April 2025
Packaging 5.0 recognizes of the increasing consumer demand for personalized products. To meet this demand, packaging technologies that combine big data and artificial intelligence are being implemented. This helps to customize products to each customer's preferences and decreases food waste during production.
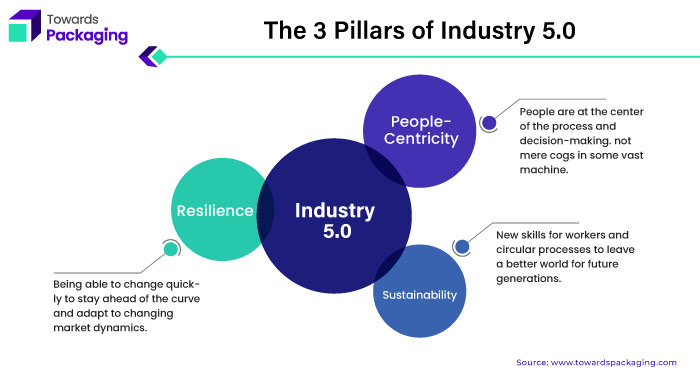
The fifth industrial revolution, which will emphasize the cooperation of humans and machines, is set to begin. By using collaborative robotics and personalization, employees are free to provide consumers with value-added tasks. Beyond manufacturing techniques, this most recent version incorporates human-centric design, sustainability, and enhanced resilience, all of which are covered in more depth below. The idea of packaging 5.0 developed from industry 4.0 as human welfare became more and more important. Both, despite certain differences, deal with the automation and digitalization of production processes.
There are two opposing perspectives regarding Industry 5.0. The first contends that the increased emphasis on sustainably and human-centeredness in this stage justifies the term's use, while the other holds that packaging 5.0 represents the integration of Industry 4.0's paradigms. Consequently, the Fourth Industrial Revolution's promises are being fulfilled rather than signalling the start of a new "industrial revolution." 91% of the respondents cited a lack of experience as the largest obstacle, which is followed by unreasonably high costs (42%), a dearth of technology solutions appropriates for their particular needs (30%), and an unacceptably rapid rate of technical improvements (26%).
There should be a seamless transition with overlapping traits and concepts from Industry 4.0 through Industry 5.0. Humanizing technology and building the most moral, sustainable, and inclusive manufacturing ecosystem possible are the main objectives of Industry 5.0.
For Instance,
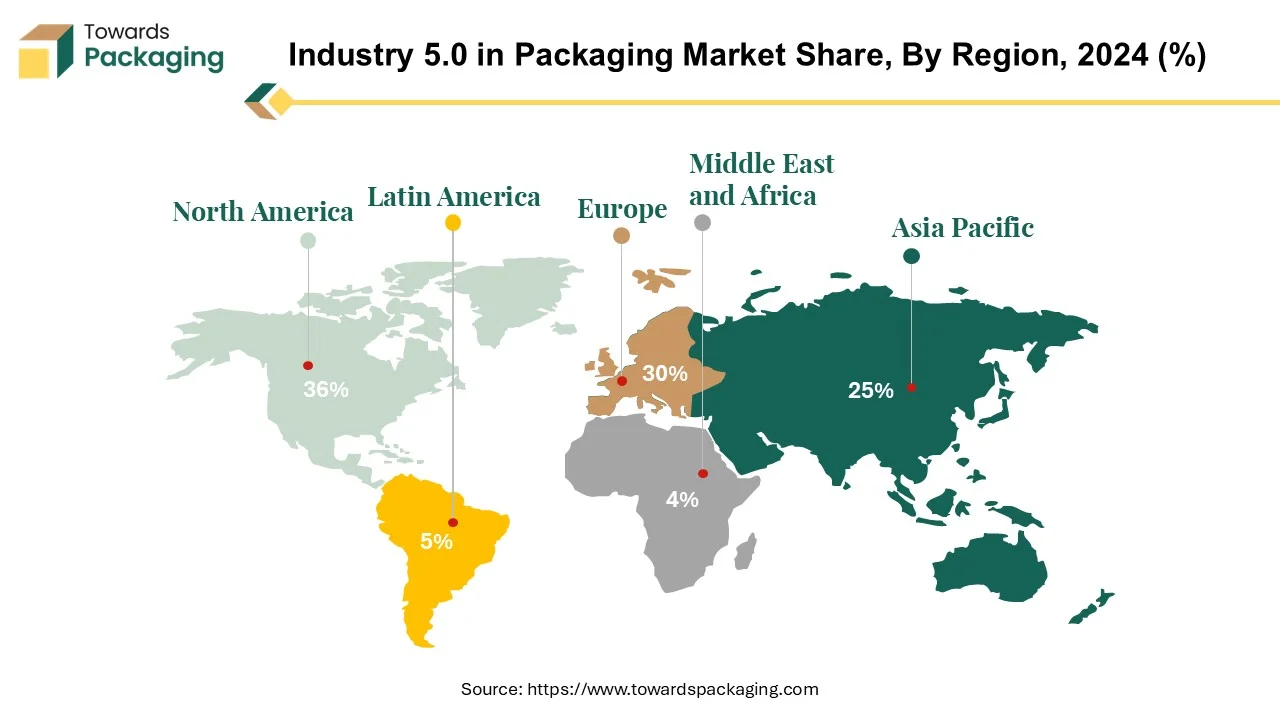
North America is the primary focus in emphasizing the packaging industry's 5.0 revolution. The region has significant industrial and economic growth that is being implemented in the packaging sector.
North America ranks the first one in terms of revolutionary and industrial transformation implementation and sectoral adoption. The packaging sector in North America is rapidly expanding. This industrial transformation will have a significant impact on packaging use, manufacturing, and distribution.
The packaging sector is rapidly and consistently developing more sustainable solutions for their products, with an emphasis on reusable options. The US company has been using reusable bottles composed of thirty percent recycled glass to package their organic milk for twenty-five years. After returning their empty bottles, customers can clean their bottles and receive two US dollars back. Before they are completely recycled, each of these bottles can be used up to five times. The company states that their return rate is slightly higher than 80%.
The future of the packaging operations 5.0 in North America is growing because of environmental concerns and the incorporation of human intelligence.
For Instance,
Europe is the second largest and fastest expanding region in the packaging Industry 5.0. An EU-wide industrial initiative centred around the constituent elements of packaging 5.0 would provide Europe's industrial potential while rewarding resilient, sustainable, regenerative, and circular economic business conduct over short-term excessive production and utilization models determined by the current growth paradigm.
The implications of an packaging 5.0 approach for the overall EU industrial strategy are significant. In addition to new capabilities and approaches to research and innovation, It demands novel approaches to policymaking in conjunction with business and industry, new designs for supply chains, value chains, and business models, new objectives for digital transformation, and horizontal and vertical coherence through action throughout all levels of government and international standards. The transformation necessary to realize all the possibilities of packaging 5.0 is fundamental. Which is, it will necessitate a business-level transformation of product/service/system design and supply chain reconfiguration that shifts away from a solitary concentration on cost optimisation or linearity and toward business systems and models that are more regenerative and restorative by design. This change can be accomplished by implementing a process-oriented, whole-system approach to restoring, renewing, and revitalizing energy, materials, and natural ecosystems.
Packaging 5.0 provides Europe a chance to redefine the nature of its global leadership by means of global collaboration, transparency (while simultaneously enhancing strategic autonomy in a manner consistent with SDGs), and leadership in establishing guidelines and standards for new manufacturing, sustainability, ethics, and a digital economy/society.
For Instance,
The core of Industry 5.0, particularly for the packaging sector, is robotics and automation. Robots for packaging are multifunctional tools that can be used to open, filling, transportation, palletize, seal, code, and label product packaging.
These robots can automate virtually every operation associated with the movement or packing of items, making them important in a wide range of industries. Presently, there are about 3.4 million industrial robots in operation worldwide. A big advancement is vision-guided robots (VGRs), which employ 2D or 3D cameras to gather images so that robots may do jobs with a high degree of accuracy.
The food and beverage packaging industry appear as a key driver of VGR market expansion. A significant majority of manufacturers, roughly 83%, are using or planning palletization and packaging automation. Furthermore, automation is widely used in a variety of processes, with 82% using it for material handling and ground movement, 80% for product receiving and storage, 77% for pallet material handling, and 75% for sorting.
The global robotics sector is expected to generate more than $43 billion in sales by 2027, driven by the expanding use of robots with artificial intelligence in industrial environments. More than 3.4 million industrial robots are already in use in factories around the world, representing a significant increase from a few years ago when technology for robotics were deployed at small sizes. Dozens of robotics firms are contributing to this intriguing field, but only a few are leading the way.
For Instance,
Food and beverage packaging is one of the leading sector in material packaging of packaging 5.0 market. Challenges faced the food and beverage sector recently, including geopolitical unpredictability and economic volatility, which have raised costs and created inflationary pressures.
The food and beverage sectors have come to understand the significance of tackling sustainability issues in light of these concerns, especially those pertaining to packaging materials. Whether they are beverage firms, convenience food makers, or retailers, all assessed organizations have set sustainable packaging goals. However, integration of these targets into specific packaging requirements is currently restricted.
Packaging 5.0 aims to promote sustainable and equitable growth in manufacturing and industrial processes through collaborative partnerships between humans and modern technologies, building on Industry 3.0 and 4.0 concepts. Questions about production lines, energy sources, fisheries processing, packaging, labeling, anti-bacterial testing, sensory analysis, and quality control were pushed aside.
A comprehensive strategy that strikes a balance between short-term gains and long-term, strategic initiatives suited to each company's distinct product offerings and market position is needed to navigate this complex field. However, many businesses face challenges because they lack internal champions and the necessary knowledge to spearhead packaging optimization initiatives. Sustainability departments frequently become the main hub for tackling these issues, underscoring the increasing significance of sustainability programs in F&B packaging tactics.
For Instance,
Glass and aluminum are highly regarded for their recyclability, capable of being recycled indefinitely, unlike many polymers often falsely labeled as recyclable. Despite generating approximately 400 million tons of plastic waste annually, plastic recycling rates fall below expectations. Unlike glass and plastic, metals degrade in quality with each recycling cycle. Paper stands out as one of the most recycled materials, constituting half of all recyclables by weight.
Aluminum constitutes merely 1% of the waste stream in the United States due to robust recycling rates. Both aluminum and glass can be recycled endlessly with significantly lower energy consumption than manufacturing from raw materials. Glass, in particular, stands out for its ease and cost-effectiveness in recycling, being primarily composed of abundant components like sand and limestone.
Electronic waste (e-waste) emerges as the fastest-growing waste type globally, often improperly disposed of, posing environmental hazards. Shockingly, forty percent of globally produced food goes to waste, with enough lost on farms alone to feed every undernourished person four times over. Despite strides in paper, glass, and aluminum recycling, the plastic recycling sector still faces significant challenges, indicating ongoing efforts are needed in waste management and recycling initiatives.
For Instance,
Flexible packaging emerged as the primary and largest type in the packaging 5.0 market. The global flexible packaging industry is valued at around USD 200 billion, with an annual growth rate ranging from 4.5% to 5.5 percent. Notably, exports account for almost 5.3% of the total domestic output in this business.
Flexible packaging converters come in a wide range of sizes, from tiny production companies with a single facility to large integrated organizations with up to 52 plant locations. This diversity demonstrates the flexible packaging industry's vast reach and scalability. Flexible packaging solutions benefit a wide range of businesses, including pet food (4%), personal care (6%), tobacco (1%), other non-food items (6%), industrial applications (4%), consumer products (8%), and the medical and pharmaceutical sectors (9%). The statistics exhibit flexible packaging's versatility and acceptance across multiple sectors, indicating its vital function in smart packaging solutions.
For Instance,
Packaging 5.0 is a consumer-centric approach to production, utilizing adaptive robots, CCPS, and human interface and recognition technologies to prioritize worker requirements while enhancing productivity. Consumer-centric design is essential for developing the expanding packaging 5.0 industry, which prioritizes the end user's experience. Under the wider structure of Industry 5.0, an evolutionary shift occurs, stressing the transformation of individuals from mere resources to valued assets within organizational dynamics. This move represents a divergence from the traditional paradigm, in which firms primarily leverage human skills to gain a competitive advantage and meet consumer needs. Instead, packaging 5.0 promotes a reciprocal partnership in which corporations serve people while acknowledging employees' intrinsic value.
This strategy goes beyond simply meeting consumer needs to include the well-being and pleasure of the workers. As a result, efforts are focused on establishing an atmosphere that promotes employee development, engagement, and fulfilment. Packaging 5.0 aims to create a sustainable ecosystem in which firms grow via mutual benefit and collaborative success by prioritizing the requirements of both customers and employees. Thus, the transition to packaging 5.0 not only amplifies consumer-centric design, but also emphasizes the importance of developing and maintaining top talent in the workforce.
For Instance,
The competitive landscape of the packaging 5.0 market is dominated by established industry giants such as Amcor PLC, Sealed Air Corporation, Mondi PLC, DS Smith PLC, WestRock Company, Sonoco Products Company, Huhtamaki Oyj, Bemis Company, Inc., Packaging Corporation of America (PCA), Berry Global Group, Inc, Constantia Flexibles Group GmbH, Graphic Packaging Holding Company, Smurfit Kappa Group, AptarGroup, Inc, CCL Industries Inc, Tekni-Plex, Coveris, RPC Group PLC, Greif, Inc and Printpack. These giants compete with upstart direct-to-consumer firms that use digital platforms to gain market share. Key competitive characteristics include product innovation, sustainable practices, and the ability to respond to changing consumer tastes.
Amcor is a global leader in developing and producing responsible packaging solutions. They focus on innovation, sustainability, and meeting the evolving needs of customers and consumers.
For Instance,
WestRock is a global packaging company that focuses on delivering sustainable, differentiated packaging solutions. They serve various industries, including food and beverage, healthcare, and consumer goods.
For Instance,
By Technology
By Application
By Region
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025