April 2025

Principal Consultant

Reviewed By
The plastic food packaging market is anticipated to grow from USD 63.15 billion in 2025 to USD 97.13 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.

Food packaging is a coordinated system that prepares food for transit, distribution, storage, retailing, and eventual consumption by the end users while maintaining optimal cost efficiency. It is essential in modern civilization because it allows for the safe and efficient handling and distribution of commercially prepared foods. Poor packaging is responsible for more than 25% of worldwide food waste, according to the World Packaging Organisation (WPO).
Plastics are commonly used in food packaging due to their versatility and adaptability for a variety of purposes. Plastic materials are chosen for specialized food packaging depending on their ability to meet the desired use criteria. Different plastics have unique features that cater to certain packaging requirements, ranging from barrier properties to moisture, oxygen, and light resistance.
Properties and applications for the most regularly used plastics in food packaging. Each plastic material is chosen for its ability to perform well within the constraints of the packaging application. Factors influencing the selection process include the type of food being packaged, the intended shelf life, transportation conditions, and regulatory requirements.
Understanding the qualities and applications of various plastics allows packaging professionals to make more educated decisions, assuring the safety, quality, and integrity of packaged food products. By using proper plastic materials, the food packaging business may improve product protection, lengthen shelf life, reduce food waste, and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable and efficient food supply chain.
For Instance,
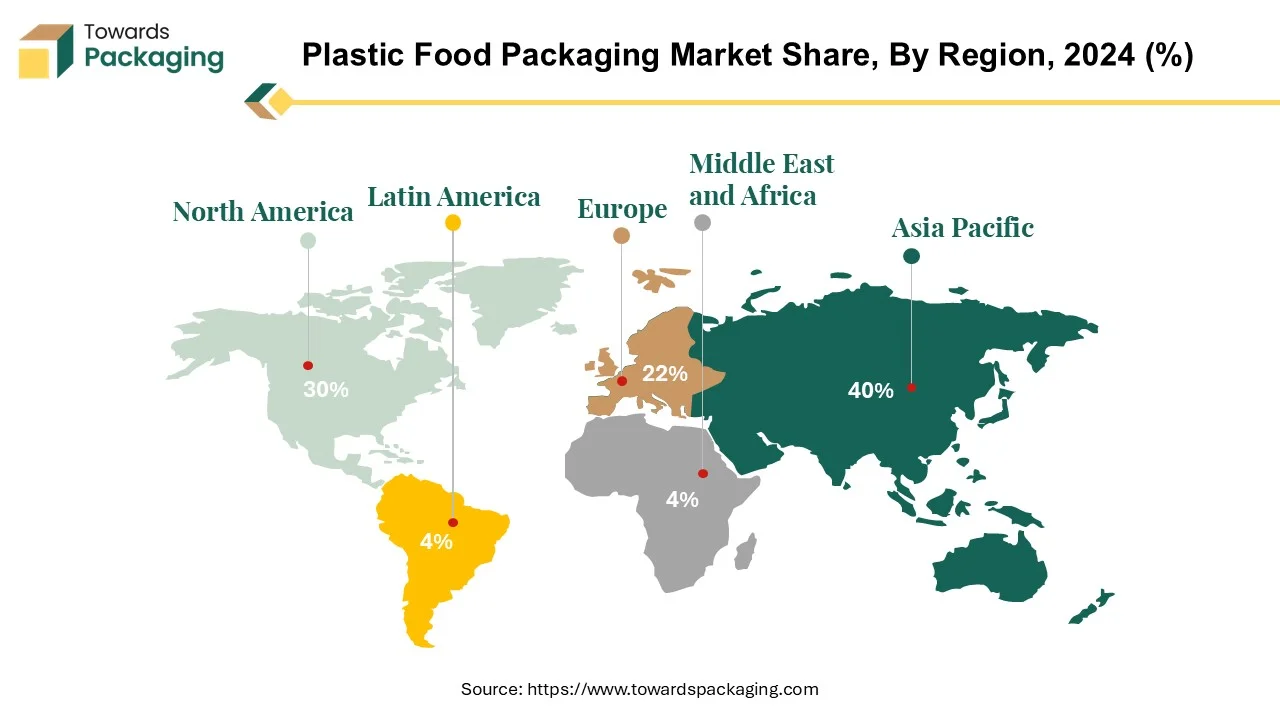
There is a great leadership in the shift to a circular economy for plastic food packaging in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, which produces more than half of the world's plastic 52% of 390.7 million tonnes overall. This area is at the forefront of attempts to combat plastic waste since it is home to some of the biggest plastic producers in the world. In the Asia-Pacific area, plastic packaging is widely used, especially in China and India, where the food and beverage industry is highly dependent on it. China's consumer sentiment is changing, leading to policies like banning specific plastic products to lessen the country's plastic pollution. It is anticipated that this change will increase the nation's need for recyclable flexible plastic packaging.

India is dedicated to the fifth-largest packaging industry in the country, which is expanding quickly and makes a substantial economic contribution. In addition, India's packaging industry has acted as a spur for innovation and technological development, which has helped a number of manufacturing industries.
Based on data particular to each country, China is the world's biggest producer of plastics, with 32 % of the world's plastic materials produced coming from this country. Other Asian nations are also important players; Japan makes about 3% of the world's plastic manufacturing, while the rest of Asia makes up 17%. The APAC region's dominance in plastic manufacturing provides an unparalleled opportunity to push sustainable practices in plastic packaging, with programmes ranging from consumer awareness to technology innovations poised to change the future of both plastic usage and waste management.
For Instance,
North America is the second-most plastic-using food packaging region in the world, after Asia. Different packaging materials frequently serve as differentiating characteristics. Food packaging has become an integral component of daily life in modern, industrialised countries. Due to a number of benefits over other materials, plastic stands out as the material of choice for food packaging. Among these are its affordability, versatility, ease of customisation, lightweight design, and wide availability. Plastic is a major material, making up around 21% of the containers and packaging sector in North America.

Plastic brings serious environmental risks despite its widespread use and success, especially when it comes to its impact on end-of-life (EOL) situations. The collection and disposal of plastic garbage represent major hazards to wildlife and ecosystems. A growing number of people are looking for solutions since they are aware of these problems, like smart plastic packaging materials and bioplastic. Because they come from renewable resources and may be composted or biodegraded, bioplastics provide a more environmentally friendly choice. Similar to this, smart plastic packaging uses cutting-edge technology to improve sustainability and functionality. Examples of these technologies include active packaging solutions for food preservation and intelligent sensors for freshness monitoring.
The environmental effects of plastic packaging must be addressed immediately because it is predicted that by 2050, the manufacture of plastic would account for 20% of global oil use. These issues can be lessened by embracing creative ideas and substitute materials, which will promote a more sustainable approach to food packaging in North America and beyond.
For Instance,
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is widely recognised for its lightweight and semi-rigid to rigid structure. It is utilised in food packaging for a range of products, including soft drinks, sports drinks, water bottles, condiments like ketchup, salad dressings, vitamins, vegetable oil, and peanut butter containers. Because of this feature, food or liquids contained within the container are guaranteed to be safe. It also has good impact resistance. It can be used for a wide range of things, including as vegetable containers, snack packs, bakery trays, and more because of its adaptability.
PET is a popular material for food packaging since it doesn't break down when it comes into touch with food, making it dependable and safe. Its corrosion resistance is just one of its many impressive qualities that make it even more ideal for packaging. A developed post-consumer collection system makes PET bottles advantageous. It is believed that 80% of the PET bottle garbage created gets collected, whilst the other portion usually ends up in landfills and only repurposes 2.5 percent of the overall waste. With the ability to recycle and reuse materials, this effective collection method adds to the sustainability of PET packaging.
Recycled PET (rPET) pellets are a viable product for food-grade bottle applications, as a significant amount of food and beverages are packed in PET bottles. In addition to lowering trash and its negative effects on the environment, this also shows how the PET packaging sector can become even more sustainable and circular. This will help to maximise resource efficiency.
For Instance,
The two most popular products in the plastic food packaging market are bags and pouches. Oil, coal, or natural gas-based plastics are now essential to packaging; they can be found in bottles, jars, trays, sacks, wraps, pouches, bags, and boxes, among other forms. Due to their affordability and versatility, plastics have largely replaced more conventional materials used in transportation packaging, such as steel, wood, and glass. They are used in strapping, shrink film, and stretch wrapping to secure cargo during transportation. Retort pouches and trays, aseptic packages, modified environment packages, frozen and oven-proof packages, active and smart packaging solutions and aseptic packages are examples of specialty packages having useful features to help with food preparation and preservation.
Pouches are completely enclosed packaging formed of co-extruded structures, monolayers, or multi-layered laminates that are intended to keep products separately. They are available in flexible forms. Plastic film metallization is a typical process used to improve opacity and barrier qualities. For the packaging of processed and fresh meats, dairy products, frozen vegetables, dry bakery goods, coffee, tea, candies, snacks, dry powders, prepared meals, sauces, cereals, and pet foods, flexible pouches are widely used in a variety of food industries. Common pouch styles include fill-through spout pouches, stand-up pouches, and side-gusseted pouches. Additionally, there are specialty pouches like dual-compartment pouches, where two components are kept separate until pressure ruptures the seal between compartments, facilitating mixing.
For Instance,
The industry that uses plastic food packaging the most is the bakery and confectionery sector, which is where these packaging solutions are most commonly used. The production of baked goods has been steadily increasing in India, and it is now the largest part of the processed food industry. The two main actors in the bakery industry, bread and biscuits, together account for around 82% of the output of all bakery products. Over three million tonnes of bakery goods, such as bread, cookies, pastries, cakes, buns, and rusk, are produced each year.

Bread and biscuits are produced by both organised and unorganised sectors, with production estimates ranging from 0.44 million tonnes to 11 million tonnes. Throughout the baking process, packaging is essential for manufacturing, preservation, storage, shipping, and marketing. Between 10% and 25% of the overall packing expenditure is comprised of packaging expenditures.
Generally, biscuits are packaged using flexible laminates of composite architectures, where each component has a distinct purpose. Moisture and gas barrier, heat sealability, printability, and cost-effectiveness are just a few of these laminates' appealing qualities. Similar to this, in response to changing market demands, bread packaging has switched to plastic films including PP, LDPE, and LLDPE-LDPE.
As environmental awareness and legal requirements expand, there is a discernible trend towards the greater use of sustainable plastics, such as post-consumer recycled materials.
For Instance,
Smart plastic in food packaging is the integration of sophisticated technology into plastic packaging materials to improve functionality and performance. These technologies allow packaging to interact with the environment, the product it holds, or the user, resulting in benefits such as increased food safety, longer shelf life, and a better consumer experience. Smart plastic packaging may include active or intelligent packaging systems that can release antimicrobial chemicals to limit bacterial development, absorb oxygen to delay food spoiling, and check product freshness using indicators such as time-temperature sensors.
Smart plastic packaging can include QR codes or RFID tags to improve traceability and authentication, letting customers to learn more about the product's origin, contents, and handling recommendations. Smart plastic food packaging leverages these advances to ensure the quality, safety, and sustainability of packaged food goods while addressing consumers' changing demands and preferences.
For Instance,
The competitive landscape of the plastic food packaging market is dominated by established industry giants such as Berry Global Group Inc, Amcor Plc, Ball Corp, Sealed Air Corp, Mondi Inc., Westrock Co, ITC, PepsiCo., Huhtamäki, Smurfit Kappa, and Sonoco. These giants compete with upstart direct-to-consumer firms that use digital platforms to gain market share. Key competitive characteristics include product innovation, sustainable practices, and the ability to respond to changing consumer tastes.
Berry Global places a strong emphasis on ongoing product research and innovation to satisfy the changing demands of the food sector. To provide package solutions with enhanced usefulness, performance, and sustainability, this entails investigating and creating novel materials, designs, and technologies.
By Material
By Product Type
By Application
By Distribution
By Region
April 2025
March 2025
March 2025
March 2025