March 2025
.webp)
Principal Consultant

Reviewed By
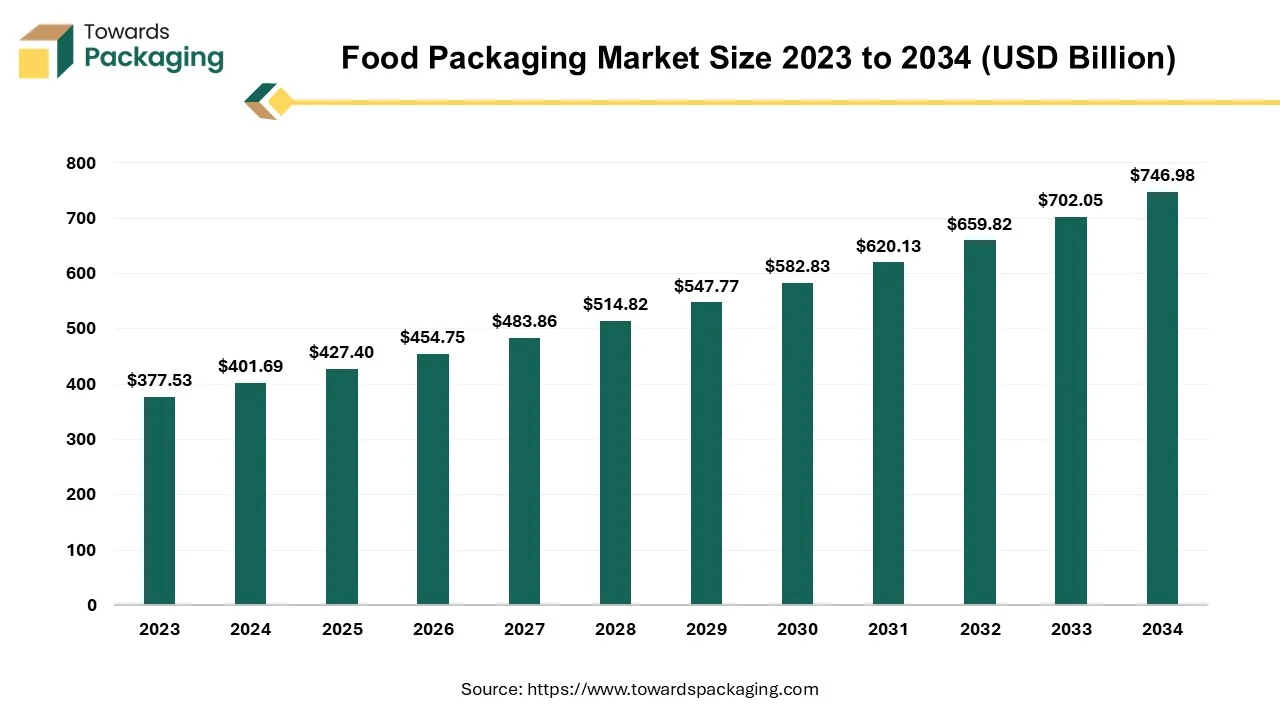
The global food packaging market is expected to grow from USD 16.47 billion in 2024, with consistent growth from 2025 to 2034. It is projected to reach USD 27.12 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.7%, driven by innovations in packaging materials and increasing consumer demand for food safety.
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the food packaging market, with India experiencing a rapid growth rate of 12.60% CAGR from 2025 to 2034, fueled by rising demand in processed food and personal care sectors.
Paper and paperboard packaging, favored for its recyclability and environmental benefits, is witnessing increased adoption for ready-to-eat meals and fresh food transportation.
Automation in food packaging, exemplified by Sealed Air's meat packaging innovations, enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and ensures consistent, safe packaging.
Advanced packaging technologies, such as intelligent packaging, offer solutions to reduce food waste, particularly for fresh produce, and extend product shelf life.
Investments and M&A activities, such as Amcor's acquisitions and SIDBI Venture Capital's funding in India's paper packaging industry, underscore growing interest in the sector.
Leading players in the competitive food packaging market include Berry Plastics Group, Amcor Plc, Sealed Air Corporation, DS Smith PLC, and Huhtamaki Oyj, driving innovation and growth.
Food packaging has evolved into a crucial and integral part of our daily lives, especially in light of the global trend of urbanization. A simple rationale drives this phenomenon. As the urban population comprises approximately half of the world's population, cities cannot provide the necessary land and environment for agricultural development. Consequently, food must be processed, packaged, and available on supermarket shelves for urban dwellers to conveniently purchase. This convenient choice aligns well with the fast-paced lifestyles of city residents, facilitating their access to food amidst their busy routines.
Adequate food packaging plays a pivotal role in enhancing the cleanliness and freshness of food while also providing valuable branding opportunities for food manufacturers. Furthermore, it serves as a crucial tool in preventing food spoilage and extending the shelf life of products, thereby minimizing food waste. It is disheartening to note that approximately 1.3 billion tons of food is wasted annually globally, which could otherwise be utilized to feed the 1 billion people experiencing food scarcity. Implementing efficient food packaging strategies can significantly reduce this wastage and address food security challenges worldwide.
As per data provided by the World Packaging Organization (WPO), the global packaging industry generates a turnover exceeding $500 billion, with food packaging being a significant sector. However, food packaging is influenced by local food preferences and cultural norms in different regions and countries.
In the case of Japan, consumers have a strong aversion to inadequate packaging, where even minor creases or flaws on the packaging can result in the rejection of supermarket food products. The importance of fish and seafood in the Japanese diet makes ensuring these items remain fresh and protected from spoilage crucial. Food packaging typically includes a small bag of starch polymer or silica gel to absorb moisture and preserve product quality. This practice aligns with Japanese consumer expectations.
On the other hand, European consumers hold a different perspective. They tend to be sceptical about the use of moisture absorption agents within food packaging, and the presence of such agents might raise suspicions about the food itself. European consumers may perceive it as an unnecessary addition and question packaged food's need for moisture control.
These divergent preferences highlight the importance of understanding and adapting to local consumer preferences regarding food packaging. Packaging strategies must consider cultural nuances and consumer expectations specific to each region to ensure product acceptance and success in the market. Customizing packaging solutions to align with local preferences is vital for establishing trust, meeting consumer demands, and effectively marketing food products in different countries and regions.
The food packaging industry has witnessed the introduction of several new and high technologies that are revolutionizing the field. One notable advancement is the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), which enables the integration of chips, sensors, and electronic label printing into traditional packaging practices.
In the coming years, "intelligent" or "active" packaging will be crucial in reducing food waste. These innovative packaging solutions are a response to global efforts by experts to devise new methods of informing customers about the perishability of food and protecting against spoilage. Such systems can display the current state of a product and simultaneously extend its shelf life through oxygen absorbers or specialized acids.
Integrating IoT technologies and intelligent packaging holds immense potential for enhancing food safety, reducing waste, and improving the overall consumer experience. By providing real-time data on product condition and implementing active measures to maintain freshness, these advancements contribute to better supply chain management and more informed consumer decision-making. As technology evolves, the food packaging industry can leverage these advancements to create sustainable packaging solutions prioritizing food quality, safety, and waste reduction.
The Asia-Pacific region has captured the largest market share in the global food packaging industry, demonstrating its dominant position and significant contribution to the overall market.
The Indian food packaging market is projected to experience a steady growth rate of 12.60% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2025 to 2034. This growth can be attributed to the rising demand for food packaging from processed food, personal care, and pharmaceuticals. The industry plays a crucial role in driving technological advancements and innovation, benefiting multiple manufacturing sectors. Factors such as a growing population, increasing disposable income levels, and evolving lifestyles are expected to boost consumption across various industries, consequently driving the demand for packaging product solutions.
Implementing Atmanirbhar (self-reliant) initiatives and strategic structural reforms is anticipated to enhance significant growth opportunities within the packaging industry in India. These measures aim to bolster domestic production capabilities, reduce import dependence, and create a favourable business environment. As a result, the industry is poised to experience significant expansion, attracting domestic and international investments. The focus on self-sufficiency and the implementation of streamlined reforms will contribute to the overall growth trajectory of the packaging sector in India, fostering increased competitiveness and driving sustainable development.
According to the Indian Institute of Packaging (IIP), there has been a substantial surge in packaging consumption in India, with a remarkable growth rate of nearly 200% over the past decade. This data highlights the increasing demand for packaging solutions across various industries within the Indian market. The significant rise in packaging consumption can be attributed to several factors, including the expansion of e-commerce, urbanization, changing consumer preferences, and the economy's overall growth. This upward trend presents significant opportunities for businesses operating in the packaging industry, as they can tap into this burgeoning market and develop innovative packaging solutions to cater to the evolving needs of Indian consumers.
The rapid proliferation of internet and television media in rural areas significantly contributes to the surge in demand for packaged products. This increasing connectivity has led to greater exposure and information access, influencing consumer preferences and purchasing behaviour. Rural residents, now more than ever, have access to a plethora of product choices through online platforms and television advertisements, resulting in a heightened demand for conveniently packaged goods. This trend presents a lucrative opportunity for businesses in the packaging industry to capitalize on the growing rural market. By aligning their strategies with the evolving media landscape, companies can effectively market and promote their packaged products to rural consumers, thus tapping into this expanding market segment and driving further growth.
In recent years, the food packaging industry in India has undergone significant transformations driven by various trends and innovations. One notable trend is adopting environmentally friendly and sustainable packaging solutions, including bioplastics, paper-based packaging, and compostable materials.
Another emerging trend in the food packaging industry is the rising demand for convenience and ready-to-eat food products. This shift in consumer preferences has sparked the development of innovative packaging solutions, including microwavable pouches, resealable trays, and shelf-stable packaging. Furthermore, intelligent packaging technologies like RFID tags, QR codes, and smart labels are gaining popularity. These technologies enable consumers to access valuable information about the product, including its origin, ingredients, and nutritional value, enhancing transparency and consumer engagement.
Although the food packaging industry in India offers substantial growth prospects, it also encounters various challenges. These include the need for standardized packaging materials, insufficient recycling, waste management infrastructure, and the high expenses associated with packaging equipment and technology. Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, leading to increased raw materials and transportation costs. These circumstances present additional hurdles for the industry to overcome.
However, amidst the challenges, several opportunities await players in the food packaging industry in India. Firstly, a growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly packaging solutions presents a chance for companies to capitalize on this market trend. Additionally, the rapid expansion of e-commerce and online food delivery services opens up avenues for innovative packaging solutions that cater to the specific needs of these channels. Moreover, consumers' rising disposable income and evolving lifestyles provide an opportunity to develop packaging designs that align with their preferences and convenience. By leveraging these opportunities, businesses can position themselves for success in the dynamic Indian food packaging market.
The paper and paperboard market can be segmented into various categories based on materials, such as corrugated boxes, boxboard, rigid boxes, folded boxes, trays, flexible packaging, paper bags, shipping bags, and sachets/pouches. The choice of packaging materials varies depending on the food and beverage served.
Paper and paperboard are widely preferred in the food and beverage industry due to their degradable nature and recyclable properties. They are considered environmentally friendly packaging options. Ready-to-eat meals, on-the-go snacks, and frozen or fresh foods are increasingly being packaged and transported in paperboard packaging to address environmental concerns.
Regarding transportation, rigid boxes are commonly favoured for their sturdiness and durability. However, when serving fresh products, flexible and molded paper or paperboards are often utilized to meet specific packaging requirements.
Overall, the paper and paperboard packaging market offer a range of options to cater to the diverse needs of the food and beverage industry. These materials provide practical and sustainable solutions for packaging and transporting various food and beverage products, aligning with the industry's increasing focus on environmental responsibility.
As technology advances, industries across various sectors have shifted from manual processes to integrating new machines and automation. The food packaging industry is no exception and has greatly benefited from the scientific advancements of our time.
Almost every food product, except for fruits and vegetables, is packaged in today's food industry using automated food packaging machines. These machines have revolutionized packaging by streamlining operations, increasing efficiency, and ensuring consistent and hygienic packaging.
Automated food packaging machines offer various capabilities, including weighing, filling, sealing, labelling, and inspecting product quality. They can handle multiple packaging formats, such as pouches, containers, bottles, and cans, depending on the specific needs of the food product. By utilizing automated food packaging machines, manufacturers can achieve higher production volumes, improved accuracy in portion control, enhanced product safety and hygiene, and reduced labour costs. These machines are designed to meet strict quality and regulatory standards, ensuring that food products are packaged efficiently and meet the required standards for shelf life, freshness, and consumer satisfaction.
The integration of automation in food packaging has significantly contributed to the industry's ability to meet the demands of consumers, retailers, and regulatory authorities. It has also played a crucial role in ensuring product integrity, extending shelf life, and reducing food waste. Utilizing automated industrial robots in the food industry offers several advantages, particularly regarding worker safety, productivity, scalability, cost-effectiveness, consistency, and traceability. One significant benefit is that automated systems increase workplace safety by reducing the risk of worker injuries.
For instance, in the processing and packaging meat items, robots can handle tasks that would otherwise require manual labour with sharp knives, minimizing the potential for accidents and harm. Moreover, automation enhances production line productivity significantly. While a human worker may process one product at a time, machines can handle tens of products simultaneously, increasing output and overall efficiency. The performance and output of automated food packaging robots can be adjusted according to manufacturers' requirements, providing flexibility in meeting production demands.
Automation offers scalability to food packagers. If there is a need to double the output, another food packaging machine can be installed, eliminating the need to scale up every aspect of the business. Automated food packaging operations generally have lower operating costs compared to manual processes. The machines primarily require electricity to function, while other running costs are minimal, making them cost-effective in the long run. Consistency in product quality is another advantage of automated food packaging. Machines handling the packaging process eliminate human errors, resulting in products with identical dimensions, weight, and visual appearance.
Automated food packaging enables end-to-end traceability of the entire production line. Manufacturers can use codes on automated labels to track and document the facilities and packaging processes that a food product has undergone, ensuring transparency and quality control. Integrating automated industrial robots in the food packaging industry offers numerous benefits, ranging from increased worker safety to improved productivity, cost-effectiveness, consistent product quality, and enhance traceability throughout the production process.
Packaging has the potential to significantly impact food preservation and reduce waste, particularly if consumers better understand its benefits and functions. As food waste continues to be a pressing issue, especially in the United States, improved packaging solutions could offer substantial environmental and economic benefits.
According to recent data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), food waste in landfills has doubled from 1990 to 2020, contributing to 58% of methane emissions from municipal solid waste landfills. Alarmingly, researchers have found that approximately 40% of the food supply is wasted each year, with 43% of this waste occurring at the consumer or household level.
A survey of over 1,000 U.S. consumers aimed to explore how packaging could help reduce household food waste and gauge consumer awareness of packaging technologies. The survey sought to understand consumers' perceptions of different packaging formats and their willingness to invest in packaging that minimizes food waste.
Key findings from the study revealed that whole fruits and vegetables, such as bananas and lettuce, are among the most wasted food items. Dairy products, prepared packaged foods, and leftovers also contribute significantly to household food waste. Notably, half-eaten packaged food products and food that spoiled before consumption are major contributors to waste, suggesting a need for better packaging designs to extend shelf life and enhance usability.
Consumers reported that packaging types such as “no packaging,” “bag/pouch,” and “tray with wrap, film, or snap-fit lid” are associated with higher levels of food waste. The study highlighted that while consumers' current understanding of packaging technologies is limited, there is a willingness to pay more for packaging that improves freshness and extends shelf life.
The researchers concluded that certain food products, particularly produce, would benefit greatly from advanced packaging technologies designed to prolong shelf life and reduce waste. Many of the wasted produce items in the study lacked packaging altogether, underscoring the need for packaging solutions that address this gap.
Intelligent packaging, which can monitor and indicate the freshness and shelf life of food products, is identified as a promising solution. Effective education about these technologies could be targeted strategically to specific population segments to maximize impact.
The study emphasizes the importance of developing innovative packaging solutions to address food waste challenges. Improved packaging designs, especially for produce and other high-waste items, can play a crucial role in extending shelf life and reducing waste. Consumer education on these advancements will be key to achieving broader acceptance and implementation of effective packaging technologies.
The food packaging market is a highly competitive and rapidly evolving industry that plays a pivotal role in the safe and efficient delivery of food products. To succeed in this dynamic market, businesses must navigate the competitive landscape and understand the key players, market trends, and strategic developments. This comparative landscape analysis provides insights into major companies' market positioning, product offerings, and competitive strategies.

By Material
By Type
By Application
By Regional Outlook
March 2025
March 2025
March 2025
March 2025