April 2025
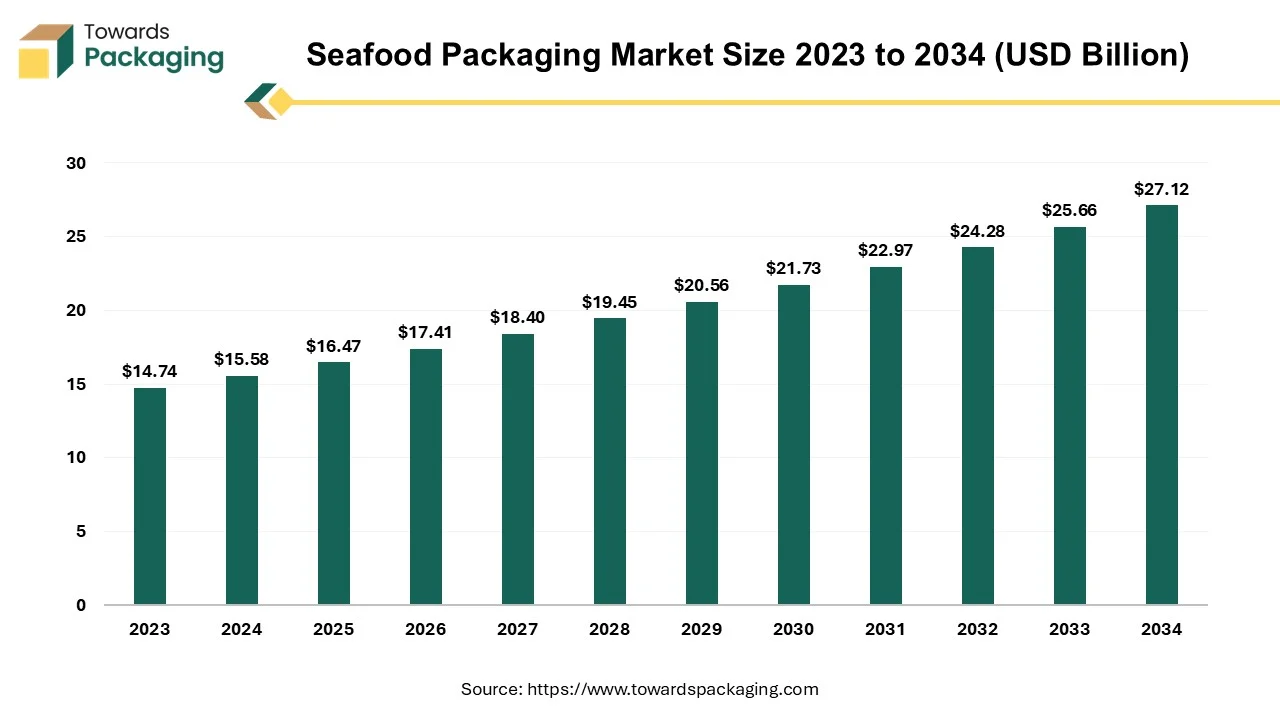
The global seafood packaging market size reached US$ 15.58 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around US$ 27.12 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The key players operating in the market are focused on adopting inorganic growth strategies like acquisition and merger to develop advance technology for manufacturing seafood packaging which is estimated to drive the global seafood packaging market over the forecast period.
Seafood packaging refers to the specialized materials and techniques used to store, transport, and preserve seafood products while maintaining freshness, safety, and quality. Since seafood is highly perishable, packaging solutions must provide temperature control, moisture resistance, and protection from contamination. Fresh & frozen seafood packaging removes oxygen to slow bacterial growth and extend shelf life. Seafood packaging prevents spoilage by maintaining optimal temperature, humidity, and oxygen levels.
Ensuring the authenticity and safety of seafood products is becoming increasingly important.
RFID/NFC Technology: Embedding RFID or NFC chips in packaging allows for real-time tracking of seafood products, enhancing supply chain transparency and consumer trust. Growth in Flexible Packaging: Flexible packaging solutions are gaining popularity due to their practicality and cost-effectiveness. Pouches and Vacuum-Sealed Bags: These formats are expected to account for a significant share of the market, offering benefits like extended shelf life and reduced storage space.
Governments are implementing policies that influence packaging practices: Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Schemes: In regions like the UK, new levies on packaging aim to offset recycling costs, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable packaging solutions to mitigate financial impacts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the seafood packaging industry by enhancing efficiency, improving product safety, optimizing sustainability, and reducing waste. The integration of AI-driven technologies ensures smarter supply chains, better quality control, and improved customer experiences. AI-powered computer vision and machine learning can detect defects, contamination, and freshness in seafood packaging. AI systems can scan packaging for tears, leaks, incorrect seals, or spoilage in real-time. AI sensors analyze color, texture, and gas levels inside packaging to determine freshness. AI-based biosensors detect harmful bacteria (e.g., Salmonella, Listeria, E. coli) in packaged seafood.
AI enhances smart packaging by integrating real-time monitoring systems for freshness, temperature, and supply chain tracking. AI algorithms analyze data from IoT sensors to ensure seafood remains in ideal conditions.AI adjusts expiration dates based on real-time storage conditions instead of fixed shelf-life estimates. AI models use historical data, temperature fluctuations, and packaging material properties to predict spoilage risk.
Growth in aquaculture production and sustainable fishing practices. Rising demand for frozen, processed, and ready-to-eat seafood. As aquaculture and wild-caught seafood production grow, more packaging materials are required for processing, storage, and distribution. Increased seafood variety (fresh, frozen, canned, processed) creates demand for specialized packaging solutions. Expanding seafood exports require durable packaging to maintain quality and freshness over long-distance shipping. Compliance with international packaging and labeling standards boosts demand for innovative packaging solutions. Expansion of supermarkets, hypermarkets, and seafood specialty stores increases the need for well-branded, attractive, and functional seafood packaging. Consumer demand for clear labeling, resealable packs, and portion-sized packaging boosts market innovation.
The key players operating in the market are facing issue due to consumer shift towards fresh & unpackaged seafood and supply chain disruptions which has estimated to restrict the growth of the seafood packaging market in the near future. Governments worldwide are enforcing strict rules on plastic usage and waste disposal, increasing compliance costs. Bans on single-use plastics and requirements for biodegradable or recyclable materials can limit traditional packaging solutions. Eco-friendly alternatives (e.g., bioplastics, compostable trays) are more expensive than conventional plastic, affecting affordability for small and mid-sized seafood businesses.
Fluctuations in raw material availability (e.g., petroleum-based plastics, recycled materials) can impact production. - Global supply chain issues (e.g., shipping delays, labor shortages) may hinder market growth. Many consumers prefer buying fresh, unpackaged seafood from local markets, reducing demand for pre-packaged seafood.
Compliance with U.S. Food and Drug Administration, EU, and other food safety standards encouraging innovation in packaging materials. Adoption of tamper-proof and traceable packaging. For instance, in February, 2025, according to the data published by the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR Regulation (EU) 2025/40), which was adopted by the EU on December 19, 2024, is to promote the advancement of packaging and related waste into a circular and competitive economy. By reducing the use of primary raw materials, making recycling all packaging on the EU market economically feasible by 2030, incorporating recycled plastic into packaging in a safe manner, and putting the packaging industry on track to become climate neutral by 2050, the PPWR went into effect in February 2025. In an effort to further harmonize national manufacturing, recycling, and reuse policies, the new law addresses the full packaging life-cycle. With the rules in place, the EU anticipates a significant reduction in water use, greenhouse gas emissions, and packaging's detrimental consequences.
The plastic segment held a dominant presence in the seafood packaging market in 2024. Plastic provides a strong barrier against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants, keeping seafood fresh and preventing spoilage. Compared to alternatives like glass or metal, plastic is cheaper to produce, transport, and store. Plastic packaging is lightweight, reducing shipping costs and making handling easier.
The shrink films segment accounted for a considerable share of the seafood packaging market in 2024. Shrink films conform tightly around seafood products, creating an airtight seal that helps retain freshness. Shrink films are more affordable compared to rigid packaging materials. The shrink films prevent contamination from external elements like dust, bacteria, and moisture.
The MAP segment dominated the seafood packaging market globally. The modified atmosphere packaging replaces oxygen with a controlled gas mix (e.g., CO₂ and N₂) to slow microbial growth and oxidation. MAP preserves the texture, color, and taste of seafood without the need for chemical preservatives. MAP packaging helps retain natural moisture, preventing dehydration and freezer burn in frozen seafood. Modified Atmosphere Packaging extends the viability of seafood for export and online delivery, reducing food waste in transit.
The fresh & frozen segment registered its dominance over the global seafood packaging market in 2024. Seafood is a rich source of high-quality protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Frozen seafood offers year-round availability, allowing consumers to enjoy fish regardless of the season. More consumers are choosing seafood due to sustainable fishing and responsible aquaculture initiatives.
The fish segment led the global seafood packaging market in 2024. Fish is the most widely consumed seafood due to its affordability, availability, and nutritional benefits. Fish benefits from Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP), vacuum sealing, and freezing to extend shelf life. Fish is available in multiple formats: fresh, frozen, canned, smoked, and processed (fillets, portions, or whole fish). Fish is heavily traded worldwide, requiring high-quality vacuum-packed, frozen, and insulated packaging to maintain quality during long-distance transport. Countries like China, Chile, Norway, and India dominate global fish exports, increasing demand for secure packaging solutions.
Asia Pacific region held the largest share of the seafood packaging market in 2024. Asia Pacific leads global seafood production, with countries like China, India, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Japan being major contributors. High seafood consumption in coastal and inland areas due to cultural preferences and affordability. Over 90% of the world's aquaculture production comes from Asia Pacific, ensuring a continuous seafood supply. The growth of fish farming (e.g., shrimp, tilapia, salmon, and carp) increases demand for advanced packaging solutions.
Growing middle-class population and busy lifestyles fuel demand for ready-to-eat and frozen seafood. Many Asia Pacific countries are enforcing plastic waste reduction policies, driving innovation in biodegradable and recyclable packaging.
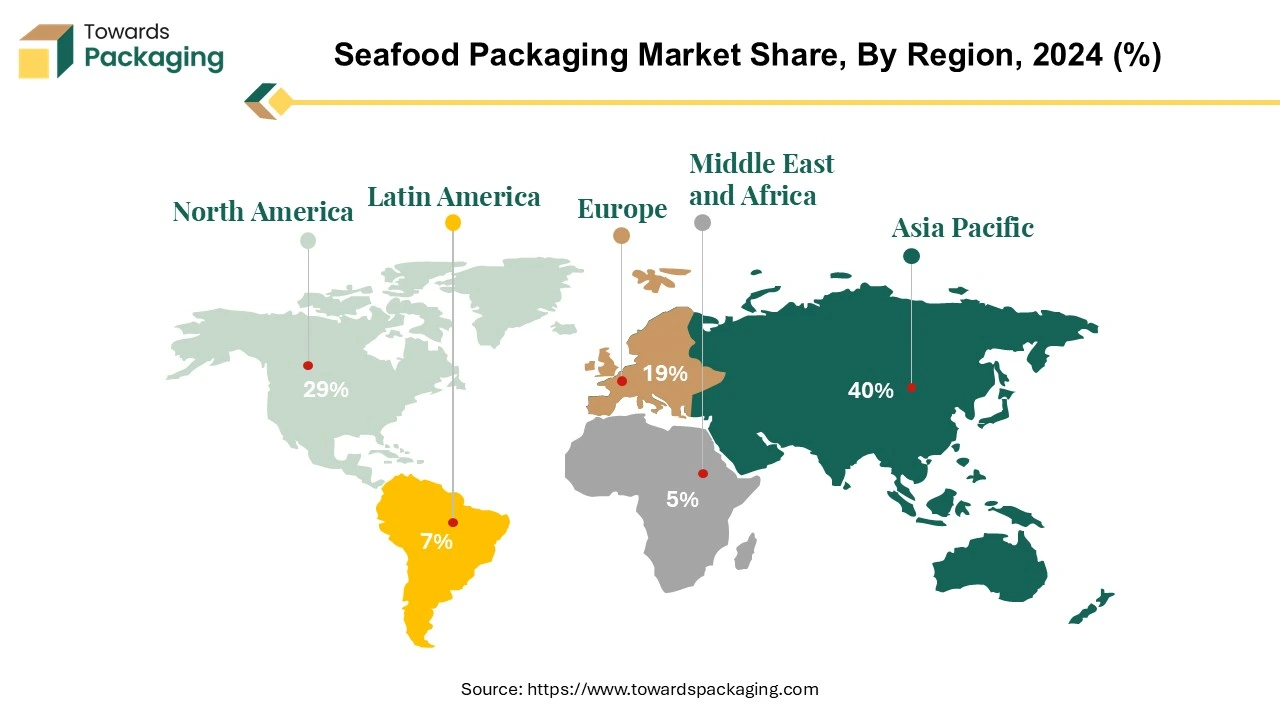
North America region is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate in the seafood packaging market during the forecast period. Improved refrigeration and insulated packaging in North America ensure seafood maintains freshness during transport. Growth in direct-to-consumer seafood delivery services is fueling demand for innovative packaging solutions. Supermarkets like Walmart, Costco, and Whole Foods emphasize premium seafood packaging to attract health-conscious buyers.
U.S. Seafood Packaging Market Trends
The U.S. is expanding sustainable fish and shrimp farming, increasing demand for packaging solutions that support freshness and branding. U.S. Food and Drug Administration and U.S. Department of Agriculture regulations require advanced packaging solutions to maintain freshness, prevent contamination, and extend shelf life.
Europe is seen to grow at a notable rate in the foreseeable future. EU bans on single-use plastics (e.g., the European Green Deal) are driving the adoption of biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable packaging. Increasing focus on carbon footprint reduction pushes companies to use eco-friendly materials like bioplastics, paper-based packaging, and recyclable trays. European consumers prioritize sustainably sourced seafood, increasing demand for packaging with eco-certifications (e.g., MSC, ASC, and EU organic labels). Europe is a major seafood importer, sourcing from Norway, Iceland, Asia, and North America. Strict EU food safety standards drive demand for high-quality, tamper-proof, and traceable seafood packaging.

By Material
By Product Type
By Packaging Technology
By Application
By Seafood Type
By Region
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025
April 2025