Material
By Packaging Type
By End-Use
By Region
December 2025
December 2025
December 2025
December 2025