April 2025
.webp)
Principal Consultant

Reviewed By
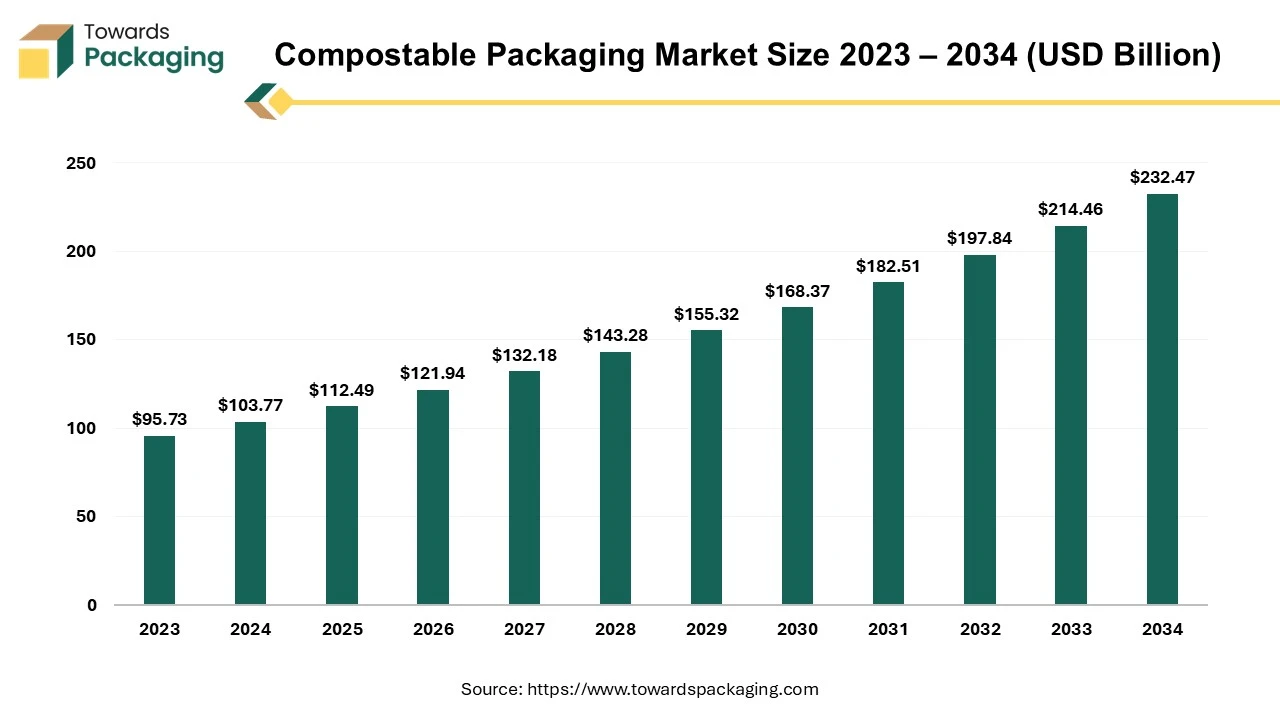
The compostable packaging market is anticipated to grow from USD 112.49 billion in 2025 to USD 232.47 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Compostable packaging, made from a combination of recycled and plant-based materials, is emerging as a strategic option for large firms looking to improve their environmental credentials while directly tackling the issue of single-use plastic packaging. This surge is driven by multinational firms' increased emphasis on sustainability, fueled by rising consumer awareness and governmental efforts like the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive.
Compostable packaging has a better end-of-life performance because microorganisms can break down it into carbon dioxide, water, inorganic chemicals, and biomass, which can be used as a natural fertilizer for agriculture. This breakdown process occurs at a rate equivalent to other organic materials and is usually accompanied by a timescale, commonly around 180 days. Compostable packaging is a sustainable solution for end-of-life disposal without leaving behind persistent environmental contamination. Packaging materials from renewable resources or waste products are remarkable since they adhere more closely to circular economy concepts.
Growing public awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable packaging solutions were driving substantial expansion in the compostable packaging market. The world is slowly realising the full potential of alternate packaging solutions, particularly compostable ones.
For Instance,
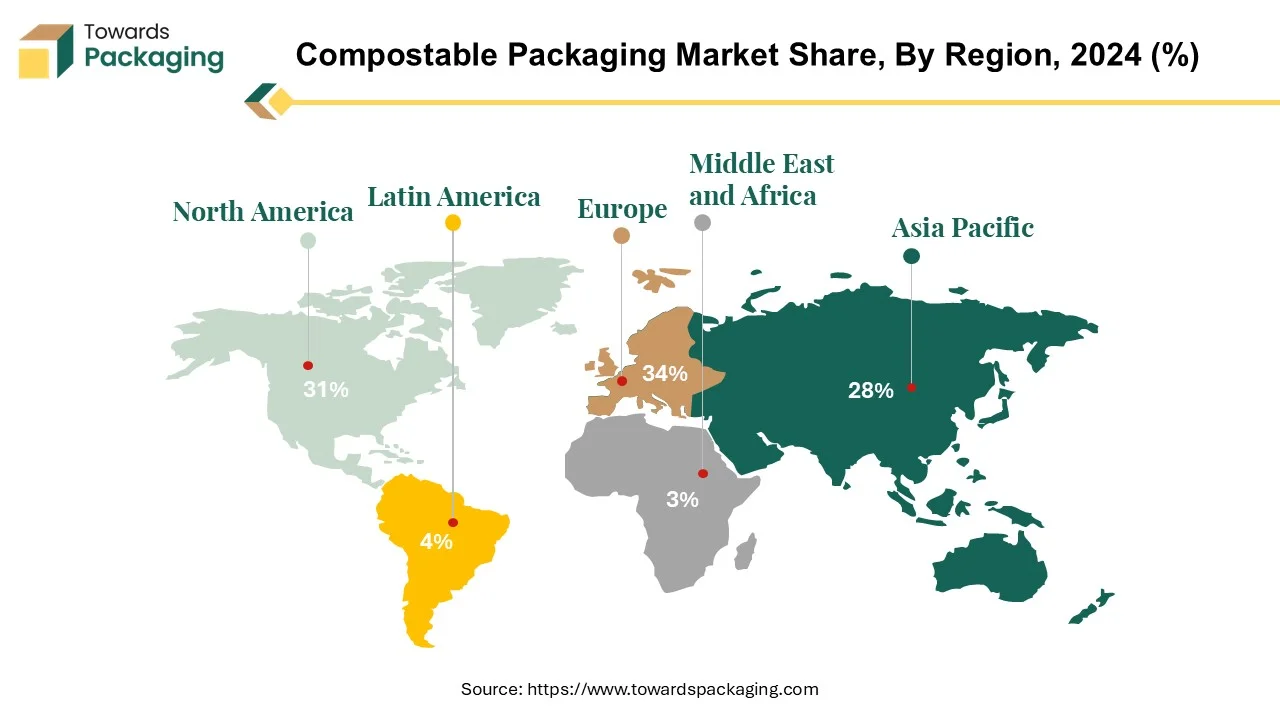
Europe is the leading region in the compostable packaging industry, owing to growing consumer awareness of the environmental effects of their purchasing decisions. This transition is seen in studies showing that more than half of European consumers are willing to invest more in sustainable items. As a result, global firms must embrace and invent eco-friendly packaging solutions that break the cycle of trash disposal.
Compelling figures highlight the importance of bio-waste management in the EU circular economy policy. Recycling 90-116 million tonnes of biowaste into premium compost can improve the quality of 3% to 7% of Europe's depleted agricultural soils, addressing the continent's long-standing soil degradation issue. Furthermore, optimizing composting operations can replace considerable amounts of phosphate, potassium, and lime fertilizers, increasing resource efficiency and environmental sustainability.

No packaging was the preferred option, but only by a slight margin, with just over half of respondents preferring flexible packaging. Some European countries, including Italy, Spain (Cataluña), Norway, Austria, the UK, Switzerland, Belgium, and Luxembourg, have a long history of using compostable bioplastic bags for bio-waste collection. However, Germany and the Netherlands have lower acceptance levels among biological recycling facility operators. This disparity reflects attitudes and behaviours towards compostable packaging adoption between EU member states.
For Instance,
Compostable packaging's potential in the United States is hampered by a lack of infrastructure for successfully managing food and organic waste. According to the Sustainable Packaging Coalition's report "Understanding the Role of compostable packaging in North America," only 27% of the US population has access to food waste composting programs, with an even smaller fraction (11%) able to divert compostable packaging away from landfills and into composting facilities.
Compostable packaging collection programs are noticeably absent from most retail shops and event sites. To fully realize the cyclical potential of compostable packaging, the United States needs to improve consumer access to composting on two fronts. This necessitates investing in composting facilities that can process food scraps and packaging and establish effective biodegradable material collection systems.
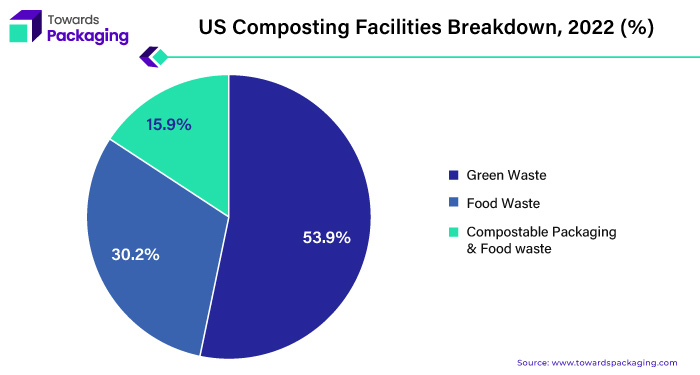
Only 15% of composting facilities in the United States accept some biodegradable packaging. While 55% of these facilities only accept green garbage, such as yard waste and agricultural leftovers, about 45% receive food waste in addition to other biodegradable materials. Approximately 29% of facilities accept food trash, with another 15% accepting packaging materials and food waste.
For Instance,
The market for compostable packaging in Asia Pacific has grown significantly in recent years due to government measures supporting sustainable practices and rising environmental awareness. Consumers and businesses are flocking to compostable packaging solutions as an eco-friendly substitute for plastic due to a focus on lowering plastic waste and pollution. This tendency is especially noticeable in the food and beverage, cosmetics, and healthcare industries, as packaging is essential to displaying and preserving products.
Manufacturers are innovating with biodegradable materials such as plant-based plastics, paper, and compostable films to meet the rising demand for environmentally responsible packaging options. Additionally, collaborations between industry players and government bodies are fostering research and development efforts to enhance further the performance and accessibility of compostable packaging solutions across the Indian market.
For Instance,
Compostable bags, composed of natural plant starch, eliminate the production of harmful substances. These bags readily decompose in composting systems through microbial action, transforming into compost. Compostable bags serve as indispensable waste management solutions for households, businesses, and zero-waste events, crafted from renewable resources. Unlike conventional plastic bags and certain biodegradable alternatives, compostable bags are derived from plant-based materials like sugar starch. When adequately moistened, these bags undergo composting, alongside their contents. Unlike conventional plastic bags and certain biodegradable alternatives, compostable bags are derived from plant-based materials like sugar starch. When adequately moistened, these bags undergo composting, alongside their contents.

For Instance,
Polylactic acid (PLA) has emerged as a critical material in compostable packaging due to its versatility and eco-friendliness. PLA is biodegradable and compostable, making it a viable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. Its ability to mirror the functioning and appearance of conventional plastics while remaining compostable has boosted its popularity in various packaging applications, including food service products, bags, and films.
| Circularity Aspect | Existing Practices/Scope | Opportunities |
| Use of Bio-plastics | In India, packaging accounts for over 60% of all bioplastic consumption. | As a result of regulations prohibiting SUPs and the emergence of bio-plastics, their proportion in the packaging industry is anticipated to rise. |
| A few FMCG businesses in India are working towards using only 100% biodegradable plastics to package cosmetics and ready-to-eat goods. | ||
| Reusable Packaging | Increased use of non-returnable glass bottles in packaging by Pepsico India. | Utilizing reusable containers in place of the current SUP containers in the expanding online meal delivery services. |
| Use of Recycled Plastics | 90% of the plastic packaging produced by Cargill Oils India is now recyclable thanks to a reformulated plastic material made in collaboration with Dow Chemical. | In non-food applications, use recycled plastic. |
| Re-design of Packaging | Lush, handcrafted cosmetics have a packaging-free line. | Avoid using excessive packaging material or build a packaging-free line of items. |
| Cremica Food Industries reduces lamination in packaging. | Switching to single-polymer plastic packaging from multi-polymer packaging. |
PLA's biocompatibility, low toxicity, and inexpensive cost compared to other biopolymers help to explain its widespread market adoption. As consumer demand for sustainable packaging grows, PLA is positioned to play an essential role in accelerating the shift to a more ecologically conscious packaging industry.
For Instance,
The food and beverage industry are a prominent adopter of compostable packaging among the different sectors pushing its expansion. Food and beverage firms are increasingly looking for compostable packaging solutions to lessen their environmental impact as customer tastes and the focus on sustainability expand. Products packaged in compostable materials are becoming increasingly popular among consumers who value eco-friendly solutions, ranging from gourmet beverages to organic snacks. Corporate sustainability objectives and regulatory pressures are pushing this change in addition to consumer demand. Food and beverage producers are spending money on R&D to create smart packaging materials that can preserve the freshness and quality of their products while also being compostable.
For Instance,
Compostable packaging is vital in supply chains due to the environmental problems caused by conventional packaging materials, especially plastics. The issue of plastic pollution is a significant worry, as traditional plastic packaging plays a major role in the growth of plastic trash. This garbage endangers wildlife, contaminates water supplies, penetrates ecosystems, and harms people's health. The persistent nature of plastics, which may withstand decades in the environment without naturally disintegrating, makes these problems even more challenging.
Conventional packaging materials, like plastics, take up a lot of room in landfills, which puts increasing pressure on their limited capacity. Compostable packaging materials provide a workable answer by reducing the load on landfill space by providing an eco-friendly substitute that can be composted. Using flexible packaging, such as compostable films, is essential for promoting circularity and reducing waste. Using compostable materials derived from renewable resources makes it easier to move towards a circular economy where resources are used for extended periods.
Compostable goods help cut greenhouse gas emissions and are consistent with environmental goals. Compared to conventional polymers, the production of biodegradable materials usually requires less fossil fuel, reducing carbon emissions. By utilizing compostable packaging, businesses may actively contribute to climate change mitigation and advancing a more sustainable, carbon-neutral supply chain.
For Instance,
A recent survey commissioned by a compostable packaging provider has revealed that a significant majority of UK adults favor replacing plastic packaging with compostable alternatives. Conducted online from 15 to 16 November and involving 1,734 participants, the survey highlights the growing public concern over plastic waste and the strong support for sustainable packaging solutions.
The data shows that 89% of respondents believe local councils should collect all recyclable or compostable packaging from households. Additionally, 85% of those surveyed would support a ban on conventional plastic packaging if compostable alternatives are available. This overwhelming support reflects the public's desire for a shift towards more sustainable packaging options.
More than 60% of respondents expressed concern about the increasing amount of plastic waste in their daily lives. Furthermore, 86% supported the idea of collecting compostable packaging alongside food waste, emphasizing the public's readiness to embrace compostable solutions as part of their waste management practices.
The UK has set ambitious goals to make all plastic packaging reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2025 and to recycle or compost 70% of plastic packaging within the same timeframe. While public support for compostable packaging is strong, the survey underscores the need for government investment and appropriate policy frameworks to develop the necessary collection infrastructure to meet consumer demand.
Overall, the survey results indicate a significant shift in public opinion towards sustainable packaging, highlighting the urgent need for systemic changes to accommodate the growing preference for compostable options.
The competitive landscape of the compostable packaging market is dominated by established industry giants such as TIPA Ltd (Israel), Rocktenn (US), Özsoy Plastik (Turkey), International Paper Company (US), Mondi (UK), SmartSolve Industries (US), Tetra Pak International SA (Switzerland), Amcor PLC (Switzerland), DS Smith (UK), Klabin SA (Brazil), WestRock Company (US), Hosgör Plastik (Turkey), Smurfit Kappa (US), Rengo Co. Ltd (Japan), Stora Enso (Sweden), BASF SE (Germany), Bemis manufacturing company (US), Clearwater Paper Corporation (US), and Eurocell S.r.l (UK) These giants compete with upstart direct-to-consumer firms that use digital platforms to gain market share. Key competitive characteristics include product innovation, sustainable practices, and the ability to respond to changing consumer tastes.
TIPA's compostable packaging for fashion has many uses, including resealable, garment bags, and zipper bags for garments, accessories, and more.
For Instance,
The plant-fiber, tree-free packaging from Ultra-Green Sustainable Packaging completely breaks down in a commercial composter within 60 to 90 days. Made entirely of recycled water and soda bottles, our clear recycled PET lids are 100% recyclable. Items made of plant fiber have ASTM 6868 certification, while bioplastic (PLA) items have ASTM 6400 certification.
By Product
By Material
By End Use
By Region
April 2025
March 2025
March 2025
March 2025