February 2025
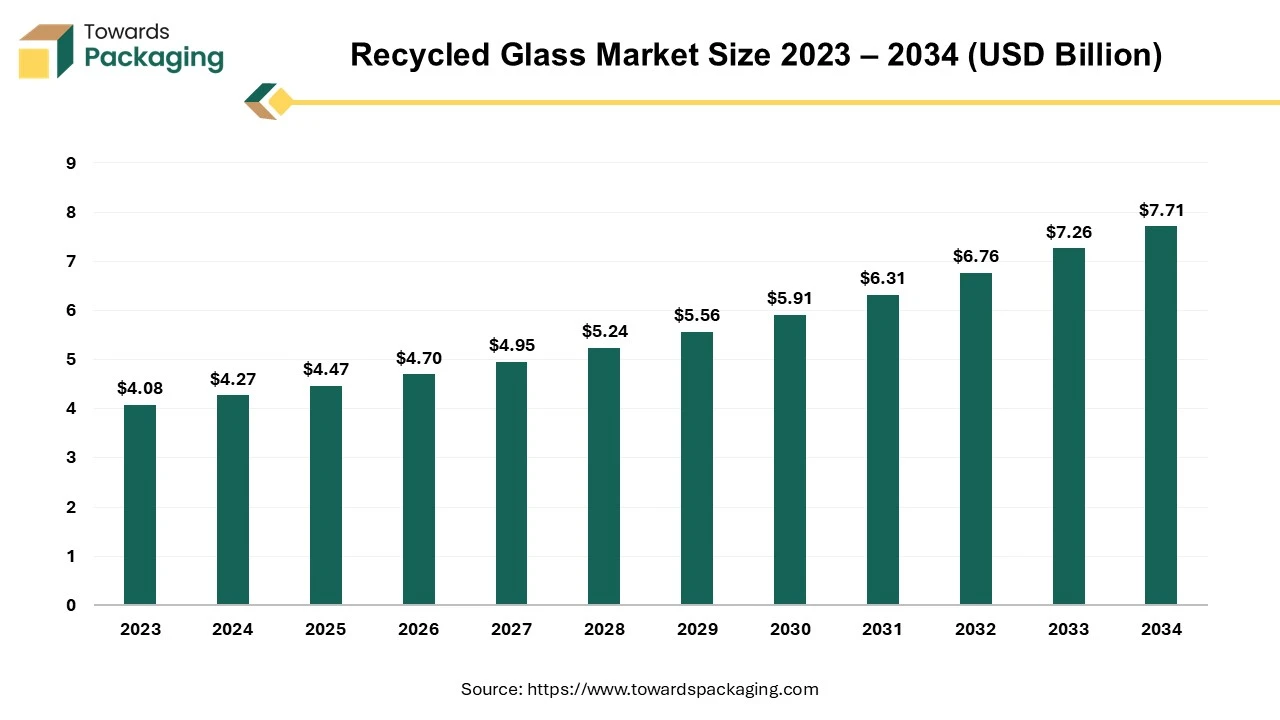
The global recycled glass market is set to expand from USD 4.27 billion in 2024 to USD 7.71 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.09% from 2025 to 2034. Market growth is driven by rising recycling initiatives, urbanization, and sustainability efforts, with Asia-Pacific anticipated to experience the fastest expansion.
Unlock Infinite Advantages: Subscribe to Annual Membership
The recycled glass market is predicted to witness strong growth in the years to come. Recycled glass is glass that has been processed from discarded glass products to be reused in manufacturing new products. Glass can be endlessly recycled without decreasing quality. According to the Glass Recycling Association, 33% of new glass container contains recycled glass and 60% of recycled glass is used for new containers or insulation. Recycling glass reduces the need for raw materials like sand, soda ash and limestone, saving energy as well as natural resources while minimizing the environmental impact. Recycled glass retains the same quality as the new glass while making it a sustainable and cost-effective material to be utilized in the packaging, construction, consumer goods and industrial applications.
The growing environmental awareness and the push for sustainability along with the stringent government regulations and policies aimed at reducing landfill waste and promoting recycling is expected to augment the growth of the recycled glass market during the forecast period. Furthermore, advancements in the recycling technologies such as automated sorting as well as processing systems are also anticipated to augment the growth of the market. Additionally, the rising adoption of the circular economy models across various industries as well as the increasing preference of the construction industry for the recycled glass as an important component in the sustainable building materials is also projected to contribute to the growth of the market in the near future.
The growing demand from the construction industry due to the by increasing infrastructure development as well as the rise of the smart cities is anticipated to support the growth of the recycled glass market during the estimated timeframe. In the building sector, creative approaches to material reuse are growing in popularity as consumers place a higher priority on sustainability. Additional measures are required to minimize the impact on the environment and contribute positively to the industry in response to the growing demands. Adopting recycled glass is one of the most recent developments in the construction sector. Recycled glass has special advantages for supporting, structural as well as decorative building components. Another new trend in the sector is deconstruction, which is supported by using recycled glass. The deconstruction process decreases carbon emissions and supports a circular economy.
Furthermore, construction teams working on renovation projects can replace old windows with recycled glass to solve window-related issues. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 25–30% of heating and cooling costs are caused by window leaks alone. Replacing windows with recycled glass can improve property security, save energy expenses for property owners, stop leaks, and minimize outside noise. Additionally, glass aggregate makes an ideal substitute for multiple common building supplies like gravel and sand. Glass aggregate may be utilized to support landscape components, make concrete mixes, and help water flowing in drainage applications. In addition, this material can be utilized for constructing patios, garden beds, pathways, and other exterior surfaces. These applications combined with the growing awareness of the environmental conservation among industry stakeholders, position the construction sector as a key growth factor for the recycled glass market within the estimated timeframe.
The high processing costs as well as contamination and sorting challenges is likely to impede the growth of the recycled glass market during the estimated timeframe. The remelted industry pays a relatively low price per tonne, but the processing costs are frequently greater. Glass recyclers typically operate on extremely thin margins, which restrict their ability to invest in new technologies that could open up new, non-remelted markets. As a result, glass that is no longer useable is frequently disposed of in landfills, which contradicts with the objectives of environmental preservation and sustainability. Glass that cannot be remelted is often less than 12 mm (1/2") and contains ceramic, stone, and porcelain (CSP) flecks. Due to this it is difficult to optically color sort and contains large quantities of multi-product impurities, this glass is undoubtedly the most hardest to recycle.
The method of smelting and refining glass needs extreme temperatures, which consumes a substantial amount of energy. This presents a financial issue for recycling operations, wherein energy costs can be high. Also, the fact that glass is indefinitely recyclable has partially worked against it because recycling the cullet is difficult as well as less profitable. It is clear that an effective recycling scheme depends on glass being in a quality suitable for its intended purpose. A certain amount of recovered glass must be remelted under certain recycling systems. Such a poorly thought-out contract undermines the economic feasibility of any recycling program and frequently results in a negative carbon dioxide footprint when there is no remelted plant within reasonable travel distance. It's not that glass shouldn't be remelted; it's just that the appropriate glass should be remelted in the right place at the right price. Furthermore, the Remelt industry's substantial reliance on the "glass-to-glass" approach hinders innovation and the possibility of broadening recycled glass applications in other sectors.
The rising adoption of glass as a sustainable alternative to plastic is expected to create substantial opportunity for the growth of the recycled glass market in the near future. Glass is an excellent choice to surpass plastic in the global movement for environmentally friendly materials. Glass is an attractive substitute for the extensive utilization of the plastics due to its unlimited recyclability as well as low environmental impact. The benefits of adopting glass are as obvious as its translucent surface, ranging from minimizing carbon emissions to minimizing ocean pollution. For every ton of recycled glass, more than a ton of natural resources are preserved, consisting of 410 pounds of soda ash, 1,300 pounds of sand, 380 pounds of limestone, and 160 pounds of feldspar, according to the Glass Packaging Institute (GPI).
Additionally, a tonne of carbon dioxide, which serves as a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, is decreased for every six tons of recycled glass. Particulates are reduced by 8%, sulfur oxides by 10% and nitrogen oxide by 4%, with an equivalent 10% increase in cullet. Glass is gaining popularity, and while the global recycling rate is relatively low (estimated at about 21%) and varies greatly by region, some regions of the world can already report excellent recycling rates. For instance, compared with various other regions of the world, glass recycling rates are often greater in European nations. The Close the Glass Loop association states that the average percentage of the glass packaging collected for recycling in the European Union was 80.1% in 2021. Similarly, in certain states, such as California, more than 80% of the glass bottles are recycled. This result illustrates the latent potential in other markets, providing huge growth opportunities for glass recyclers to scale up while also supporting sustainability aims.
The implementation of the artificial intelligence (AI) marks as a substantial advancement in the management of the recycled glass. In addition to increasing the efficacy of the glass recycling, this modern technology is essential for minimizing the landfill waste and increase the quality of the recovered glass products. Artificial intelligence (AI) is being utilized extensively to sort the glass bottles and jars, which are frequently utilized as containers for the food and beverages. It is projected that this technology would increase the glass recycling rates as well as substantially decrease the amount of sorting that is currently done by hand. For instance
PFU (one of the Ricoh Group's top scanner manufacturers) recently introduced a state-of-the-art AI tool. With the utilization of the image recognition technology, it can 99.8% accurately determine the color and composition of bottles that are moving along a conveyor belt. The robotic arms that sort things are instructed by the system. These can separate bottles by color, such as opaque or brown glass, and sort up to 70 bottles per minute. Even non-empty bottles and plastic bottles that wind up in glass recycling can be identified and separated by the robot. Additionally, as AI gains more data, it will handle more complex separations since it has the ability to relearn.
Furthermore, a cleaner recycling stream is guaranteed by its capacity to provide the real-time monitoring and prompt response to the contamination issues, which is important for both environmental and financial reasons. AI technologies also reduce the possibility of the worker injuries and create a safer workplace. AI is probably going to be a key to opening up new opportunities for recycled glass. The capacity of the technology to streamline processes and adapt to the new requirements of the industry positions it as an important driver for the expansion of the recycled glass market.
The cullet segment held largest share of 74.51% in the year 2024. Cullet refers to recycled glass scrap which is broken up and divided into tiny fragments. Besides silica sand, it is frequently utilized as a raw material in the manufacturing of new items. Utilizing cullet minimizes the energy needed to melt the glass, which contributes to the conservation of the natural resources. As cullet is formed using recycled glass, its use also decreases the quantity of waste produced by the glass industry. Additionally, cullet blowing supports the formation of distinctive textures and color changes in glass that are not possible with other materials. The glass industry makes extensive use of this safe as well as sustainable process. Furthermore, cullet is easily recyclable and can be repeatedly melted and reformed without losing quality and this makes it an ideal material for creating new glass products such as bottles, jars, and containers.
The bottle & containers segment held largest share of 42.31% in the year 2024. Glass bottles and containers are widely utilized in the industries such as food and beverages, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics due to their non-toxic, non-reactive and highly recyclable properties. As glass can be recycled endlessly without losing its quality it acts as a key material for brands seeking to meet sustainability goals as well as reduce their environmental footprint. Additionally, glass delivers a shelf impact that is unmatched by other packaging material owing to its unique clarity, shape, and texture, which neither cardboard nor plastics can have. The product can be clearly seen due to the glass's transparency and the material's strength adds to its high-end attraction. Furthermore, glass containers are free of chemicals like bisphenol-A or more recent substitutes that might infiltrate into the contents and risk the health of the consumers. This is further expected to support the segmental growth of the market in the near future.
Europe held largest market share of 36.45% in the year 2024. This is due to the well-established collection systems as well as the advanced infrastructures for the glass recycling in the region. As per the Close the Glass Loop, the glass packaging collection in 2022 increased and reached 12.4 million tonnes, a rise of almost 542,000 tonnes as compared to the year before. The glass packaging value chain's commitment and determination to increase the supply of post-consumer glass for the production of new glass bottles and jars are demonstrated by the growth in collected glass volumes. It also implies that attempts to collect glass are on the rise throughout Europe. Additionally, the presence of the stringent regulations such as the European Green Deal and the Circular Economy Action Plan are also further expected to contribute to the regional growth of the market. Also, the commitment to reducing the carbon emissions along with the achieving the net-zero goals by 2050 are also expected to support the regional growth of the market.
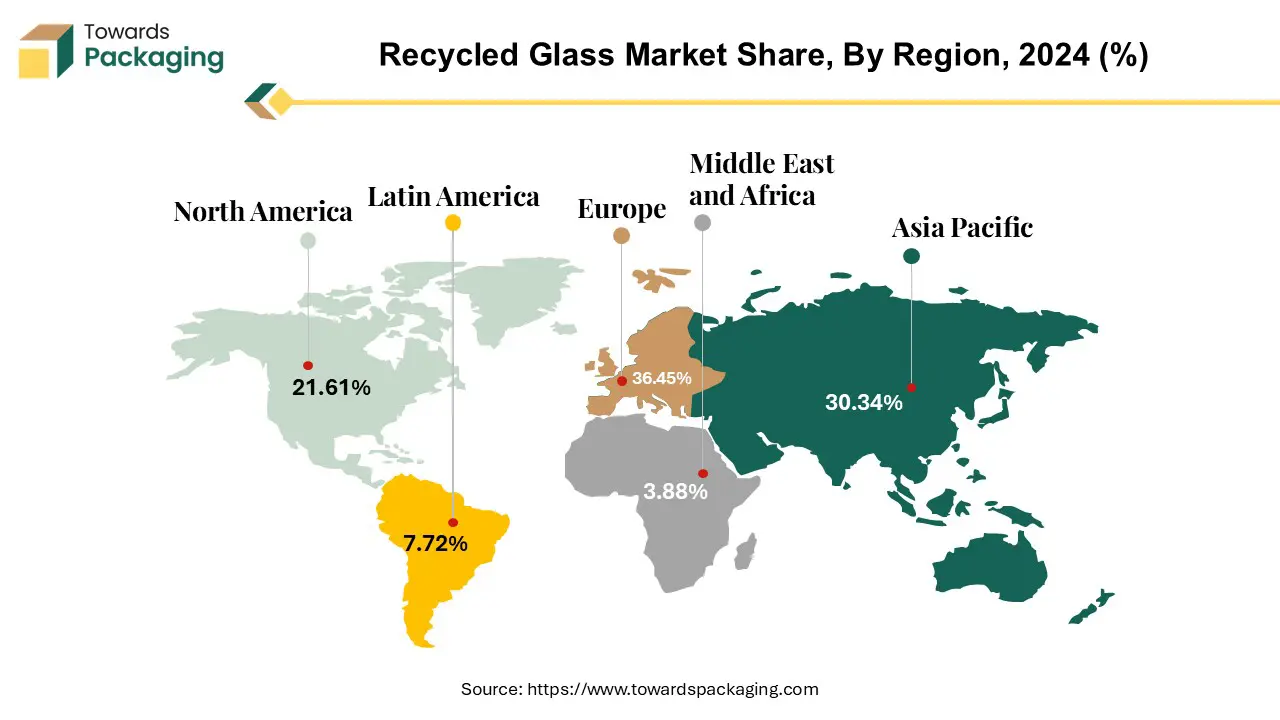
Asia Pacific is likely to grow at a considerable CAGR of 8.20% during the forecast period. This is due to the growing population and rapid urbanization in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations. Additionally, the increasing initiatives to recycle and collect glass waste are also expected to contribute to the regional growth of the market. For instance, in September 2024, AGC and Seven-Eleven Japan revealed Japan's first effective program to recycle glass waste from shop equipment to be utilized in new retail spaces. The partnership consists of gathering and recycling roughly 4 tons of glass from thirty Seven-Eleven locations. The project involved gathering, processing, and refining glass from old store shelves to create new flat glass panels. The glass parts of refrigerated display cases in new stores subsequently made use of these panels. In May 2024, AGC manufactured the reclaimed glass at its Kashima facility. Furthermore, the growing beverage and packaging industry as well as the growing middle class and higher consumption of glass products is likely to contribute to the regional growth of the market.

By Product
By Application
By Region
February 2025
February 2025
February 2025
February 2025