April 2025
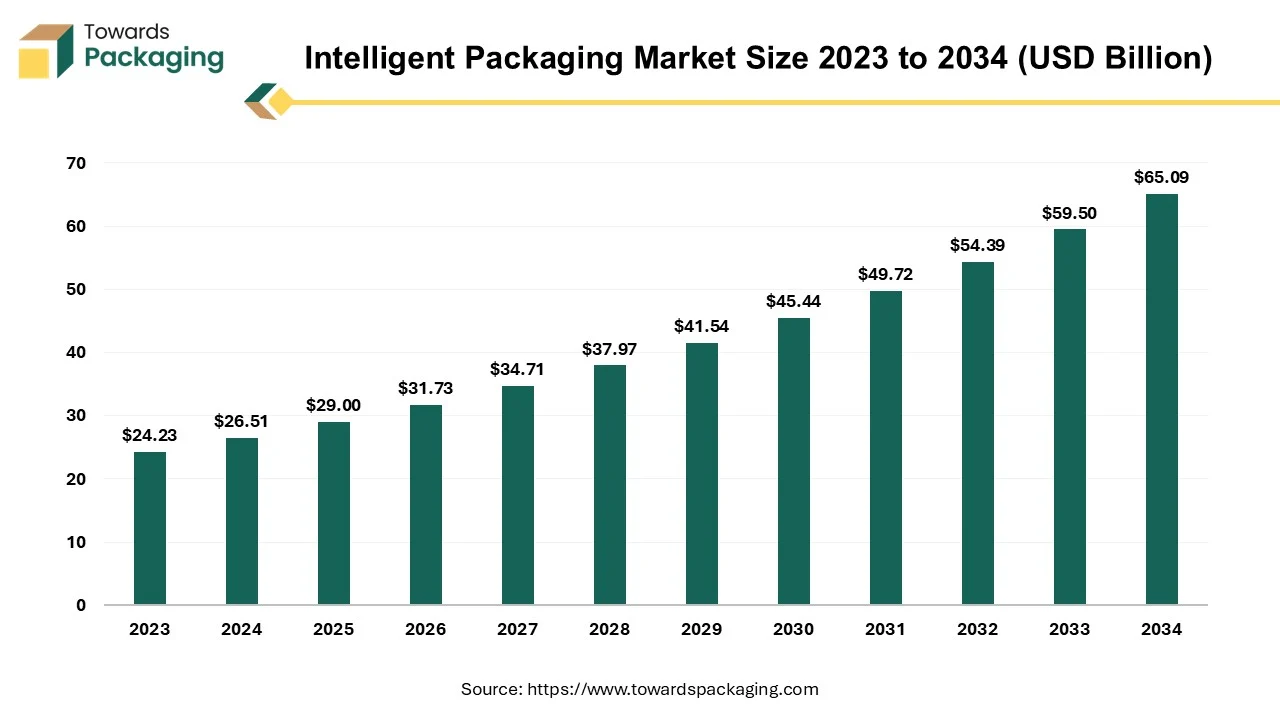
The global intelligent packaging market is set to grow from USD 29 billion in 2025 to USD 65.09 billion by 2034, with an expected CAGR of 9.4% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing intelligent packaging which is estimated to drive the global intelligent packaging market over the forecast period.
Intelligent packaging creates interactive and useful packaging solutions by fusing cutting-edge technologies with conventional packaging. It is made to satisfy consumer demands for longer shelf lives, safer food products, and better customer service. The packaging interacts with the environment and provides clients with extra benefits by utilizing cutting-edge technology like sensors, RFID tags, and QR codes. It can trace the goods along the supply chain, keep an eye on its condition, and give customers pertinent information. Furthermore, cutting-edge elements like augmented reality (AR) experiences are frequently used in smart packaging to improve the overall customer experience.
Sensors are used in sensor-based packaging to track environmental variables like pressure, temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide. Products like food, medications, and medical equipment that need particular environmental conditions to preserve quality and safety benefit from this technology. When the product is subjected to adverse conditions, the sensors can send out an alert, enabling remedial action to be conducted before the product is compromised.
Sensors and indicators that track freshness, humidity, temperature, and leaks are increasingly integrated into packaging. Especially important for perishables, pharmaceuticals, and sensitive electronics. The intelligent packaging assists in ensuring quality and safety during transportation and storage.
Use of QR codes, RFID tags, NFC (Near Field Communication), and barcodes enables better tracking and traceability. Enhances supply chain visibility and allows consumers to access product information instantly (e.g., origin, nutritional details, authenticity).
Packaging that interacts with the product or environment to extend shelf life. Examples include oxygen scavengers, moisture absorbers, antimicrobial coatings, and ethylene absorbers. Highly used in beverage, food, and pharmaceutical sectors.
Increasing integration of biodegradable and recyclable materials in intelligent packaging. Brands are combining smart functions with sustainability to meet consumer and regulatory expectations.
Brands are using intelligent packaging to enhance customer interaction. Augmented reality experiences, gamification, and personalized content accessed via packaging create unique touchpoints.
The need for anti-counterfeit measures, temperature monitoring, and traceability in medicines and vaccines is driving adoption. Smart packaging helps ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Integration with blockchain technology provides secure, tamper-proof product histories. Builds consumer trust by enabling verification of ethical sourcing and product authenticity.
Intelligent packaging supports the growing e-commerce and direct-to-consumer models. Helps with real-time tracking, condition monitoring, and secure delivery.
Advancements in printed electronics, miniaturization, and cost-effective sensors are making intelligent packaging more accessible. Enables wider adoption across mid-tier brands, not just premium products.
Stricter food safety laws and anti-fraud regulations are pushing businesses to adopt smart packaging. Helps prevent issues like foodborne illnesses and counterfeit pharmaceuticals.
AI algorithms analyze data from embedded sensors (like temperature, humidity, gas levels) to predict spoilage or degradation of products. AI integration assists in businesses and consumers reduce waste, optimize inventory, and ensure timely usage. For instance, a food package with AI-backed sensors can alert the retailer or customer if the product is nearing spoilage based on environmental data.
AI processes large amounts of data from RFID, GPS, and IoT sensors in packaging to give real-time tracking and condition monitoring. Detects anomalies (like unexpected delays, tampering, or exposure to damaging conditions). The artificial intelligence integration supports just-in-time delivery models and improves supply chain efficiency. AI-powered pattern recognition verifies genuine packaging through unique digital fingerprints, smart labels, and blockchain-backed QR codes. The artificial intelligence integration assists to combat counterfeit goods, especially in pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics. For instance, Scannable smart packaging verified by AI can immediately confirm product authenticity.
AI detects defects in packaging (like leaks, weak seals, or misprints) during production using computer vision systems. AI assists to track packaging return and reuse systems, ensuring proper reuse or recycling of smart packaging components. Promotes a closed-loop supply chain for sustainability. AI analyzes usage and interaction data from intelligent packaging to offer consumer insights. AI can sync intelligent packaging with smart home ecosystems (e.g., fridges notifying expiry dates or reordering items automatically).
Rising Demand for Intelligent Packaging & Counterfeit Prevention
Fake pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and food products are a global concern. Smart packaging with QR codes, holograms, RFID, and blockchain technology provides authentication and traceability. Consumers and regulators alike demand fresher, safer food. Intelligent packaging (like temperature sensors, freshness indicators) assists monitor quality throughout the supply chain. Hence, to prevent counterfeit incidents there is increase in the demand for intelligent packaging, which has estimated to drive the growth of the intelligent packaging market over the forecast period.
Lack of Standardization & Limited Consumer Awareness
The key players operating in the intelligent packaging market are facing issue like high cost of implementation, lack of standardization, and limited consumer awareness, which has estimated the restrict the growth of the intelligent packaging market. The market lacks global standards and regulations for intelligent packaging technologies. Variations in data protocols, communication formats, and safety regulations develop integration challenges. Difficult for manufacturers to ensure compatibility across regions and systems. Many consumers are still unaware of intelligent packaging features and benefits (like freshness indicators, traceability, or smart labels). Without strong consumer demand, companies may hesitate to invest heavily.
Longer and more complex supply chains have observed to in rise the risk of damage, theft, and counterfeiting. The intelligent packaging provides end-to-end visibility. Strong venture capital interest and corporate R&D expenditure are accelerating innovation in the smart packaging space.
Shoppers want to know where their products come from, how they were made, and whether they’re safe. Smart label and NFC technology let consumers scan packaging for instance information. Hence rising consumer awareness & demand for transparency has estimated to create lucrative opportunity for the growth of the intelligent packaging market in the near future.
The interactive packaging/data carriers segment held a dominant presence in the intelligent packaging market in 2024. Consumers and businesses alike want to know where the product comes from, how it was handled, and if it’s authentic. Data carriers like RFID tags, QR codes, NFC chips, and barcodes assists to offer end-to-end visibility across the supply chain. Interactive packaging is essential for industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods where counterfeiting and compliance are concerns. Interactive packaging allows brands to connect with consumers directly via scannable codes that link to promotional content, usage instructions, or sustainability information. Interactive packaging solutions assists to meet compliance by providing detailed, dynamic, and updatable information.
The primary packaging segment accounted for a considerable share of the intelligent packaging market in 2024. Primary packaging is the first layer that comes in direct contact with the product. It plays an important role in preserving product integrity, freshness, and safety especially for sensitive categories like pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Intelligent features like sensors, temperature, freshness indicators, and moisture detectors are most effective when embedded in primary packaging. Various brand owners prefer smart features at the primary packaging level to prevent tampering and ensure consumer trust. Scanable labels can show carbon footprint, recycling tips, and material sourcing, directly to consumers.
The boxes & cartons segment registered its dominance over the global intelligent packaging market in 2024. Boxes & cartons are universally utilized across food, beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, ecommerce, and electronics. This versatility makes them an ideal carrier for integrating smart features like NFC tags, QR codes, temperature sensors, tracking devices and freshness indicators. Boxes and cartons offer a large printable surface, ideal for: interactive graphics, AR experiences, smart labels, and sustainability messaging. Brands can utilize these surfaces to offer consumers more engaging and informative experiences. Especially in sectors like pharma and food exports, smart cartons assist brands comply with regulations around authenticity, traceability, and safety.
The food & beverages segment to dominate the intelligent packaging market globally. Intelligent packaging solutions like time-temperature indicators, freshness sensors, and leak detectors help monitor the condition of perishable products. With the food & beverages sector expanding globally, especially in processed and ready-to-eat categories, the need for real-time monitoring becomes critical. Expansion of the food industry expands cross-border trade, requiring better tracking for logistics, authenticity, and regulatory compliance. Intelligent packaging enables secure delivery by monitoring external factors (temperature, humidity) during transit. Intelligent packaging with authentication tags and tamper-evident seals ensures product integrity and boosts consumer trust. The food & beverage industry is increasingly adopting sustainable and intelligent packaging to meet consumer expectations.
North America region held the largest share of the intelligent packaging market in 2024, owing to support infrastructure and continuous research and development in the region. North America, especially the U.S., has a massive packaged food and beverage sector, which is one of the biggest users of intelligent packaging (like freshness indicators, time-temperature indicators, QR codes, etc.). Growing demand for convenience foods, meal kits, and ready-to-eat products in North America drives the need for packaging that can ensure product quality and traceability. Agencies like the FDA and USDA have stringent regulations around food safety, pharmaceuticals, and supply chain transparency. Intelligent packaging helps companies comply. Big brands are committing to intelligent packaging in North America region that minimizes waste and increases recyclability. North America is a huge pharmaceutical market. Intelligent packaging ensures drug integrity, anti-counterfeiting, and patient adherence to medication schedules.
U.S. Intelligent Packaging Market Trends
U.S. intelligent packaging market is growing owing to strong food & beverages and packaging industries in the country. The U.S. has one of the largest food & beverage industries globally. U.S. companies are leaders in IoT, sensors, cloud computing, and RFID technology — all critical for intelligent packaging. Strict drug safety regulations (like the Drug Supply Chain Security Act - DSCSA) drive demand for intelligent packaging to track and verify medicines. The U.S. FDA has high standards for traceability and safety in food and pharma. U.S. consumers demand transparency — they expect packaging to offer data on origin, ingredients, freshness, and sustainability. The U.S. government supports R&D through grants and incentives for smart manufacturing and supply chain improvements, including intelligent packaging solutions.
Asia Pacific region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the intelligent packaging market during the forecast period. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia have rapidly growing populations and urbanization. Rising middle-class incomes mean more demand for safe, high-quality packaged food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals. Asia Pacific is the largest food consumption region globally. Countries like China, India, and Japan are major pharma producers and exporters, requiring intelligent packaging for global compliance and safety. Increasing government focus on food safety and anti-counterfeiting, especially in China and India. Policies encouraging traceability in the supply chain (e.g., China’s focus on food traceability systems). Counterfeiting is a major issue in Asia Pacific, especially for luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and food products. Countries like China, South Korea, and Japan are leaders in electronics manufacturing, making smart packaging components more affordable and accessible. Asia Pacific is the world’s largest e-commerce market. Asia Pacific region benefits from lower production costs for packaging materials and components.
China Intelligent Packaging Market Trends
China intelligent packaging market is growing owing to massive E-commerce platform. After several food safety scandals, the Chinese government has made traceability a national priority. China leads globally in e-commerce, including grocery and fresh food delivery. China is the world’s factory — it produces both packaging materials and the electronic components (like RFID tags, sensors, etc.) at scale and low cost. Counterfeit goods are a major issue in China (and globally). China is advancing rapidly in IoT, AI, and blockchain. Integration of these technologies into packaging is being led by Chinese companies to improve supply chain transparency. China is a leading producer and consumer of pharmaceuticals. China’s “Dual Carbon” goals (carbon peaking and neutrality) are pushing industries to adopt sustainable packaging. Chinese government subsidies for smart manufacturing help scale innovations.
Europe region is seen to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. The EU has some of the world’s strictest food safety regulations. European consumers are highly conscious of product origin, sustainability, and ethical sourcing. Europe invests heavily in R&D, with many EU-funded projects focusing on smart packaging innovations (nanotechnology, printed electronics, bio-based sensors). European countries are enforcing strict anti-counterfeiting measures in pharmaceuticals and luxury goods. European industries are quick to adopt Industry 4.0 technologies. Europe is home to global leaders in packaging like Mondi, Smurfit Kappa, Amcor, and Stora Enso, who are investing heavily in intelligent packaging technologies.

By Technology
By Level of Packaging
By Application
By End Use
By Region
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025