April 2025
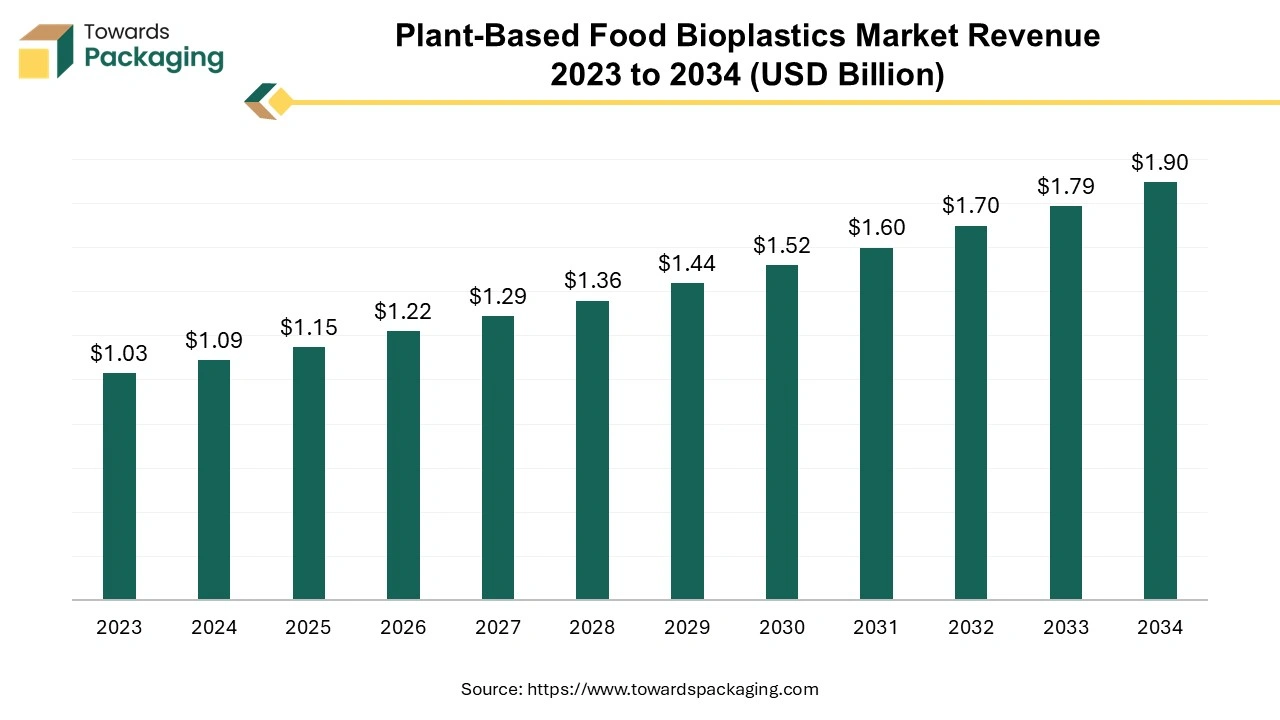
The plant-based food bioplastics market is forecast to grow from USD 1.15 billion in 2025 to USD 1.90 billion by 2034, driven by a CAGR of 5.7% from 2025 to 2034.
Unlock Infinite Advantages: Subscribe to Annual Membership
The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing plant-based food bioplastics which is estimated to drive the global plant-based food bioplastics market over the forecast period.
The food packaging developed from renewable biological sources, such as starch, cellulose, or proteins obtained from plant is known as plant-based food bioplastics. Unlike traditional plastics made from petroleum, these bioplastics are designed to be eco-friendlier. They can be biodegradable or compostable, meaning they can break down more easily in natural environments. These materials are often utilized for packaging food, utensils, and other products, aiming to reduce plastic waste and reliance on fossil fuels.
The plant-based food bioplastic is made from different types of material mentioned here as follows: starch-based bioplastics, polylactic acid (PLA), cellulose-based bioplastics, and protein-based bioplastics. The starch-based bioplastics are manufactured from sources like potatoes, tapioca, corn, or starch-based plastics which can be processed to form films or rigid materials. They are often used for food packaging and disposable items. The cellulose- based bioplastics are derived from plant fibers; cellulose can be transformed into films or molded products. This type of bioplastic is known for its strength and barrier properties, making it suitable for food packaging.
The use of plant-based food bioplastics lower carbon footprint and production of bioplastics typically results in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional plastics. These bioplastics can be designed for various applications, including food packaging, utensils, and even agricultural films. Before bioplastics start breaking down, they can be recycled. This makes it easier for customers to properly dispose of their garbage and prolongs the life of the bioplastic packaging materials so they can be used again before they decompose. The global packaging industry size is estimated to grow at a 3.16% CAGR between 2025 and 2034.
AI integration can significantly enhance the plant-based food bioplastics industry by material optimization, improving process efficiency, supply chain management, enhancing quality control, and providing sustainability analysis. AI can analyze and predict the properties of various plant-based materials, helping to identify the best combinations for bioplastics. This can lead to improved strength, flexibility, and biodegradability. Machine learning algorithms can optimize manufacturing processes by analyzing data to reduce waste, improve energy efficiency, and streamline production workflows.
AI can enhance supply chain efficiency by predicting demand, optimizing logistics, and ensuring the timely availability of raw materials, which can lower costs and reduce environmental impact. AI-powered vision systems can monitor production quality in real-time, identifying defects or inconsistencies early in the process to ensure high-quality products. Analyzing consumer data through AI can help companies understand market trends and preferences, guiding product development to better meet consumer demand. AI tools can assess the environmental impact of different bioplastic formulations and processes, enabling companies to make more sustainable choices in their production methods.
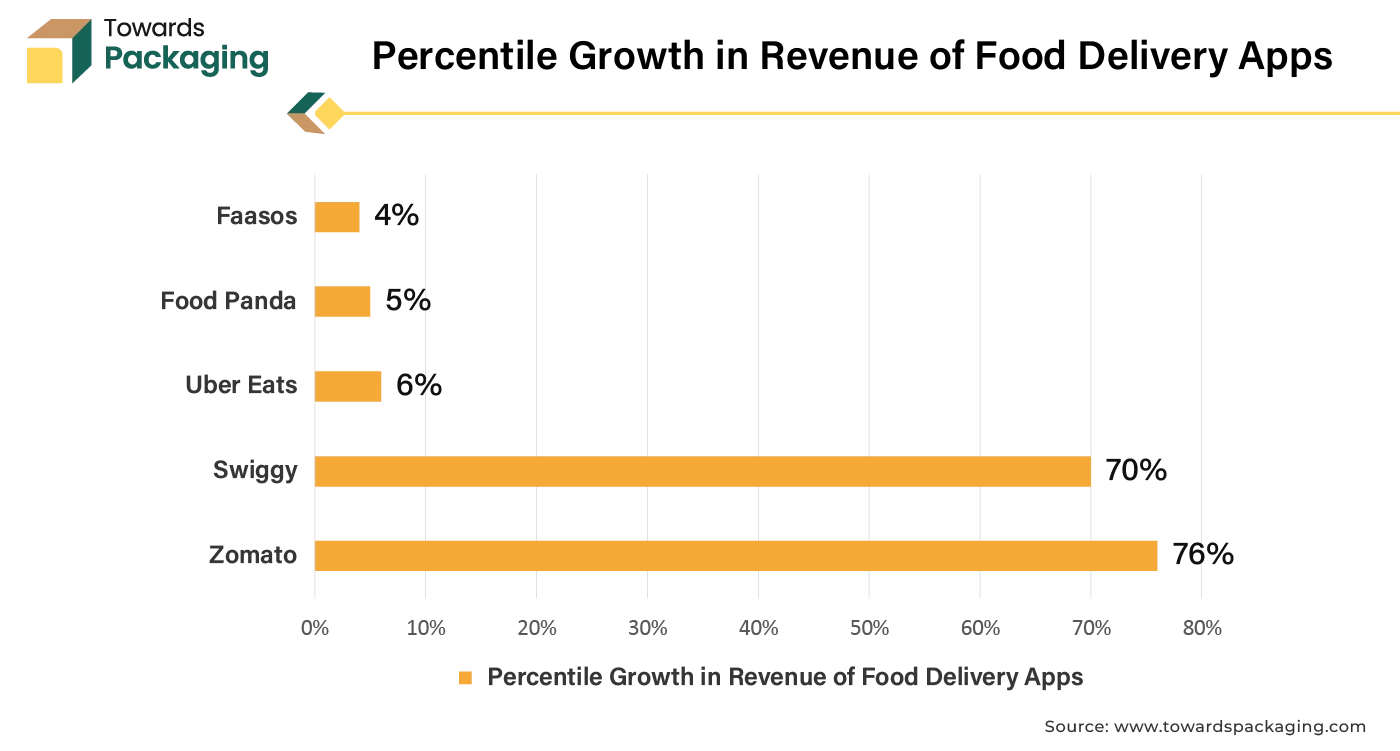
Due to rapid urbanization and busy-lifestyle more consumers turn to online food services. Due to rising health awareness the consumers are focused on food quality and packaging. As more consumers turn to online food services, there's an increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions. Bioplastics made from plant materials can be marketed as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. In addition, food delivery companies are under pressure to reduce their environmental impact, further driving the adoption of plant-based bioplastics for packaging. Hence, increase in the trend of online food delivery has risen the demand for the bioplastic packaging, which is estimated to drive the global plant-based food bioplastics market in the near future.
The key players operating in the market are facing challenges in obtaining raw material for the and technology for the development of the plant-based bioplastic packaging, which is observed the hamper the growth of the plant-based food bioplastics market. Sourcing sustainable plant materials can be challenging, affecting supply chains. Bioplastics may not match the durability, flexibility, and barrier properties of conventional plastics, limiting their applications. Inconsistent regulations and standards for bioplastics across regions can hinder market growth. Higher Production costs of bioplastics are often higher than traditional plastics, making them less competitive in price. Many consumers are still unfamiliar with bioplastics, affecting demand. Continued innovation is needed to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of bioplastics. Lack of proper facilities for recycling bioplastics can limit their adoption. These factors collectively impact the scalability and adoption of plant-based bioplastics in various markets.
Increasing awareness of plastic pollution and its impact on the environment drives consumers demand and companies to seek sustainable alternatives. As now-a-days consumers are prioritizing eco-friendly products, influencing brands to adopt sustainable packaging solutions. Rising initiatives by the government for developing bioplastic development hub is creating opportunity for university to carry out research and development to innovate bioplastic material using plants. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting the inorganic growth strategies like collaboration to develop plant-based food bioplastics, which is estimated to create lucrative opportunity for the growth of the plant-based food bioplastics market in the near future.
In June 2024, Lignin Industries AB, plastic fabrication company, revealed the introduction of the bio-plastic manufactured using forest residues. The Swedish greentech business Lignin Industries AB has declared that its Renol technology, a bio-based substance made from lignin, which is frequently found in trees, will be mass-marketed. By turning lignin, an organic substance, into "renewable, circular" bioplastics, Lignin Industries says it has created a means of reducing dependency on plastics made from fossil fuels. It appears that trees are the most prevalent source of lignin, an organic polymer. In addition to helping with water retention and structure, it keeps pollutants out. The firm invented Renol, a bio-based substance made from lignin. The technology is used at a factory south of Stockholm, Sweden, and has several commercial use cases and applications that are either in advanced research stages or ready for launch.
The biodegradable and compostable packaging segment held a dominant presence in the global plant-based food bioplastics market in 2024. The shift towards a circular economy supports the utilization of biodegradable and compostable materials for packaging which can be returned to the environment safely after use. Rising concern over plastic pollution and its impact on the environment encourages consumers and companies to seek biodegradable and compostable packaging. The key players operating in the market are focused on developing compostable and biodegradable packaging, which is estimated to drive the growth of the segment over the forecast period.
The flexible packaging segment accounted for a significant share of the plant-based food bioplastics market in 2024. The flexible packaging is versatile in nature which means it can be utilized for extensive range of products, including beverages, snacks, and perishable goods, appealing to various sectors. Advanced flexible packaging delivers barrier protection against light, moisture, and oxygen, extending shelf life and maintaining product quality. Flexible packaging is lighter and takes up less space, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like collaboration for developing compostable flexible packaging, which is estimated to drive the growth of the segment in the near future.
Europe led the plant-based food bioplastics market in 2024. The European Union (EU) has implemented strict regulations and policies that promote sustainability, such as the European Green Deal and the Circular Economy Action Plan. These initiatives encourage the use of renewable and biodegradable materials like bioplastics, reducing reliance on fossil-based plastics. European consumers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly products. There is high awareness of environmental issues, which has led to a surge in demand for sustainable packaging solutions, including plant-based bioplastics. Many European food companies are responding to consumer demand by adopting bioplastics for packaging to enhance their sustainability credentials.
North America held a considerable share of the global plant-based food bioplastics market in 2024. The U.S. and Canada held notable share in the North American market, primarily due to stringent environmental regulations and a strong consumer preference for sustainable products. The market is characterized by the presence of major players like NatureWorks LLC and BASF, focusing on innovative bioplastic solutions. Increasing adoption of plant based materials in beverages and food packaging sectors is estimated to drive the growth of the plant-based food bioplastics market in North America.
Tetra Pak said that demand for plant-based plastic alternatives among North American brands was rising. For instance, certain caps and carton coatings are made of polymers produced from sugarcane.
Tetra Pak reported that the company has increased the global scale for plant-based products broadly.
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the plant-based food bioplastics market during the forecast period. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is witnessing rapid growth due to rising population and urbanization. Governments are increasingly recognizing the need for sustainable solutions, pushing for bioplastics in packaging. For instance, in July 2024, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), a national research and development (R&D) organisation in India, revealed the introduction of the National Mission on Sustainable Packaging solutions programme.
By using the combined strengths of eight cooperating SIR(Scientific & Industrial Research) labs and industry partners, the effort seeks to achieve a net-zero future through integrated, advanced, and indigenous technologies. Dr. N Kalaiselvi, director general of the CSIR and secretary of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, announced this mission, which is headed by the CSIR-National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (NIIST).
Through material development, creative recycling and reuse techniques, and state-of-the-art testing and monitoring facilities, the SIR-funded program seeks to create a holistic response to the demands of sustainable packaging.
Glass bottles, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), multilayer packaging substitutes, novel biobased and biodegradable materials, and an integrated smart packaging solution for the food industry are all included in the strategy. Establishing the India's first biodegradability testing and monitoring facility is another goal of the mission by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
By Type
By Application
By Region
April 2025
April 2025
March 2025
March 2025