November 2025
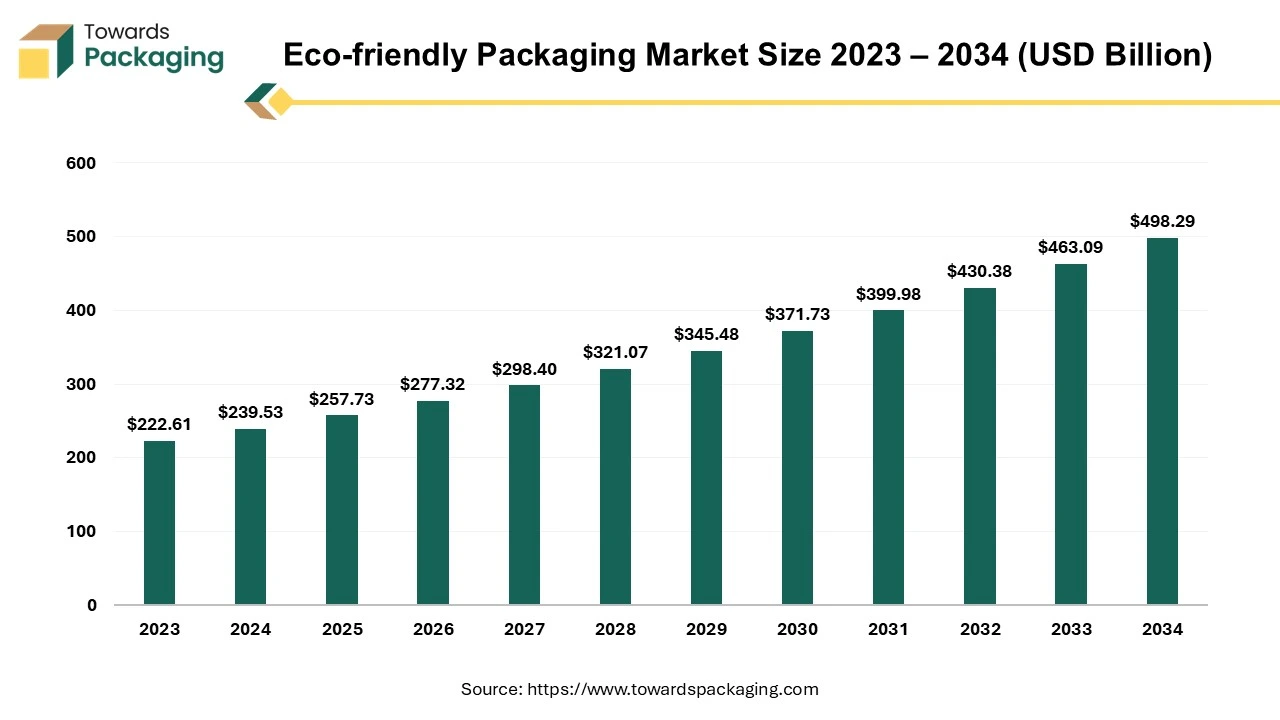
The eco-friendly packaging market reached USD 239.53 billion in 2024 and is set to grow from USD 257.73 billion in 2025 to USD 498.29 billion by 2034 at a 7.6% CAGR. We cover full segment statistics by type (recyclable led 2024), material (paper & paperboard led 2024), product (bags led 2024), technique (alternate fiber led 2024), layer (primary led 2024), and application (food & beverages led 2024). Our regional data detail Asia Pacific’s 2024 lead and North America’s fastest growth, alongside Europe, Latin America, and MEA breakouts. Company analysis includes market shares e.g., Smurfit WestRock 8.6%, Amcor 6.0%, International Paper 5.4%, Mondi 4.6%, DS Smith 4.1%, Tetra Pak 3.8%, Stora Enso 3.3%, Huhtamaki 3.0%, Ball 2.8%, SEE 2.5%, UPM 2.0%.
Eco-friendly packaging refers to packaging solutions designed to minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle from production to disposal. It emphasizes sustainability, biodegradability, and recyclability while still protecting the product effectively. Key characteristics of eco-friendly packaging is that it is manufactured from sustainable materials. For examples: recycled paper, bamboo, cornstarch, bagasse (sugarcane waste), bioplastics, or compostable polymers.
Breaks down naturally into non-toxic components, often within a commercial or home composting environment. Eco-friendly packaging can be easily recycled into new materials or repurposed, reducing the need for virgin raw materials. Eco-friendly packaging is produced using energy-efficient methods, often with fewer emissions and reduced resource usage. The eco-friendly packaging is free from harmful chemicals or additives, especially important in food packaging. The eco-friendly packaging uses fewer materials and avoids excessive packaging (sometimes called "right-sizing").
| Metric | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 239.53 Billion |
| Projected Market Size in 2034 | USD 498.29 Billion |
| CAGR (2025 - 2034) | 7.6% |
| Leading Region | Asia Pacific |
| Market Segmentation | By Type, By Material Type, By Product Type, By Technique, By Layer, By Application and By Region |
| Top Key Players | International Paper, WestRock Company, Oji Holdings Corporation, Smurfit Kappa, Mondi plc, Segezha Group, Klabin SA, Billerudkorsnas, Stora Enso. |
Rising demand for materials like polylactic acid (PLA), bagasse, mushroom-based packaging, and seaweed films. Especially strong in food, beverage, and personal care industries.
Brands are moving away from multi-layered materials that are hard to recycle. Mono-materials (e.g., all-PE or all-PP) simplify recycling and meet circular economy goals.
Companies are adopting minimal packaging designs, refill systems, and bulk dispensers to reduce waste. Popular in cosmetics, household goods, and organic foods.
Packaging made from bamboo, wheat straw, palm leaves, and recycled paper pulp is growing. It helps to reduce reliance on virgin paper or plastic sources.
Advancements in coated papers, bioplastics, and edible films improve barrier properties while staying sustainable. Smart packaging integration (e.g., QR codes) for tracking sustainability info.
Government bans and taxes on single-use plastics (e.g., in the India, EU, Canada,) push businesses to adopt greener alternatives. Certifications like Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), BPI, and OK Compost are gaining importance.
Brands are marketing eco-friendly packaging as part of their sustainability narrative. Consumers increasingly demand transparency on packaging origin, recyclability, and end-of-life impact.
Closed-loop systems, packaging take-back programs, and refill models are growing. Especially relevant in retail and e-commerce.
| Rank | Manufacturer (global) | 2024 share (%) |
| 1 | Smurfit WestRock | 8.6 |
| 2 | Amcor | 6 |
| 3 | International Paper | 5.4 |
| 4 | Mondi | 4.6 |
| 5 | DS Smith | 4.1 |
| 6 | Tetra Pak | 3.8 |
| 7 | Stora Enso | 3.3 |
| 8 | Huhtamaki | 3 |
| 9 | Ball Corporation | 2.8 |
| 10 | SEE (Sealed Air) | 2.5 |
| 11 | UPM (incl. specialty packaging materials) | 2 |
| — | All other manufacturers (highly fragmented) | 53.9 |
AI-driven simulations can create packaging with minimal material use while maintaining strength and protection. Generative design tools allow engineers to explore lightweight, sustainable structures automatically. AI analyses chemical properties to identify and test new biodegradable or compostable materials faster than traditional research and development. The eco-friendly packaging accelerates development of next-gen bio-based plastics and coatings.
AI helps companies forecast demand, reduce overproduction, and optimize inventory management - cutting waste from unsold packaging. AI-powered logistics can reduce carbon footprint by optimizing routes and loads. AI-enhanced computer vision systems improve sorting of recyclables in waste facilities by identifying materials more accurately. The AI integration enables closed-loop recycling systems by enhancing material recovery rates. AI can perform real-time environmental impact assessments for packaging options, guiding decisions toward lower-emission choices. Useful for ESG reporting and sustainability labelling.
The rise of e-commerce has increased the need for sustainable shipping materials (e.g., recyclable mailers, paper tape, fiber-based cushioning) to minimize packaging waste. E-commerce requires individual packaging for every item, often with secondary and tertiary packaging (boxes, fillers, mailers). This leads to massive packaging consumption, pushing companies to shift towards sustainable materials to reduce environmental impact.
Consumers expect eco-conscious delivery options and are more aware of the waste generated by online orders. Brands that use biodegradable, recyclable, or compostable packaging gain reputation. Eco-friendly packaging helps online sellers stand out in a crowded market place. It reinforces a brand’s sustainability commitment, boosting customer retention and trust.
Eco-friendly materials may lack moisture, grease, or oxygen barriers, making them unsuitable for certain food or medical packaging. Durability, shelf life, and structural strength can be inferior to traditional options. Even when sustainable options are available, improper disposal by consumers (e.g., throwing compostable packaging in regular trash) limits effectiveness. Confusion over labels like “biodegradable,” “recyclable,” and “compostable” leads to misuse. Sustainable materials (like PLA, bagasse, or molded pulp) may not be available in all regions. Dependence on specific crops or bio-sources can lead to supply chain instability.
The key players operating in the market came across industries which are setting ambitious ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) goals, which includes switching to green packaging to improve brand image and compliance. The key players operating in the market are utilizing sustainable packaging often prefer a competitive edge and stronger customer loyalty, especially among younger demographics.
The recyclable segment held a dominant presence in the eco-friendly packaging market in 2024. Unlike compostable or biodegradable materials, recycling systems are already established in many regions globally. Consumers are more familiar with how to properly dispose of recyclable materials. Recyclable materials like paperboard, aluminium, and certain plastics (like PET and HDPE) are relatively affordable and scalable.
Lower production and processing costs make recyclable packaging attractive to both large and small businesses. Governments worldwide are encouraging or mandating the use of recyclable packaging over single-use plastics. Many extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws require companies to use packaging that is easily recyclable.
Consumers widely recognize recycling as an environmentally responsible action, making recyclable packaging a trusted green option. Clear recycling symbols and instructions help drive adoption and compliance. Recyclable packaging is used in food & beverage, cosmetics, electronics, and e-commerce, giving it a broad application base. It can be adapted to many packaging forms - bottles, boxes, trays, wrappers, etc.
Recyclable packaging materials can be reintegrated into the production cycle, reducing raw material consumption and waste. Major retailers (like Walmart, Amazon) and global brands (like Unilever, Nestlé) require recyclable packaging as part of their sustainability commitments.
The paper and paper board segment accounted for a significant share of the eco-friendly packaging market in 2024. Paper and paperboard break down naturally in the environment, making them ideal for reducing long-term pollution. They are often accepted in home composting systems and industrial composting facilities.
These materials are easy to recycle and already have well-established collection and processing infrastructure in many countries. Paper-based packaging can be recycled multiple times, reducing the need for virgin material. Sourced from trees and agricultural waste, paper is renewable, especially when sourced from FSC-certified or sustainably managed forests.
Seen by consumers as clean, natural, and eco-conscious, paper packaging enhances brand image and aligns with sustainability trends. Paperboard is lightweight, reducing transportation emissions, and it’s easy to print, fold, and shape, making it ideal for a wide range of products and branding. Compared to newer bio-based plastics or specialty compostable films, paperboard is often more affordable and scalable, especially for small and medium businesses.
The paper and paperboard is used for a wide array of products, food packaging, mailers, cartons, trays, wraps, and cups. The paper and paperboard can be coated or laminated with biodegradable films or water-based coatings to improve barrier properties.
The bags segment registered its dominance over the global eco-friendly packaging market in 2024. Widely used in retail, grocery, food service, apparel, and e-commerce, making bags one of the most versatile packaging formats. Replaces single-use plastic bags with paper bags, reusable fabric bags, and compostable bioplastic bags. Many countries have enacted plastic bag bans or taxes, creating a major push toward eco-friendly alternatives like paper, jute, cotton, and starch-based bags. Consumers prefer bags that are reusable, recyclable, or compostable, and eco-bags often align with lifestyle values such as minimalism and sustainability.
Eco-friendly bags offer ample surface area for custom printing, allowing companies to promote their brand and sustainability commitments. Often utilized as part of green marketing campaigns. Bags can be manufactured from a wide range of sustainable materials: Kraft paper (biodegradable and recyclable), Cotton and jute (durable and reusable) and PLA or corn starch-based plastics (compostable). Compared to traditional plastic bags, many eco-bags have lower lifecycle emissions, especially when reused multiple times. Retailers are switching to eco-friendly bag options due to regulatory pressure, cost savings on plastic taxes, and positive consumer response.
The alternate fiber packaging segment led the global eco-friendly packaging market. Alternative fibers like bamboo and hemp grow much faster than traditional wood sources, making them more sustainable and renewable. They require less water, pesticides, and land than trees, improving environmental efficiency. These materials generally have a lower carbon footprint than plastic or virgin paperboard due to reduced energy and chemical use in production.
Many are by-products or waste materials (like bagasse from sugar production), reducing the need for virgin inputs. Most alternate fiber materials are naturally biodegradable, and some are certified compostable, making them ideal for single-use packaging that won’t harm the environment after disposal. Technological advances have made alternate fibers more durable, moisture-resistant, and food-safe, allowing them to replace plastic in packaging for food, beverages, cosmetics, and electronics. With increasing bans on single-use plastics, alternate fiber packaging offers a regulation-compliant substitute that is both functional and sustainable.
Consumers associate alternate fiber materials with natural, organic, and eco-conscious products, boosting brand value and loyalty. They often have a distinct, premium texture and appearance, enhancing product aesthetics. Many alternate fiber-based packages are recyclable in paper streams or can be upcycled into new fiber-based products, contributing to a circular economy.
The primary packaging segment held a dominant presence in the eco-friendly packaging market in 2024. The eco-friendly packaging reduces landfill waste and ocean pollution. Minimizes the use of non-renewable resources like petroleum (used in traditional plastics). Supports circular economy principles through recyclability or biodegradability. Many eco-friendly materials are non-toxic, chemical-free, and safer for products like food, cosmetics, or pharmaceuticals. The eco-friendly packaging avoids harmful substances (like BPA or phthalates) that can leach from conventional plastics. Increasing global regulations (e.g., EU Green Deal, plastic bans) require companies to shift to sustainable packaging. The eco-friendly packaging helps avoid legal penalties and product recalls. Eco-conscious consumers prefer brands that use sustainable packaging.
The food and beverages segment accounted for a significant share of the eco-friendly packaging market in 2024. Due to busy lifestyle people are preferring packed food and beverages which has driven the segment growth. Food and beverage products are consumed daily, generating massive packaging needs. This constant demand drives innovation and investment in sustainable alternatives. Governments worldwide have imposed strict regulations on single-use plastics and non-biodegradable packaging, especially in the food sector, pushing companies to adopt eco-friendly materials.
Increasing consumer preference for sustainable, organic, and environmentally responsible products is especially strong in food and beverages, where health and ethics influence buying decisions. Perishable goods require effective yet sustainable packaging that ensures freshness while being compostable, recyclable, or biodegradable. Companies in this segment often use eco-friendly packaging as a key marketing tool to attract eco-conscious consumers and build brand loyalty. The rise of online food and grocery delivery increases packaging use, prompting companies to shift toward sustainable options to reduce environmental impact.
Asia Pacific region held the largest share of the eco-friendly packaging market in 2024, owing to rising emphasis on usage of eco-friendly packaging due to increasing pollution in the region. Many Asia Pacific countries are introducing strict regulations to minimize plastic use and promote sustainable packaging (e.g., India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules, China’s ban on single-use plastics). Growing public concern over pollution and waste is pushing consumers and businesses towards greener alternatives.
The rapid rise of e-commerce in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia increases demand for sustainable packaging solutions to reduce the environmental impact of delivery packaging. The increasing urban population leads to higher consumption, which boosts demand for packaged goods and, subsequently, for sustainable packaging. Major companies in the region are adopting ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards and switching to eco-friendly packaging to align with global trends.
India Eco-friendly Packaging Trends
India is one of the most opportunistic countries when it comes to packaging solutions, as the government is significantly pushing towards sustainability. For instance, the Indian government banned single-use plastics in 2022, which is marked as an effective step in promoting reusable materials. The younger generation, including Gen Z and Millennials, is more educated regarding sustainability, which is leading towards the use of green label packaging for multiple products. The rising influence of social media in the country is playing a crucial role in eliminating plastic pollution.
China Eco-friendly Packaging Trends
China eco-friendly packaging market is driven by the technology advancement and high consumer demand. China’s abundant natural resources facilitate the adoption of plant-based packaging materials like bamboo and sugarcane bagasse. These materials are renewable, biodegradable, and increasingly used across various industries. Additionally, smart packaging technologies are emerging, enhancing functionality while reducing waste. Chinese consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
Surveys indicate that many are willing to pay more for products with eco-friendly packaging. This shift in consumer behaviour is encouraging companies to adopt greener packaging solutions.
North America region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the eco-friendly packaging market during the forecast period. The U.S. and Canada enforce strict packaging and recycling laws (e.g., California's Plastic Pollution Prevention and Packaging Producer Responsibility Act). Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) frameworks are being widely adopted, pushing companies to take responsibility for the full lifecycle of their packaging.
Consumers in North America are increasingly eco-conscious, driving demand for biodegradable, recyclable, and compostable packaging. Brands in North America are under pressure to meet sustainability expectations or risk losing market share.
Major corporations (like Amazon, Walmart, and PepsiCo) have set aggressive sustainability goals, including 100% recyclable or reusable packaging targets within the next decade. These companies often lead innovation and investment in sustainable packaging technologies. North America benefits from strong R&D capabilities and manufacturing infrastructure, enabling faster adoption of cutting-edge materials like molded fiber, bioplastics, and smart packaging. Investments in circular economy initiatives are supporting material recovery and closed-loop packaging systems, especially in urban centers.
U.S. Eco-friendly Packaging Trends
U.S. eco-friendly packaging market is drive by the innovation and launch of new eco-friendly packaging by the key players operating in the country. The U.S. is a hub for innovation in materials science, contributing to the development of biodegradable plastics, plant-based materials, and reusable packaging systems.
DS Smith's "GoChill Cooler" is made of eco-friendly, wax-free corrugated board, which lowers waste and carbon emissions while offering customers a way to keep food and drinks fresh while they're on the go. Customers who appreciate more environmentally friendly packaging options will love the moisture-resistant design, especially when they're spending time outside.
The stringent environmental regulations in the country are significantly promoting the growth of the eco-friendly packaging market. For instance, California’s SB 54 Plastic Pollution Producer Responsibility Act, focuses on mandating the use of single-use plastic to be compostable or recyclable by 2032. The corporates, especially in the food and beverage industry, are also promoting the use of sustainable packaging solutions, which would mandate eliminating plastic pollution. The e-commerce industry is also one of the leading contributors to packaging solutions, which is taking initiatives to reduce packaging waste.
Europe region is seen to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. The European Green Deal, EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD), and Single-Use Plastics Directive mandate reduced plastic use and improved recyclability. Producers are required to meet recycling, composting, and material recovery targets, pushing companies toward sustainable packaging solutions. European consumers are among the most eco-conscious globally, favouring products with biodegradable, recyclable, or reusable packaging. Demand for transparency and eco-labeling further incentivizes companies to adopt green packaging practices.
The EU promotes a circular economy with policies that support reuse, recycling, and closed-loop material systems. Many countries (like Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden) have advanced recycling infrastructures and strict waste separation systems. European businesses face high ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) expectations from investors and customers. Many retailers and manufacturers have pledged to eliminate unnecessary plastic and use only sustainable packaging by 2025 or 2030. Europe is a leader in developing biodegradable polymers, molded fiber packaging, and compostable films. Innovations are also supported by EU-funded research programs, encouraging cross-border collaboration.
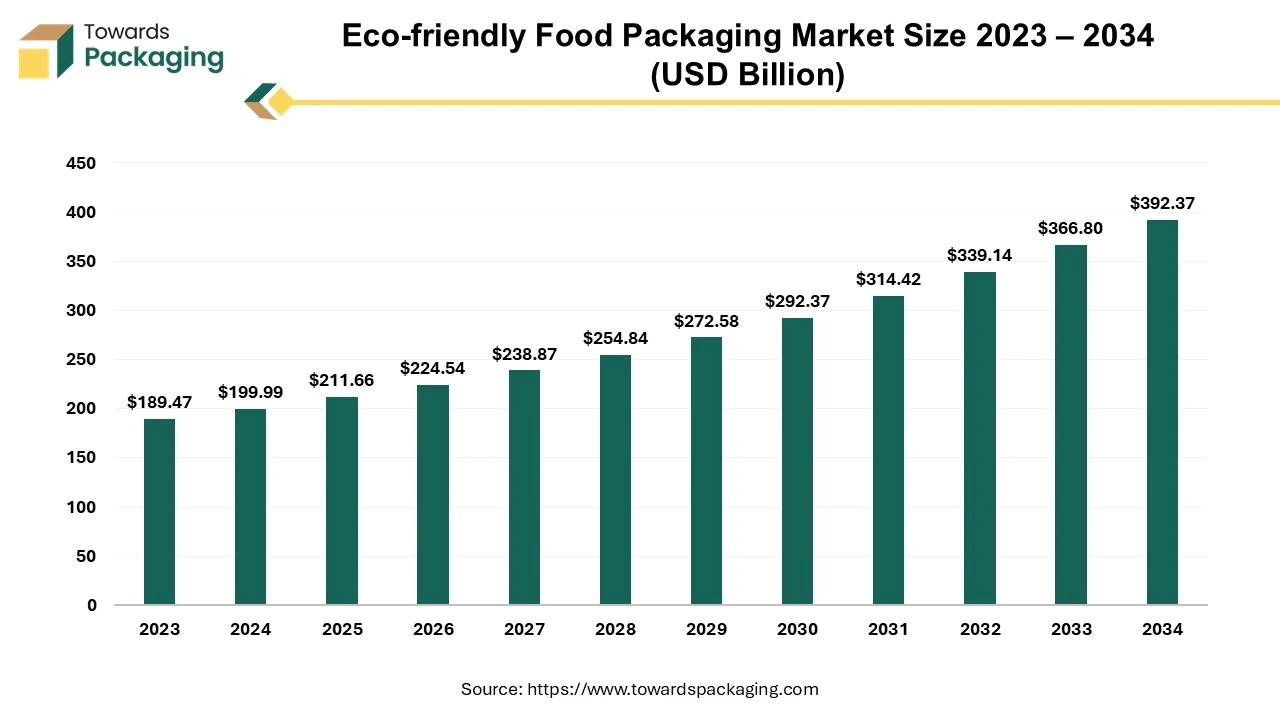
The global eco-friendly food packaging market size reached US$ 199.99 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around US$ 392.37 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 6.97% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
The eco-friendly food packaging market is predicted to witness strong growth in the years to come. Eco-friendly food packaging materials can be recycled, composted, biodegradable or used again. Plastic food packaging can cause endocrine system disruption and accumulate in the ocean, among other health and environmental hazards. Eco-friendly packaging, fortunately, has many advantages for consumers, companies, and the environment. Plant-based extracts such as wheat, bamboo and wood, as well as sustainable bioplastics are frequently utilized in sustainable packaging for food. According to the research, eco-friendly packaging has a much lower rate of chemicals and also non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) migrating into food and the body than plastics. Eco-friendly alternatives are therefore safer compared to plastic packaging.
The eco-friendly flexible packaging market is booming, poised for a revenue surge into the hundreds of millions from 2025 to 2034, driving a revolution in sustainable transportation. The market is fueled by growing environmental awareness, bans on single-use plastics, and advancements in sustainable materials. With Europe emerging as the fastest-growing area and Asia Pacific holding the greatest share in 2024, the eco-friendly flexible packaging market is expanding quickly. The most popular material type was recyclable plastics, but bioplastics are predicted to rise significantly. Packaging was dominated by pouch forms, and the market for wraps and sachets will grow considerably.
Recyclable packaging was becoming more popular, but compostable and biodegradable packaging was the product functionality. Food and beverages accounted for the largest end use, while personal care and pharmaceuticals are set to grow quickly. Industrial supply was the main distribution channel, but online retail is poised for notable expansion.
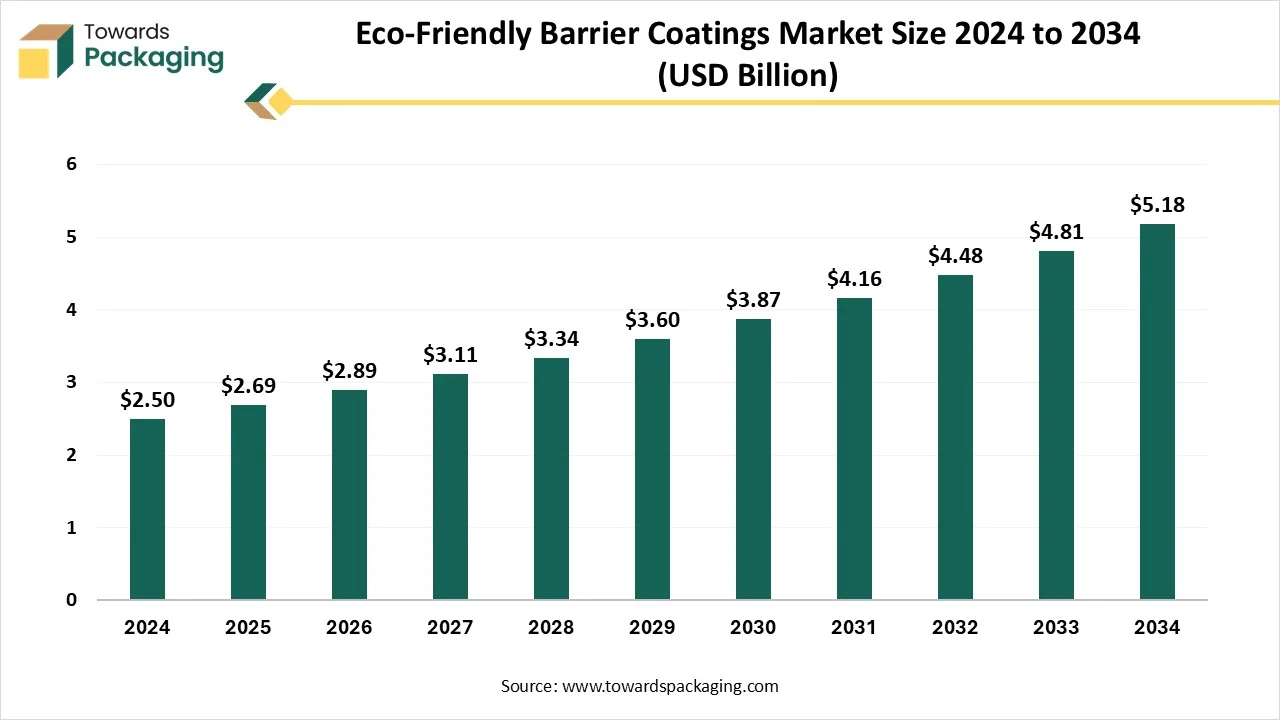
The eco-friendly barrier coatings market is projected to reach USD 5.18 billion by 2034, expanding from USD 2.69 billion in 2025, at an annual growth rate of 7.55% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rapid development of the packaging sector to meet the demand for several industries such as personal care, cosmetics, food & beverages, and many others has influenced innovation. There is a huge demand for recyclable, sustainable, and degradable packaging resolution, this encouraged the development in the market. The presence of strict ecological guidelines, innovative technology, and development of eco-friendly substitutes has pushed the expansion of this market.
The eco-friendly barrier coatings market refers to the industry focused on the development, production, and application of sustainable, bio-based, water-based, or recyclable coatings that provide barrier properties such as moisture resistance, oxygen blocking, grease resistance, and chemical protection while minimizing environmental impact. These coatings are widely used in packaging, automotive, construction, electronics, and industrial applications to replace conventional petroleum-based solutions.

By Type
By Material Type
By Product Type
By Technique
By Layer
By Application
By Region
November 2025
October 2025
October 2025
October 2025